一文了解.Net Core 3.1 Web API基础知识
Posted 三天不学习
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一文了解.Net Core 3.1 Web API基础知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、前言
随着近几年前后端分离、微服务等模式的兴起,.Net Core也似有如火如荼之势 ,自16年发布第一个版本到19年底的3.1 LTS版本,以及将发布的.NET 5,.NET Core一路更迭,在部署和开发工具上也都支持了跨平台应用。一直对.Net Core有所关注,但未涉及太多实际应用,经过一番学习和了解后,于是分享出来。本文主要以.Net Core Web API为例,讲述.Net Core的基本应用及注意事项,对于想通过WebAPI搭建接口应用的开发者,应该能提供一个系统的轮廓和认识,同时和更多的.Net Core开发者交流互动,探本勘误,加强对知识的理解,并帮助更多的人。本文以贴近基本的实际操作为主,部分概念或基础步骤不再赘述,文中如有疏漏,还望不吝斧正。
二、Swagger调试Web API
开发环境:Visual Studio 2019
为解决前后端苦于接口文档与实际不一致、维护和更新文档的耗时费力等问题,swagger应运而生,同时也解决了接口测试问题。话不多说,直接说明应用步骤。
- 新建一个ASP.NET Core Web API应用程序,版本选择.ASP.NET Core 3.1;
- 通过Nuget安装包:Swashbuckle.AspNetCore,当前示例版本5.5.0;
- 在Startup类的ConfigureServices方法内添加以下注入代码:
services.AddSwaggerGen(c => c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo Title = "My API", Version = "v1", Description = "API文档描述", Contact = new OpenApiContact Email = "5007032@qq.com", Name = "测试项目", //Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/") , License = new OpenApiLicense Name = "BROOKE许可证", //Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/") ); );Startup类的Configure方法添加如下代码:
//配置Swagger app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "My API V1"); c.RoutePrefix = "api";// 如果设为空,访问路径就是根域名/index.html,设置为空,表示直接在根域名访问;想换一个路径,直接写名字即可,比如直接写c.RoutePrefix = "swagger"; 则访问路径为 根域名/swagger/index.html );Ctrl+F5进入浏览,按上述配置修改路径为:http://localhost:***/api/index.html,即可看到Swagger页面:
然而到这里还没完,相关接口的注释说明我们看不到,通过配置XML文件的方式继续调整代码如下,新增代码见加粗部分:
services.AddSwaggerGen(c => c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo Title = "My API", Version = "v1", Description = "API文档描述", Contact = new OpenApiContact Email = "5007032@qq.com", Name = "测试项目", //Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/") , License = new OpenApiLicense Name = "BROOKE许可证", //Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/") ); var xmlFile = $"Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name.xml"; var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile); c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath); );上述代码通过反射生成与Web API项目相匹配的XML文件名,AppContext.BaseDirectory属性用于构造 XML 文件的路径,关于OpenApiInfo内的配置参数用于文档的一些描述,在此不作过多说明。
这样,我们以三斜杠(///)方式给类方法属性等相关代码添加注释后,刷新Swagger页面,即可看到注释说明。
然后右键Web API项目、属性、生成,配置XML文档的输出路径,以及取消不必要的XML注释警告提醒(增加1591):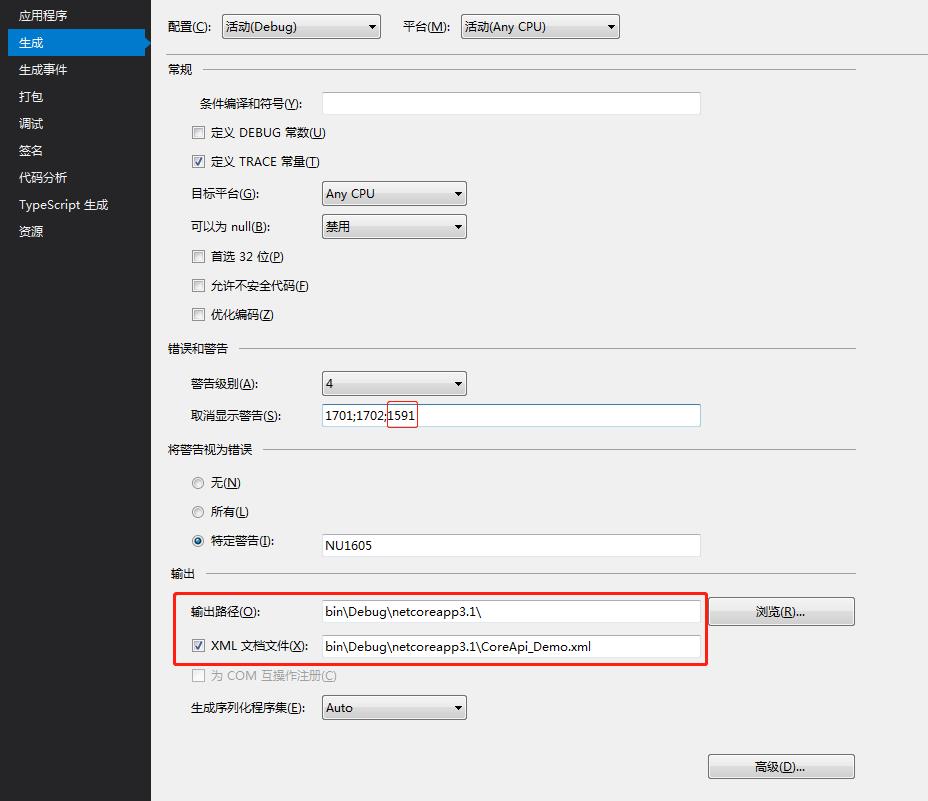
如果不想将XML文件输出为debug下的目录,譬如想要放在项目根目录(但不要修改成磁盘绝对路径),可调整相关代码如下,xml文件的名字也可以改成自己想要的:var basePath = Path.GetDirectoryName(typeof(Program).Assembly.Location);//获取应用程序所在目录 var xmlPath = Path.Combine(basePath, "CoreAPI_Demo.xml"); c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath, true);同时,调整项目生成的XML文档文件路径为:..\\CoreAPI_Demo\\CoreAPI_Demo.xml
- 隐藏相关接口
对于不想暴漏给Swagger展示的接口,我们可以给相关Controller或Action头加上:[ApiExplorerSettings(IgnoreApi = true)]
- 调整系统默认输出路径
项目启动后,默认会访问自带的weatherforecast,如果想调整为其他路径,譬如打开后直接访问Swagger文档,那么调整Properties目录下的launchSettings.json文件,修改launchUrl值为api(前述配置的RoutePrefix值):"$schema": "http://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json", "iisSettings": "windowsAuthentication": false, "anonymousAuthentication": true, "iisExpress": "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:7864", "sslPort": 0 , "profiles": "IIS Express": "commandName": "IISExpress", "launchBrowser": true, "launchUrl": "api", "environmentVariables": "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development" , "CoreApi_Demo": "commandName": "Project", "launchBrowser": true, "launchUrl": "api", "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5000", "environmentVariables": "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
三、配置文件
以读取appsettings.json文件为例,当然你也定义其他名称的.json文件进行读取,读取方式一致,该文件类似于Web.config文件。为方便示例,定义appsettings.json文件内容如下:
"ConnString": "Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=Demo;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=DemoUser;Password=123456;MultipleActiveResultSets=True;",
"ConnectionStrings":
"mysqlConnection": "server=127.0.0.1;database=mydemo;uid=root;pwd=123456;charset=utf8;SslMode=None;"
,
"SystemConfig":
"UploadFile": "/Files",
"Domain": "http://localhost:7864"
,
"JwtTokenConfig":
"Secret": "fcbfc8df1ee52ba127ab",
"Issuer": "abc.com",
"Audience": "Brooke.WebApi",
"AccessExpiration": 30,
"RefreshExpiration": 60
,
"Logging":
"LogLevel":
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
,
"AllowedHosts": "*"
1、配置文件的基本读取
public class Startup
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
Configuration = configuration;
public IConfiguration Configuration get;
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services.AddControllers();
//读取方式一
var ConnString = Configuration["ConnString"];
var MySQLConnection = Configuration.GetSection("ConnectionStrings")["MySQLConnection"];
var UploadPath = Configuration.GetSection("SystemConfig")["UploadPath"];
var LogDefault = Configuration.GetSection("Logging").GetSection("LogLevel")["Default"];
//读取方式二
var ConnString2 = Configuration["ConnString"];
var MySQLConnection2 = Configuration["ConnectionStrings:MySQLConnection"];
var UploadPath2 = Configuration["SystemConfig:UploadPath"];
var LogDefault2 = Configuration["Logging:LogLevel:Default"];
以上介绍了2种读取配置信息的方式,如果要在Controller内使用,类似地,进行注入并调用如下:
public class ValuesController : ControllerBase
private IConfiguration _configuration;
public ValuesController(IConfiguration configuration)
_configuration = configuration;
// GET: api/<ValuesController>
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
var ConnString = _configuration["ConnString"];
var MySQLConnection = _configuration.GetSection("ConnectionStrings")["MySQLConnection"];
var UploadPath = _configuration.GetSection("SystemConfig")["UploadPath"];
var LogDefault = _configuration.GetSection("Logging").GetSection("LogLevel")["Default"];
return new string[] "value1", "value2" ;
2、读取配置文件到自定义对象
以SystemConfig节点为例,定义类如下:
public class SystemConfig
public string UploadPath get; set;
public string Domain get; set;
调整代码如下:
public class Startup
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
Configuration = configuration;
public IConfiguration Configuration get;
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services.AddControllers();
services.Configure<SystemConfig>(Configuration.GetSection("SystemConfig"));
然后Controller内进行注入调用:
[Route("api/[controller]/[action]")]
[ApiController]
public class ValuesController : ControllerBase
private SystemConfig _sysConfig;
public ValuesController(IOptions<SystemConfig> sysConfig)
_sysConfig = sysConfig.Value;
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<string> GetSetting()
var UploadPath = _sysConfig.UploadPath;
var Domain = _sysConfig.Domain;
return new string[] "value1", "value2" ;
3、绑定到静态类方式读取
定义相关静态类如下:
public static class MySettings
public static SystemConfig Setting get; set; = new SystemConfig();
调整Startup类构造函数如下:
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration, IWebHostEnvironment env)
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true);
Configuration = builder.Build();
//Configuration = configuration;
configuration.GetSection("SystemConfig").Bind(MySettings.Setting);//绑定静态配置类
接下来,诸如直接使用:MySettings.Setting.UploadPath 即可调用。
四、文件上传
接口一般少不了文件上传,相比.net framework框架下webapi通过byte数组对象等复杂方式进行文件上传,.Net Core WebApi有了很大变化,其定义了新的IFormFile对象来接收上传文件,直接上Controller代码:
后端代码
[Route("api/[controller]/[action]")]
[ApiController]
public class UploadController : ControllerBase
private readonly IWebHostEnvironment _env;
public UploadController(IWebHostEnvironment env)
_env = env;
public ApiResult UploadFile(List<IFormFile> files)
ApiResult result = new ApiResult();
//注:参数files对象去也可以通过换成: var files = Request.Form.Files;来获取
if (files.Count <= 0)
result.Message = "上传文件不能为空";
return result;
#region 上传
List<string> filenames = new List<string>();
var webRootPath = _env.WebRootPath;
var rootFolder = MySettings.Setting.UploadPath;
var physicalPath = $"webRootPath/rootFolder/";
if (!Directory.Exists(physicalPath))
Directory.CreateDirectory(physicalPath);
foreach (var file in files)
var fileExtension = Path.GetExtension(file.FileName);//获取文件格式,拓展名
var saveName = $"rootFolder/Path.GetRandomFileName()fileExtension";
filenames.Add(saveName);//相对路径
var fileName = webRootPath + saveName;
using FileStream fs = System.IO.File.Create(fileName);
file.CopyTo(fs);
fs.Flush();
#endregion
result.IsSuccess = true;
result.Data["files"] = filenames;
return result;
前端调用
接下来通过前端调用上述上传接口,在项目根目录新建wwwroot目录(.net core webapi内置目录 ),添加相关js文件包,然后新建一个index.html文件,内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
</style>
<script src="res/scripts/jquery-1.10.2.min.js"></script>
<script src="res/scripts/jquery.form.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//方法1
function AjaxUploadfile()
var upload = $("#files").get(0);
var files = upload.files;
var data = new FormData();
for (var i = 0; i < files.length; i++)
data.append("files", files[i]);
//此处data的构建也可以换成:var data = new FormData(document.getElementById("myform"));
$.ajax(
type: "POST",
url: "/api/upload/uploadfile",
contentType: false,
processData: false,
data: data,
success: function (result)
alert("success");
$.each(result.data.files, function (i, filename)
$("#filePanel").append('<p>' + filename + '</p>');
);
,
error: function ()
alert("上传文件错误");
);
//方法2
function AjaxUploadfile2()
$("#myform").ajaxSubmit(
success: function (result)
if (result.isSuccess)
$.each(result.data.files, function (i, filename)
$("#filePanel").append('<p>' + filename + '</p>');
);
else
alert(result.message);
);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form id="myform" method="post" action="/api/upload/uploadfile" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" id="files" name="files" multiple /> <br /><br />
<input type="button" value="FormData Upload" onclick="AjaxUploadfile();" /><br /><br />
<input type="button" value="ajaxSubmit Upload" onclick="AjaxUploadfile2();" /><br /><br />
<div id="filePanel"></div>
</form>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function ()
);
</script>
</body>
</html>上述通过构建FormData和ajaxSubmit两种方式进行上传,需要注意的是contentType和processData两个参数的设置;另外允许一次上传多个文件,需设置multipart属性。
在访问wwwroot下的静态文件之前,必须先在Startup类的Configure方法下进行注册:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
app.UseStaticFiles();//用于访问wwwroot下的文件
启动项目,通过访问路径:http://localhost:***/index.html,进行上传测试,成功后,将在wwwroot下的Files目录下看到上传的文件。
五、统一WebApi数据返回格式
定义统一返回格式
为了方便前后端使用约定好的数据格式,通常我们会定义统一的数据返回,其包括是否成功、返回状态、具体数据等;为便于说明,定义一个数据返回类如下:
public class ApiResult
public bool IsSuccess get; set;
public string Message get; set;
public string Code get; set;
public Dictionary<string, object> Data get; set; = new Dictionary<string, object>();
这样,我们将每一个action接口操作封装为ApiResult格式进行返回。新建一个ProductController示例如下:
[Produces("application/json")]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
[HttpGet]
public ApiResult Get()
var result = new ApiResult();
var rd = new Random();
result.Data["dataList"] = Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new
Name = $"商品-index",
Price = rd.Next(100, 9999)
);
result.IsSuccess = true;
return result;
- Produces:定义数据返回的方式,给每个Controller打上[Produces("application/json")]标识,即表示以json方式进行数据输出。
- ApiController:确保每个Controller有ApiController标识,通常,我们会定义一个基类如:BaseController,其继承自ControllerBase,并将其打上[ApiController]标识,新建的controller都继承该类;
- Route:路由访问方式,如不喜欢RESTful方式,可加上Action,即:[Route("api/[controller]/[action]")];
- HTTP 请求:结合前面配置的Swagger,必须确保每个Action都有具体的请求方式,即必须是HttpGet、HttpPost、HttpPut、HttpDelete中的一种,通常情况下,我们使用HttpGet、HttpPost足以。
如此,即完成的数据返回的统一。
解决T时间格式
.Net Core Web Api默认以首字母小写的类驼峰式命名返回,但遇到DateTime类型的数据,会返回T格式时间,如要解决T时间格式,定义一个时间格式转换类如下:
public class DatetimeJsonConverter : JsonConverter<DateTime>
public override DateTime Read(ref Utf8JsonReader reader, Type typeToConvert, JsonSerializerOptions options)
if (reader.TokenType == JsonTokenType.String)
if (DateTime.TryParse(reader.GetString(), out DateTime date))
return date;
return reader.GetDateTime();
public override void Write(Utf8JsonWriter writer, DateTime value, JsonSerializerOptions options)
writer.WriteStringValue(value.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
然后在Startup类的ConfigureServices中调整services.AddControllers代码如下:
services.AddControllers()
.AddJsonOptions(configure =>
configure.JsonSerializerOptions.Converters.Add(new DatetimeJsonConverter());
);
六、模型验证
模型验证在ASP.NET MVC已存在,使用方式基本一致。指对向接口提交过来的数据进行参数校验,包括必填项、数据格式、字符长度、范围等等。一般的,我们会将POST提交过来的对象定义为一个实体类进行接收,譬如定义一个注册类如下:
public class RegisterEntity
/// <summary>
/// 手机号
/// </summary>
[Display(Name = "手机号")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "0不能为空")]
[StringLength(11, ErrorMessage = "0最多1个字符")]
public string Mobile get; set;
/// <summary>
/// 验证码
/// </summary>
[Display(Name = "验证码")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "0不能为空")]
[StringLength(6, ErrorMessage = "0最多1个字符")]
public string Code get; set;
/// <summary>
/// 密码
/// </summary>
[Display(Name = "密码")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "0不能为空")]
[StringLength(16, ErrorMessage = "0最多1个字符")]
public string Pwd get; set;
Display标识提示字段的名称,Required表示必填,StringLength限制字段的长度,当然还有其他一些内置特性,具体可参考官方文档,列举一些常见的验证特性如下:
- [CreditCard]:验证属性是否具有信用卡格式。 需要 JQuery 验证其他方法。
- [Compare]:验证模型中的两个属性是否匹配。
- [EmailAddress]:验证属性是否具有电子邮件格式。
- [Phone]:验证属性是否具有电话号码格式。
- [Range]:验证属性值是否在指定的范围内。
- [RegularExpression]:验证属性值是否与指定的正则表达式匹配。
- [Required]:验证字段是否不为 null。 有关此属性的行为的详细信息,请参阅 [Required] 特性。
- [StringLength]:验证字符串属性值是否不超过指定长度限制。
- [Url]:验证属性是否具有 URL 格式。
- [Remote]:通过在服务器上调用操作方法来验证客户端上的输入。
上述说明了基本的模型验证使用方法,以这种方式,同时结合T4模板,通过表对象生成模型验证实体,省却了在action中编写大量验证代码的工作。当然,一些必要的较为复杂的验证,或结合数据库操作的验证,则单独写到action或其他应用模块中。
那么上述模型验证在Web API中是怎么工作的呢?在Startup类的ConfigureServices添加如下代码:
//模型参数验证
services.Configure<ApiBehaviorOptions>(options =>
options.InvalidModelStateResponseFactory = (context) =>
var error = context.ModelState.FirstOrDefault().Value;
var message = error.Errors.FirstOrDefault(p => !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(p.ErrorMessage))?.ErrorMessage;
return new JsonResult(new ApiResult Message = message );
;
);添加注册示例Action代码:
/// <summary>
/// 注册
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ApiResult> Register(RegisterEntity model)
ApiResult result = new ApiResult();
var _code = CacheHelper.GetCache(model.Mobile);
if (_code == null)
result.Message = "验证码过期或不存在";
return result;
if (!model.Code.Equals(_code.ToString()))
result.Message = "验证码错误";
return result;
/**
相关逻辑代码
**/
return result;
如此,通过配置ApiBehaviorOptions的方式,并读取验证错误信息的第一条信息并返回,即完成了Web API中Action对请求参数的验证工作,关于错误信息Message的返回,也可略作封装,在此略。
七、日志使用
虽然.Net Core WebApi有自带的日志管理功能,但不一定能较容易地满足我们的需求,通常会采用第三方日志框架,典型的如:NLog、Log4Net,简单介绍NLog日志组件的使用;
NLog的使用
① 通过NuGet安装包:NLog.Web.AspNetCore,当前项目版本4.9.2;
② 项目根目录新建一个NLog.config文件,关键NLog.config的其他详细配置,可参考官方文档,这里作简要配置如下;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<nlog xmlns="http://www.nlog-project.org/schemas/NLog.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
autoReload="true"
throwExceptions="false"
internalLogLevel="Off"
internalLogFile="NlogRecords.log">
<!--Nlog内部日志记录为Off关闭-->
<extensions>
<add assembly="NLog.Web.AspNetCore" />
</extensions>
<targets>
<target name="log_file" xsi:type="File" fileName="$basedir/logs/$shortdate.log"
layout="$longdate | $level:uppercase=false | $message $onexception:$exception:format=tostring $newline $stacktrace $newline" />
</targets>
<rules>
<!--跳过所有级别的Microsoft组件的日志记录-->
<logger name="Microsoft.*" final="true" />
<!--<logger name="logdb" writeTo="log_database" />-->
<logger name="*" minlevel="Trace" writeTo="log_file" />
</rules>
</nlog>
<!--https://github.com/NLog/NLog/wiki/Getting-started-with-ASP.NET-Core-3-->③ 调整Program.cs文件如下;
public class Program
public static void Main(string[] args)
//CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
var logger = NLog.Web.NLogBuilder.ConfigureNLog("nlog.config").GetCurrentClassLogger();
try
logger.Debug("init main");
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
catch (Exception exception)
//NLog: catch setup errors
logger.Error(exception, "Stopped program because of exception");
throw;
finally
// Ensure to flush and stop internal timers/threads before application-exit (Avoid segmentation fault on Linux)
NLog.LogManager.Shutdown();
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
).ConfigureLogging(logging =>
logging.ClearProviders();
logging.SetMinimumLevel(Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.LogLevel.Trace);
).UseNLog();//依赖注入Nlog;
其中Main函数里的捕获异常代码配置省略也是可以的,CreateHostBuilder下的UseNLog为必设项。
Controller通过注入调用如下:
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[]
"Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool", "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching"
;
private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger;
public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger)
_logger = logger;
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()
_logger.LogInformation("测试一条日志");
var rng = new Random();
return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast
Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index),
TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55),
Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)]
)
.ToArray();
本地测试后,即可在debug下看到logs目录下生成的日志文件。
八、依赖注入
使用.Net Core少不了和依赖注入打交道,这也是.Net Core的设计思想之一,关于什么是依赖注入(DI),以及为什么要使用依赖注入,这里不再赘述,先来看一个简单示例的依赖注入。
public interface IProductRepository
IEnumerable<Product> GetAll();
public class ProductRepository : IProductRepository
public IEnumerable<Product> GetAll()
Startup类进行注册:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services.AddScoped<IProductRepository, ProductRepository>();
请求 IProductRepository 服务并用于调用 GetAll 方法:
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
private readonly IProductRepository _productRepository;
public ProductController(IProductRepository productRepository)
_productRepository = productRepository;
public IEnumerable<Product> Get()
return _productRepository.GetAll();
通过使用DI模式,来实现IProductRepository 接口。其实前述已多次出现通过构造函数进行注入调用的示例。
生命周期
services.AddScoped<IMyDependency, MyDependency>();
services.AddTransient<IMyDependency, MyDependency>();
services.AddSingleton<IMyDependency, MyDependency>();- Transient:每一次请求都会创建一个新实例;
- Scoped:每个作用域生成周期内创建一个实例;
- Singleton:单例模式,整个应用程序生命周期内只创建一个实例;
这里,需要根据具体的业务逻辑场景需求选择注入相应的生命周期服务。
实际应用中,我们会有很多个服务需要注册到ConfigureServices内,一个个写入显然繁琐,而且容易忘记漏写,一般地,我们可能会想到利用反射进行批量注入,并通过扩展的方式进行注入,譬如:
public static class AppServiceExtensions
/// <summary>
/// 注册应用程序域中的服务
/// </summary>
/// <param name="services"></param>
public static void AddAppServices(this IServiceCollection services)
var ts = System.Reflection.Assembly.Load("CoreAPI.Data").GetTypes().Where(s => s.Name.EndsWith("Repository") || s.Name.EndsWith("Service")).ToArray();
foreach (var item in ts.Where(s => !s.IsInterface))
var interfaceType = item.GetInterfaces();
foreach (var typeArray in interfaceType)
services.AddTransient(typeArray, item);
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services.AddAppServices();//批量注册服务
诚然,这样配合系统自带DI注入是能完成我们的批量注入需求的。但其实也有更多选择,来帮我们简化DI注册,譬如选择其他第三方组件:Scrutor、Autofac…
1、Scrutor的使用
Scrutor是基于微软注入组件的一个扩展库,简单示例如下:
services.Scan(scan => scan
.FromAssemblyOf<Startup>()
.AddClasses(classes => classes.Where(s => s.Name.EndsWith("Repository") || s.Name.EndsWith("Service")))
.AsImplementedInterfaces()
.WithTransientLifetime()
);以上代码通过Scan方式批量注册了以Repository、Service结尾的接口服务,其生命周期为Transient,该方式等同于前述的以反射方式的批量注册服务。
关于Scrutor的其他用法,大家可以参见官方文档,这里只做下引子。
2、Autofac
一般情况下,使用MS自带的DI或采用Scrutor,即可满足实际需要,如果有更高的应用需求,如要求属性注入、甚至接管或取代MS自带的DI,那么你可以选择Autofac,关于Autofac的具体使用,在此不作详叙。
九、缓存
MemoryCache使用
按官方说明,开发人员需合理说用缓存,以及限制缓存大小,Core运行时不会根据内容压力限制缓存大小。对于使用方式,依旧还是先行注册,然后控制器调用:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
services.AddMemoryCache();//缓存中间件
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
private IMemoryCache _cache;
public ProductController(IMemoryCache memoryCache)
_cache = memoryCache;
[HttpGet]
public DateTime GetTime()
string key = "_timeKey";
// Look for cache key.
if (!_cache.TryGetValue(key, out DateTime cacheEntry))
// Key not in cache, so get data.
cacheEntry = DateTime.Now;
// Set cache options.
var cacheEntryOptions = new MemoryCacheEntryOptions()
// Keep in cache for this time, reset time if accessed.
.SetSlidingExpiration(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
// Save data in cache.
_cache.Set(key, cacheEntry, cacheEntryOptions);
return cacheEntry;
上述代码缓存了一个时间,并设置了滑动过期时间(指最后一次访问后的过期时间)为3秒;如果需要设置绝对过期时间,将SetSlidingExpiration 改为SetAbsoluteExpiration即可。浏览刷新,每3秒后时间将更新。
附一个封装好的Cache类如下:
public class CacheHelper
public static IMemoryCache _memoryCache = new MemoryCache(new MemoryCacheOptions());
/// <summary>
/// 缓存绝对过期时间
/// </summary>
///<param name="key">Cache键</param>
///<param name="value">缓存的值</param>
///<param name="minute">minute分钟后绝对过期</param>
public static void SetChache(string key, object value, int minute)
if (value == null) return;
_memoryCache.Set(key, value, new MemoryCacheEntryOptions()
.SetAbsoluteExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(minute)));
/// <summary>
/// 缓存相对过期,最后一次访问后minute分钟后过期
/// </summary>
///<param name="key">Cache键</param>
///<param name="value">缓存的值</param>
///<param name="minute">滑动过期分钟</param>
public static void SetChacheSliding(string key, object value, int minute)
if (value == null) return;
_memoryCache.Set(key, value, new MemoryCacheEntryOptions()
.SetSlidingExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(minute)));
/// <summary>
///设置缓存,如果不主动清空,会一直保存在内存中.
/// </summary>
///<param name="key">Cache键值</param>
///<param name="value">给Cache[key]赋的值</param>
public static void SetChache(string key, object value)
_memoryCache.Set(key, value);
/// <summary>
///清除缓存
/// </summary>
///<param name="key">cache键</param>
public static void RemoveCache(string key)
_memoryCache.Remove(key);
/// <summary>
///根据key值,返回Cache[key]的值
/// </summary>
///<param name="key"></param>
public static object GetCache(string key)
//return _memoryCache.Get(key);
if (key != null && _memoryCache.TryGetValue(key, out object val))
return val;
else
return default;
/// <summary>
/// 通过Key值返回泛型对象
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static T GetCache<T>(string key)
if (key != null && _memoryCache.TryGetValue<T>(key, out T val))
return val;
else
return default;
十、异常处理
定义异常处理中间件
这里主要针对全局异常进行捕获处理并记录日志,并以统一的json格式返回给接口调用者;说异常处理前先提下中间件,关于什么是中间件,在此不在赘述,一个中间件其基本的结构如下:
public class CustomMiddleware
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
_next = next;
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
await _next(httpContext);
下面我们定义自己的全局异常处理中间件,代码如下:
public class CustomExceptionMiddleware
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly ILogger<CustomExceptionMiddleware> _logger;
public CustomExceptionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILogger<CustomExceptionMiddleware> logger)
_next = next;
_logger = logger;
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
try
await _next(httpContext);
catch (Exception ex)
_logger.LogError(ex,"Unhandled exception...");
await HandleExceptionAsync(httpContext, ex);
private Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext httpContext, Exception ex)
var result = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new isSuccess = false, message = ex.Message );
httpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/json;charset=utf-8";
return httpContext.Response.WriteAsync(result);
/// <summary>
/// 以扩展方式添加中间件
/// </summary>
public static class CustomExceptionMiddlewareExtensions
public static IApplicationBuilder UseCustomExceptionMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
return builder.UseMiddleware<CustomExceptionMiddleware>();
然后在Startup类的Configure方法里添加上述扩展的中间件,见加粗部分:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
if (env.IsDevelopment())
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
//全局异常处理
app.UseCustomExceptionMiddleware();
在HandleExceptionAsync方法中,为方便开发和测试,这里将系统的错误返回给了接口调用者,实际生产环境中可统一返回固定的错误Message消息。
异常状态码的处理
关于http状态码,常见的如正常返回的200,其他401、403、404、502等等等等,因为系统有时候并不总是返回200成功,对于返回非200的异常状态码,WebApi也要做到相应的处理,以便接口调用者能正确接收,譬如紧接下来的JWT认证,当认证令牌过期或没有权限时,系统实际会返回401、403,但接口并不提供有效的可接收的返回,因此,这里列举一些常见的异常状态码,并以200方式提供给接口调用者,在Startup类的Configure方法里添加代码如下:
app.UseStatusCodePages(async context =>
//context.HttpContext.Response.ContentType = "text/plain";
context.HttpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/json;charset=utf-8";
int code = context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode;
string message =
code switch
401 => "未登录",
403 => "访问拒绝",
404 => "未找到",
_ => "未知错误",
;
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status200OK;
await context.HttpContext.Response.WriteAsync(Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new
isSuccess = false,
code,
message
));
);代码很简单,这里使用系统自带的异常处理中间件UseStatusCodePages,当然,你还可以自定义过滤器处理异常,不过不推荐,简单高效直接才是需要的。
关于.NET Core的异常处理中间件,还有其他诸如 UseExceptionHandler、UseStatusCodePagesWithRedirects等等,不同的中间件有其适用的环境,有的可能更适用于MVC或其他应用场景上,找到合适的即可。
题外话:大家也可以将UseStatusCodePages处理异常状态码的操作封装到前述的全局异常处理中间件中。
十一、应用安全与JWT认证
关于什么是JWT,在此不作赘述。实际应用中,为了部分接口的安全性,譬如需要身份认证才能访问的接口资源,对于Web API而言,一般会采用token令牌进行认证,服务端结合缓存来实现。
那为什么要选择JWT认证呢?原因无外乎以下:服务端不进行保存、无状态、适合移动端、适合分布式、标准化等等。关于JWT的使用如下:
通过NuGget安装包:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer,当前示例版本3.1.5;
ConfigureServices进行注入,默认以Bearer命名,这里你也可以改成其他名字,保持前后一致即可,注意加粗部分,代码如下:
appsettings.json添加JWT配置节点(见前述【配置文件】),添加JWT相关认证类:
public static class JwtSetting
public static JwtConfig Setting get; set; = new JwtConfig();
public class JwtConfig
public string Secret get; set;
public string Issuer get; set;
public string Audience get; set;
public int AccessExpiration get; set;
public int RefreshExpiration get; set;
采用前述绑定静态类的方式读取JWT配置,并进行注入:
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration, IWebHostEnvironment env)
//Configuration = configuration;
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true);
Configuration = builder.Build();
configuration.GetSection("SystemConfig").Bind(MySettings.Setting);//绑定静态配置类
configuration.GetSection("JwtTokenConfig").Bind(JwtSetting.Setting);//同上
public IConfiguration Configuration get;
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
#region JWT认证注入
JwtSecurityTokenHandler.DefaultInboundClaimTypeMap.Clear();
services.AddAuthentication("Bearer")
.AddJwtBearer("Bearer", options =>
options.RequireHttpsMetadata = false;
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
ValidIssuer = JwtSetting.Setting.Issuer,
ValidAudience = JwtSetting.Setting.Audience,
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(JwtSetting.Setting.Secret))
;
);
#endregion
给Swagger添加JWT认证支持,完成后,Swagger页面会出现锁的标识,获取token后填入Value(Bearer token形式)项进行Authorize登录即可,Swagger配置JWT见加粗部分:
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo
Title = "My API",
Version = "v1",
Description = "API文档描述",
Contact = new OpenApiContact
Email = "5007032@qq.com",
Name = "测试项目",
//Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/")
,
License = new OpenApiLicense
Name = "BROOKE许可证",
//Url = new Uri("http://t.abc.com/")
);
// 为 Swagger JSON and UI设置xml文档注释路径
//var basePath = Path.GetDirectoryName(typeof(Program).Assembly.Location);//获取应用程序所在目录(不受工作目录影响)
//var xmlPath = Path.Combine(basePath, "CoreAPI_Demo.xml");
//c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath, true);
var xmlFile = $"Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
#region JWT认证Swagger授权
c.AddSecurityDefinition("Bearer", new OpenApiSecurityScheme
Description = "JWT授权(数据将在请求头header中进行传输) 直接在下框中输入Bearer token(中间是空格)",
Name = "Authorization",
In = ParameterLocation.Header,
Type = SecuritySchemeType.ApiKey,
BearerFormat = "JWT",
Scheme = "Bearer"
);
c.AddSecurityRequirement(new OpenApiSecurityRequirement()
new OpenApiSecurityScheme
Reference = new OpenApiReference
Type = ReferenceType.SecurityScheme,
Id = "Bearer"
,
new string[]
);
#endregion
);Starup类添加Configure注册,注意,需放到 app.UseAuthorization();前面:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
app.UseAuthentication();//jwt认证
app.UseAuthorization();
这样,JWT就基本配置完毕,接下来实施认证登录和授权,模拟操作如下:
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ApiResult> Login(LoginEntity model)
ApiResult result = new ApiResult();
//验证用户名和密码
var userInfo = await _memberService.CheckUserAndPwd(model.User, model.Pwd);
if (userInfo == null)
result.Message = "用户名或密码不正确";
return result;
var claims = new Claim[]
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name,model.User),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role,"User"),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Sub,userInfo.MemberID.ToString()),
;
var key = new SymmetricSecurityKey(System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(JwtSetting.Setting.Secret));
var expires = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: JwtSetting.Setting.Issuer,
audience: JwtSetting.Setting.Audience,
claims: claims,
notBefore: DateTime.Now,
expires: expires,
signingCredentials: new SigningCredentials(key, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256));
//生成Token
string jwtToken = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
//更新最后登录时间
await _memberService.UpdateLastLoginTime(userInfo.MemberID);
result.IsSuccess= 1;
result.ResultData["token"] = jwtToken;
result.Message = "授权成功!";
return result;
上述代码模拟登录操作(账号密码登录,成功后设置有效期一天),生成token并返回,前端调
以上是关于一文了解.Net Core 3.1 Web API基础知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章