zabbix 从数据库查询数据的月度平均值指标
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了zabbix 从数据库查询数据的月度平均值指标相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 1.通过hosts表查找host的IDselect host,hostid from hosts where host='Zabbix server';
+---------------+--------+
| host | hostid |
+---------------+--------+
| Zabbix server | 10084 |
+---------------+--------+
2.通过items表查找主的监控项和key以及itemid
select itemid,name,key_ from items where hostid=10084 and key_='web_time';
+--------+----------+----------+
| itemid | name | key_ |
+--------+----------+----------+
| 66786 | web_time | web_time |
+--------+----------+----------+
3.通过itemid查询主机的监控项目
select avg(value) from trends where itemid=66786 and from_unixtime(clock)>= '2020-12-01' and from_unixtime(clock)< '2021-01-01' \G
或者存在于
select avg(value_avg) from zabbix.trends_uint where itemid=66720 and from_unixtime(clock)>= '2020-12-01' and from_unixtime(clock)< '2021-01-01' \G
从zabbix的数据库获取数据
如何从Zabbix数据库中获取监控数据
做过Zabbix的同学都知道,Zabbix通过专用的Agent或者SNMP收集相关的监控数据,然后存储到数据库里面实时在前台展示。Zabbix监控数据主要分为以下两类:
历史数据:history相关表,从history_uint表里面可以查询到设备监控项目的最大,最小和平均值,即存储监控数据的原始数据。
趋势数据:trends相关表,趋势数据是经过Zabbix计算的数据,数据是从history_uint里面汇总的,从trends_uint可以查看到监控数据每小时最大,最小和平均值,即存储监控数据的汇总数据。
Zabbix可以通过两种方式获取历史数据:
1.通过Zabbix前台获取历史数据
通过Zabbix前台查看历史数据非常简单,可以通过检测中->最新数据 的方式查看。也可以点击右上角的As plain test按钮保存成文本文件。
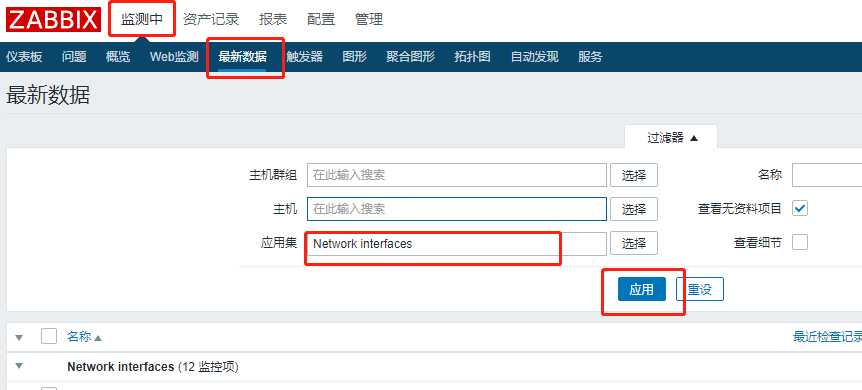
2.通过前台获取的数据进行处理和二次查询有很多限制,因此可以通过SQL语句直接从后台DB查询数据。
首先大家应该熟悉SQL语句Select 常用用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] Select_List [INTO [New_Table_name]FROM { Table_name | View_name} [ [,{table2_name | view2_name} [,...] ][ WHERE Serch_conditions ][ GROUP BY Group_by_list ][ HAVING Serch_conditions ][ ORDER BY Order_list [ASC| DEsC] ] |
说明:
1)SELECT子句指定要查询的特定表中的列,它可以是*,表达式,列表等。
2)INTO子句指定要生成新的表。
3)FROM子句指定要查询的表或者视图。
4)WHERE子句用来限定查询的范围和条件。
5)GROUP BY子句指定分组查询子句。
6)HAVING子句用于指定分组子句的条件。
7)ORDER BY可以根据一个或者多个列来排序查询结果,在该子句中,既可以使用列名,也可以使用相对列号,ASC表示升序,DESC表示降序。
8)mysql聚合函数:sum(),count(),avg(),max(),avg()等都是聚合函数,当我们在用聚合函数的时候,一般都要用到GROUP BY 先进行分组,然后再进行聚合函数的运算。运算完后就要用到Having子句进行判断了,例如聚合函数的值是否大于某一个值等等。
从Zabbix数据库中查询监控项目方法,这里已查询主机的网卡流量为例子:
1)通过hosts表查找host的ID。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mysql> select host,hostid from hosts where host="WWW05";+-------+--------+| host | hostid |+-------+--------+| WWW05 | 10534 |+-------+--------+1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
2)通过items表查找主的监控项和key以及itemid。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mysql> select itemid,name,key_ from items where hostid=10534 and key_="net.if.out[eth0]";+--------+-----------------+------------------+| itemid | name | key_ |+--------+-----------------+------------------+| 58860 | 发送流量: | net.if.out[eth0] |+--------+-----------------+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
3)通过itemid查询主机的监控项目(history_uint或者trends_uint),单位为M。
主机流入流量:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
mysql> select from_unixtime(clock) as DateTime,round(value/1024/1024,2) as Traffic_in from history_uint where itemid="58855" and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-20‘ and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-21‘ limit 20;+---------------------+------------+| DateTime | Traffic_in |+---------------------+------------+| 2014-09-20 00:00:55 | 0.10 || 2014-09-20 00:01:55 | 0.09 || 2014-09-20 00:02:55 | 0.07 || 2014-09-20 00:03:55 | 0.05 || 2014-09-20 00:04:55 | 0.03 || 2014-09-20 00:05:55 | 0.06 || 2014-09-20 00:06:55 | 0.12 || 2014-09-20 00:07:55 | 0.05 || 2014-09-20 00:08:55 | 0.10 || 2014-09-20 00:09:55 | 0.10 || 2014-09-20 00:10:55 | 0.12 || 2014-09-20 00:11:55 | 0.12 || 2014-09-20 00:12:55 | 0.13 || 2014-09-20 00:13:55 | 3.16 || 2014-09-20 00:14:55 | 0.23 || 2014-09-20 00:15:55 | 0.24 || 2014-09-20 00:16:55 | 0.26 || 2014-09-20 00:17:55 | 0.23 || 2014-09-20 00:18:55 | 0.14 || 2014-09-20 00:19:55 | 0.16 |+---------------------+------------+20 rows in set (0.82 sec) |
主机流出流量:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
mysql> select from_unixtime(clock) as DateTime,round(value/1024/1024,2) as Traffic_out from history_uint where itemid="58860" and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-20‘ and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-21‘ limit 20;+---------------------+-------------+| DateTime | Traffic_out |+---------------------+-------------+| 2014-09-20 00:00:00 | 4.13 || 2014-09-20 00:01:00 | 3.21 || 2014-09-20 00:02:00 | 2.18 || 2014-09-20 00:03:01 | 1.61 || 2014-09-20 00:04:00 | 1.07 || 2014-09-20 00:05:00 | 0.92 || 2014-09-20 00:06:00 | 1.23 || 2014-09-20 00:07:00 | 2.76 || 2014-09-20 00:08:00 | 1.35 || 2014-09-20 00:09:00 | 3.11 || 2014-09-20 00:10:00 | 2.99 || 2014-09-20 00:11:00 | 2.68 || 2014-09-20 00:12:00 | 2.55 || 2014-09-20 00:13:00 | 2.89 || 2014-09-20 00:14:00 | 4.98 || 2014-09-20 00:15:00 | 6.56 || 2014-09-20 00:16:00 | 7.34 || 2014-09-20 00:17:00 | 6.81 || 2014-09-20 00:18:00 | 7.67 || 2014-09-20 00:19:00 | 4.11 |+---------------------+-------------+20 rows in set (0.74 sec) |
4)如果是两台设备,汇总流量,假如公司出口有两台设备,可以用下面的SQL语句汇总每天的流量。下面SQL语句是汇总上面主机网卡的进出流量的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
mysql> select from_unixtime(clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") as DateTime,sum(round(value/1024/1024,2)) as Traffic_total from history_uint where itemid in (58855,58860) and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-20‘and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-21‘ group by from_unixtime(clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") limit 20;+------------------+---------------+| DateTime | Traffic_total |+------------------+---------------+| 2014-09-20 00:00 | 4.23 || 2014-09-20 00:01 | 3.30 || 2014-09-20 00:02 | 2.25 || 2014-09-20 00:03 | 1.66 || 2014-09-20 00:04 | 1.10 || 2014-09-20 00:05 | 0.98 || 2014-09-20 00:06 | 1.35 || 2014-09-20 00:07 | 2.81 || 2014-09-20 00:08 | 1.45 || 2014-09-20 00:09 | 3.21 || 2014-09-20 00:10 | 3.11 || 2014-09-20 00:11 | 2.80 || 2014-09-20 00:12 | 2.68 || 2014-09-20 00:13 | 6.05 || 2014-09-20 00:14 | 5.21 || 2014-09-20 00:15 | 6.80 || 2014-09-20 00:16 | 7.60 || 2014-09-20 00:17 | 7.04 || 2014-09-20 00:18 | 7.81 || 2014-09-20 00:19 | 4.27 |+------------------+---------------+20 rows in set (1.52 sec) |
5)查询一天中主机流量的最大值,最小值和平均值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mysql> select date as DateTime,round(min(traffic)/2014/1024,2) as TotalMinIN,round(avg(traffic)/1024/1024,2) as TotalAvgIN,round(max(traffic)/1024/1024,2) as TotalMaxIN from (select from_unixtime(clock,"%Y-%m-%d") as date,sum(value) as traffic from history_uint where itemid in (58855,58860) and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-20‘ and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-21‘ group by from_unixtime(clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") ) tmp;+------------+------------+------------+------------+| DateTime | TotalMinIN | TotalAvgIN | TotalMaxIN |+------------+------------+------------+------------+| 2014-09-20 | 0.01 | 4.63 | 191.30 |+------------+------------+------------+------------+1 row in set (1.74 sec) |
6)查询主机组里面所有主机CPU Idle平均值(原始值)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
mysql> select from_unixtime(hi.clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") as DateTime,g.name as Group_Name,h.host as Host, hi.value as Cpu_Avg_Idle from hosts_groups as hg join groups g on g.groupid = hg.groupid join items i on hg.hostid = i.hostid join hosts h on h.hostid=i.hostid join history hi on i.itemid = hi.itemid where g.name=‘上海机房--项目测试‘ and i.key_=‘system.cpu.util[,idle]‘ and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-24‘ and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-25‘ group by h.host,from_unixtime(hi.clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") limit 10;+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+| DateTime | Group_Name | Host | Cpu_Avg_Idle |+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+| 2014-09-24 00:02 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 94.3960 || 2014-09-24 00:07 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 95.2086 || 2014-09-24 00:12 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 95.4308 || 2014-09-24 00:17 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwe01 | 95.4580 || 2014-09-24 00:22 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 95.4611 || 2014-09-24 00:27 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 95.2939 || 2014-09-24 00:32 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 96.0896 || 2014-09-24 00:37 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 96.5286 || 2014-09-24 00:42 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 96.8086 || 2014-09-24 00:47 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 96.6854 |+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+10 rows in set (0.75 sec) |
7)查询主机组里面所有主机CPU Idle平均值(汇总值)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
mysql> select from_unixtime(hi.clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") as Date,g.name as Group_Name,h.host as Host, hi.value_avg as Cpu_Avg_Idle from hosts_groups as hg join groups g on g.groupid = hg.groupid join items i on hg.hostid = i.hostid join hosts h on h.hostid=i.hostid join trends hi on i.itemid = hi.itemid where g.name=‘上海机房--项目测试‘ and i.key_=‘system.cpu.util[,idle]‘ and from_unixtime(clock)>=‘2014-09-10‘ and from_unixtime(clock)<‘2014-09-11‘ group by h.host,from_unixtime(hi.clock,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%i") limit 10;+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+| Date | Group_Name | Host | Cpu_Avg_Idle |+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+| 2014-09-10 00:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9826 || 2014-09-10 01:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9826 || 2014-09-10 02:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9825 || 2014-09-10 03:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9751 || 2014-09-10 04:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9843 || 2014-09-10 05:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9831 || 2014-09-10 06:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9829 || 2014-09-10 07:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9843 || 2014-09-10 08:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9849 || 2014-09-10 09:00 | 上海机房--项目测试 | testwb01 | 99.9849 |+------------------+----------------------------+----------+--------------+10 rows in set (0.01 sec) |
8)其它与Zabbix相关的SQL语句。
查询主机已经添加但没有开启监控主机:
|
1
|
select host from hosts where status=1; |
查询NVPS的值:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mysql> SELECT round(SUM(1.0/i.delay),2) AS qps FROM items i,hosts h WHERE i.status=‘0‘ AND i.hostid=h.hostid AND h.status=‘0‘ AND i.delay<>0; +--------+| qps |+--------+| 503.40 |+--------+1 row in set (0.11 sec) |
查询IDC机房的资产信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mysql> select name,os,tag,hardware from host_inventory where hostid in (select hostid from hosts_groups where groupid=69) limit 2;+-------+----------------------------+------+-------------------+| name | os | tag | hardware |+-------+----------------------------+------+-------------------+| SHDBM | CentOS release 5.2 (Final) | i686 | ProLiant DL360 G5 || SHDBS | CentOS release 5.2 (Final) | i686 | ProLiant DL360 G5 |+-------+----------------------------+------+-------------------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
查询Zabbix interval分布情况:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
mysql> select delay,count(*),concat(round(count(*) / (select count(*) from items where status=0)*100,2),"%") as percent from items where status=0 group by delay order by 2 desc;+-------+----------+---------+| delay | count(*) | percent |+-------+----------+---------+| 3600 | 41168 | 38.92% || 300 | 35443 | 33.51% || 600 | 16035 | 15.16% || 60 | 12178 | 11.51% || 0 | 902 | 0.85% || 36000 | 46 | 0.04% || 30 | 1 | 0.00% |+-------+----------+---------+7 rows in set (0.68 sec) |
总结:通过SQL语句可以查询出任何监控项目的数据,并且在SQL语句的末尾通过into outfile ‘/tmp/zabbix_result.txt‘直接把查询的结果保存到系统上面,方便后续操作.
引用:http://www.xici.net/d221092545.html
以上是关于zabbix 从数据库查询数据的月度平均值指标的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章