数据库拆分之垂直拆分
Posted tanyunlong_nice
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据库拆分之垂直拆分相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
当单机数据库遇到瓶颈后,我们最常见的就是读写分离和主从同步,那么当再遇到瓶颈后怎么办呢?我们的解决办法就是垂直拆分。
一、什么是垂直拆分
数据的切分(Sharding)根据其切分规则的类型,可以分为两种切分模式。垂直拆分就是把一个数据库的不同业务单元的数据分到不同数据库中。
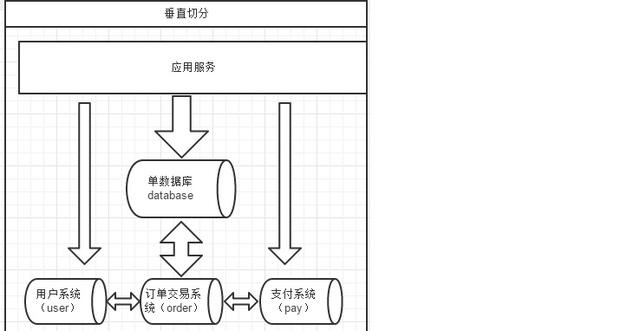
二、优缺点
优点:
拆分后业务清晰,拆分规则明确。
系统之间整合或扩展容易。
数据维护简单。
缺点:
部分业务表无法join,只能通过接口方式解决,提高了系统复杂度。
受每种业务不同的限制存在单库性能瓶颈,不易数据扩展跟性能提高。
事务处理复杂。
由于垂直切分是按照业务的分类将表分散到不同的库,所以有些业务表会过于庞大,存在单库读写与存储瓶颈,所以就需要水平
拆分来做解决。
三、实现方式
数据库的拆分有很多中间件都可以实现,如mycat,这里我们介绍一种比较方便的由Spring提供的方式。强大的Spring已经为我们提供了AbstractRoutingDataSource这个类做支持。
实现数据源切换的功能就是自定义一个类扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类,其实该相当于数据源DataSourcer的路由中介,可以实现在项目运行时根据相应key值切换到对应的数据源DataSource上。先看看AbstractRoutingDataSource的源码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.AbstractDataSource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
/**
* Abstract @link javax.sql.DataSource implementation that routes @link #getConnection()
* calls to one of various target DataSources based on a lookup key. The latter is usually
* (but not necessarily) determined through some thread-bound transaction context.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0.1
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
private boolean lenientFallback = true;
private DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup = new JndiDataSourceLookup();
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
/**
* Specify the map of target DataSources, with the lookup key as key.
* The mapped value can either be a corresponding @link javax.sql.DataSource
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* @link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup).
* <p>The key can be of arbitrary type; this class implements the
* generic lookup process only. The concrete key representation will
* be handled by @link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object) and
* @link #determineCurrentLookupKey().
*/
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources)
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
/**
* Specify the default target DataSource, if any.
* <p>The mapped value can either be a corresponding @link javax.sql.DataSource
* instance or a data source name String (to be resolved via a
* @link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup).
* <p>This DataSource will be used as target if none of the keyed
* @link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources match the
* @link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key.
*/
public void setDefaultTargetDataSource(Object defaultTargetDataSource)
this.defaultTargetDataSource = defaultTargetDataSource;
/**
* Specify whether to apply a lenient fallback to the default DataSource
* if no specific DataSource could be found for the current lookup key.
* <p>Default is "true", accepting lookup keys without a corresponding entry
* in the target DataSource map - simply falling back to the default DataSource
* in that case.
* <p>Switch this flag to "false" if you would prefer the fallback to only apply
* if the lookup key was @code null. Lookup keys without a DataSource
* entry will then lead to an IllegalStateException.
* @see #setTargetDataSources
* @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
public void setLenientFallback(boolean lenientFallback)
this.lenientFallback = lenientFallback;
/**
* Set the DataSourceLookup implementation to use for resolving data source
* name Strings in the @link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources map.
* <p>Default is a @link JndiDataSourceLookup, allowing the JNDI names
* of application server DataSources to be specified directly.
*/
public void setDataSourceLookup(DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup)
this.dataSourceLookup = (dataSourceLookup != null ? dataSourceLookup : new JndiDataSourceLookup());
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet()
if (this.targetDataSources == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<Object, DataSource>(this.targetDataSources.size());
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : this.targetDataSources.entrySet())
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(entry.getKey());
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(entry.getValue());
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null)
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
/**
* Resolve the given lookup key object, as specified in the
* @link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources map, into
* the actual lookup key to be used for matching with the
* @link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key.
* <p>The default implementation simply returns the given key as-is.
* @param lookupKey the lookup key object as specified by the user
* @return the lookup key as needed for matching
*/
protected Object resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(Object lookupKey)
return lookupKey;
/**
* Resolve the specified data source object into a DataSource instance.
* <p>The default implementation handles DataSource instances and data source
* names (to be resolved via a @link #setDataSourceLookup DataSourceLookup).
* @param dataSource the data source value object as specified in the
* @link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources map
* @return the resolved DataSource (never @code null)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case of an unsupported value type
*/
protected DataSource resolveSpecifiedDataSource(Object dataSource) throws IllegalArgumentException
if (dataSource instanceof DataSource)
return (DataSource) dataSource;
else if (dataSource instanceof String)
return this.dataSourceLookup.getDataSource((String) dataSource);
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal data source value - only [javax.sql.DataSource] and String supported: " + dataSource);
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException
if (iface.isInstance(this))
return (T) this;
return determineTargetDataSource().unwrap(iface);
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException
return (iface.isInstance(this) || determineTargetDataSource().isWrapperFor(iface));
/**
* Retrieve the current target DataSource. Determines the
* @link #determineCurrentLookupKey() current lookup key, performs
* a lookup in the @link #setTargetDataSources targetDataSources map,
* falls back to the specified
* @link #setDefaultTargetDataSource default target DataSource if necessary.
* @see #determineCurrentLookupKey()
*/
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource()
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null))
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
if (dataSource == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
return dataSource;
/**
* Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be
* implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context.
* <p>Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs
* to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the
* @link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey method.
*/
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
javadoc 的大概意思为getConnection()根据查找lookup key键对不同目标数据源的调用,通常是通过(但不一定)某些线程绑定的事物上下文来实现。通过这我们知道可以实现:
- 多数据源的动态切换,在程序运行时,把数据源数据源动态织入到程序中,灵活的进行数据源切换。
- 基于多数据源的动态切换,我们可以实现读写分离,这么做缺点也很明显,无法动态的增加数据源。
从源码可以看出AbstractRoutingDataSource继承了AbstractDataSource并实现了InitializingBean,AbstractRoutingDataSource的getConnection()方法调用了determineTargetDataSource()的该方法,这里重点看determineTargetDataSource()方法代码,方法里使用到了determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,它是AbstractRoutingDataSource类的抽象方法,也是实现数据源切换要扩展的方法,该方法的返回值就是项目中所要用的DataSource的key值,拿到该key后就可以在resolvedDataSource中取出对应的DataSource,如果key找不到对应的DataSource就使用默认的数据源。
四、具体实现
在实际开发中,过多的代码侵入会增加系统的耦合性,对于可能多处用到的数据源切换,我们这里使用spring 的类 配合面向对面SpringAOP和自定义注解再合适不过了。
首先我们来定义一个自定义注解,关于这块的学习可以参考我的博客列表自定义注解这一块。
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface DataSource
enum DataSourceType
MASTER("master"), SLAVE("slave");
private String value;
DataSourceType(String value)
this.value = value;
public String getValue()
return value;
DataSourceType value();
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey()
return DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSource();
第三步 使用ThreadLocal保证每个线程都能返回对应的key
public class DynamicDataSourceHolder
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void setDataSource(String type)
contextHolder.set(type);
public static String getDataSource()
if(null == contextHolder.get())
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource(DataSource.DataSourceType.MASTER.getValue());
return contextHolder.get();
public static void clearDataSource()
contextHolder.remove();
第四步 AOP解析自定义注解为每个线程的threadLocal赋值
public class DataSourceAspect
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceAspect.class);
/**
* 拦截目标方法,获取由@DataSource指定的数据源标识,设置到线程存储中以便切换数据源
*
* @param point
* @throws Exception
*/
public void intercept(JoinPoint point) throws Exception
// 判断切面在是否在类
Class<?> target = point.getTarget().getClass();
for (Class<?> clazz : target.getInterfaces())
resolveDataSource(clazz);
// 判断切面是否在方法
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
for (Method method : target.getMethods())
if (method.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(methodName))
resolveDataSource(method);
/**
* 提取目标对象注解和类型注解中的数据源标识
*/
private void resolveDataSource(Class<?> clazz)
try
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class))
DataSource source = clazz.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource(source.value().getValue());
catch (Exception e)
logger.error(clazz + ":" + e.getMessage());
/**
* 提取目标方法注解和类型注解中的数据源标识
*/
private void resolveDataSource(Method method)
try
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class))
DataSource source = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource(source.value().getValue());
catch (Exception e)
logger.error(method + ":" + e.getMessage());
第五步,我们需要声明多数据源
<bean id="masterDatasource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="dbType" value="mysql"/>
<property name="url" value="$mysql.url" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="$mysql.driverClassName"/>
<property name="username" value="$mysql.username"/>
<property name="password" value="$mysql.password"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="$mysql.initialSize" />
<property name="maxActive" value="$mysql.maxActive"/>
<!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="$mysql.maxWait" />
<!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="$mysql.testWhileIdle" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="$mysql.testOnBorrow" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="$mysql.testOnReturn" />
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value="20" />
</bean>
<!-- 多数据源配置 -->
<bean id="dynamicDataSource" class="xx.xxxx.holder.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<entry key="slave" value-ref="slaveDatasource"/>
<entry key="master" value-ref="masterDatasource"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- 默认使用 master 的数据源 -->
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="masterDatasource"></property>
</bean>到此,我们的数据库切换基本完成,之后只要在需要使用的Dao 层中 声明注解的枚举value
参考文章:使用Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource实现多数据源切换
《大型网站系统与JAVA中间件实战》
以上是关于数据库拆分之垂直拆分的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章