#打卡不停更# HarmonyOS 基于ArkUI(ETS) 实现雷达扫描
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了#打卡不停更# HarmonyOS 基于ArkUI(ETS) 实现雷达扫描相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
作者:杨尚晓
前言
雷达扫描是一个比较有科技感的东西,对于科幻迷来说,科幻电影里基本都能看到的画面,一个大大的屏幕上,可以看到雷达扫描的绿幕效果。 下面我们使用三种方式来实现这样的雷达效果。
项目说明
- 工具版本:DevEco Studio 3.0 Release
- SDK版本:3.1.1.2(API Version 8 Release)
- 主要组件:canvas, Row, Image
效果
-
使用Image图片组件方式实现
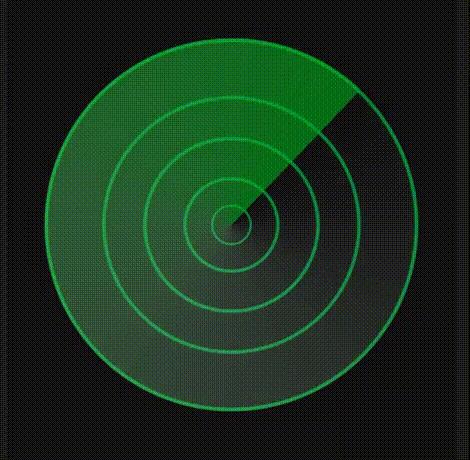
-
使用canvas组件实现
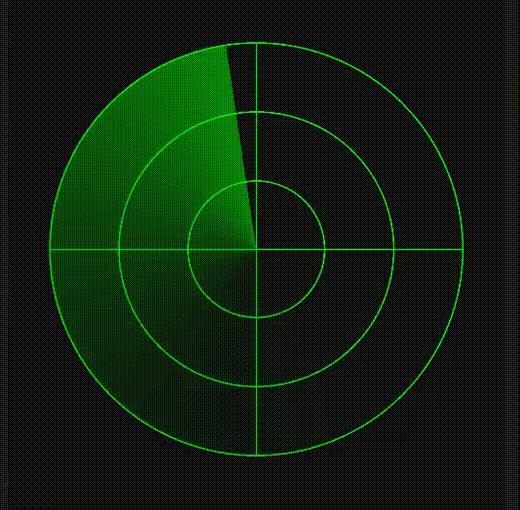
-
使用Row组件的渐变属性实现
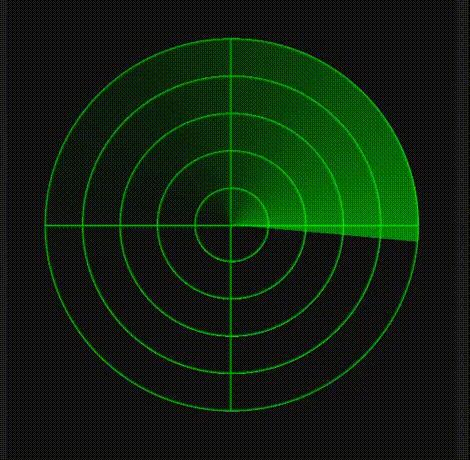
实现过程
需要注意,一个页面里只能有一个@Entry修饰符,所以,下面三种方法在预览的时候,需要注意注释只保留一个@Entry
1. 使用Image方法实现
使用Image组件的方法是最简单的,直接制作两张图片,一张底图,一张扫描的图


将两张图片通过叠加,将扫描的图片通过圆心宣旋转即可,下面使用代码来实现
@Entry
@Component
struct RadarImg
@State angle:number = 0;
aboutToAppear()
setTimeout(()=>
this.angle = 360
,200)
build()
Row()
Stack()
Image($r("app.media.radar_grid"))
.width(300)
.height(300)
Image($r(app.media.radar_sector))
.width(300)
.height(300)
.rotate(
z: 1,
angle: this.angle
)
.animation(
duration: 2000,
curve:Curve.Linear,
iterations: -1,
)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
.width(100%)
.height(100%)
整体比较简单,旋转主要用到了animation属性,这些在官网API文档可以查看。虽然使用Image组件实现比较简单,但是却是可以实现一些复杂的雷达UI。
2. 使用canvas实现
使用canvas实现的需要用到两个组件,第一个是Canvas组件,用来绘制底图网格,第二个是Row组件,使用角渐变属性实现旋转的扇形。 这里为什么不都使用canvas实现呢,找了一圈,canvas只有线性渐变和径向渐变,切没有角度渐变属性,所以,为了方便就用了row来实现吧。 下面直接上代码。
Row的渐变方式在下一个方法讲解,最终都还是使用animation属性动画实现扇形的旋转效果
@Entry
@Component
struct RadarCanvas
private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true);
private ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings)
@State angle:number = 0
// 绘制网格
drawGrid = (): void =>
let ctx = this.ctx;
ctx.lineWidth = 1
ctx.strokeStyle = green
// arr数组是需要绘制的底图圈圈
let arr:Array<number> = [150, 100, 50]
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.arc(150, 150, arr[i] - 0.5, 0, 2 * Math.PI)
ctx.stroke()
// 绘制十字架
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(0,150)
ctx.lineTo(300,150)
ctx.stroke()
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(150,0)
ctx.lineTo(150,300)
ctx.stroke()
aboutToAppear()
setTimeout(()=>
this.angle = 360
,200)
build()
Row()
Stack()
Canvas(this.ctx)
.onReady(()=>
this.drawGrid()
)
.width(300)
.height(300)
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.sweepGradient(
center: [150,150],
start: 0,
end: 359,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.4],
[rgba(0,255,0,0.5),1],
]
)
.rotate(
z: 1,
angle: this.angle
)
.animation(
duration: 2000,
iterations: -1,
curve: Curve.Linear
)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
.width(100%)
.height(100%)
3. 使用Row组件实现
使用Row组件实现的方法稍微复杂一些,这里用到了4个Row组件,其实对于前端童鞋来说,这里可能会比较好里一些,其实就是类似通过div和css来实现的,row组件是div,其属性是css样式。
废话不多说,直接上代码开搞
3.1 实现圆圈圈
首先使用径向渐变属性(radialGradient)来实现底部圈圈的效果 radialGradient属性有几个需要注意的值,radius是渐变的半径,这里使用30。 渐变颜色colors组用了三个数据,可以看出,前两个其实是透明度为0的。 可以理解为
- 第一个渐变颜色到第二个渐变颜色用了90%
- 第二个渐变颜色到第三个渐变颜色,用了10%(100%-90%)
- 也就是说在渐变半径为30的情况下,有90%是透明的,只有10%是透明到green颜色的,这样得到了一个圈圈
- 然后又设置了repeating属性(重复着色)为true
- 所以在半径为150的圆内,可以设置 150 / 3 = 5个圆圈圈
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.radialGradient(
center: [150,150],
radius: 30,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0.9],
[green, 1],
],
repeating: true,
)
我们看看效果

3.2 实现十字架
实现十字架使用了两个Row组件,使用线性渐变属性(linearGradient)分别绘制了一横一竖的效果。 可以看到颜色组colors使用了5个颜色来实现,1,2,4,5的颜色都是透明的
- 第一个颜色到第二个颜色都是透明的,渐变范围是0到49%,
- 第二个颜色到第三个颜色渐变范围是50% - 49% = 1%,也就是在其50%(中间)的地方绘制了一个1%的green线条
- 第三个颜色到第四个颜色不变
- 第三个到第五个颜色也是透明,渐变范围也是50%
上面绘制好之后,我们通过angle属性将线条旋转90度得到一个十字架
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.linearGradient(
angle: 0,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.49],
[green,0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),1]
]
)
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.linearGradient(
angle: 90,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.49],
[green,0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),1]
]
)
来看看效果

3.3 实现旋转扇形
扇形也是用到Row组件,其角度渐变属性(sweepGradient)来实现的。
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.sweepGradient(
center: [150,150],
start: 0,
end: 359,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),this.flag],
[rgba(0,255,0,0.5),1],
]
)
来看看效果

最后设置rotate旋转属性,设置旋转轴为z轴,角度angle为动态更新,这样animation动画属性才会更新。 最终代码 扇形的代码
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.sweepGradient(
center: [150,150],
start: 0,
end: 359,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),this.flag],
[rgba(0,255,0,0.5),1],
]
)
.rotate(
z: 1,
angle: this.angle
)
.animation(
duration: 2000,
iterations: -1,
curve: Curve.Linear
)
这里添加一个扫描周边设备的效果,动态设置了一个数据源,通过ForEach来动态渲染
ForEach(this.scanData,(item: any) =>
Column()
Image($r(app.media.icon))
.width(28)
.height(28)
.backgroundColor(#fff)
.borderRadius(19)
Text(item.name)
.fontColor(#fff)
.margin(top: 5)
.fontSize(10)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
.position(x: item.x, y: item.y)
.scale(x: this.w, y: this.h)
.animation(
duration: 1000,
iterations: 1,
curve: Curve.Friction
)
.opacity(this.opt)
)
最终的代码
// 雷达扫描组件
@Entry
@Component
struct Radar
@State angle:number = 0;
@State scanData: any = []
@State w:number = 0;
@State h:number = 0;
@State opt:number = 1
@State flag:number = 0.4
aboutToAppear()
setTimeout(()=>
this.angle = 360
,200)
setTimeout(()=>
animateTo(
duration: 1000, // 动画时长
curve: Curve.Linear, // 动画曲线
iterations: -1, // 播放次数
playMode: PlayMode.AlternateReverse, // 动画模式
onFinish: () =>
console.info(play end)
, () =>
this.opt = 0.3
)
,2000)
setTimeout(()=>
this.scanData = [
id: 1,
x: 190,
y: 200,
name: 空调
,
id: 1,
x: 80,
y: 240,
name: 插座
,
]
setTimeout(()=>
this.w = 1;
this.h = 1;
,200)
,1000)
build()
Row()
Stack()
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.radialGradient(
center: [150,150],
radius: 30,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0.9],
[green, 1],
],
repeating: true,
)
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.linearGradient(
angle: 0,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.49],
[green,0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),1]
]
)
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.linearGradient(
angle: 90,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0), 0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.49],
[green,0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0.5],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),1]
]
)
Row()
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(150)
.sweepGradient(
center: [150,150],
start: 0,
end: 359,
colors: [
[rgba(0,0,0,0),0],
[rgba(0,0,0,0),this.flag],
[rgba(0,255,0,0.5),1],
]
)
.rotate(
z: 1,
angle: this.angle
)
.animation(
duration: 2000,
iterations: -1,
curve: Curve.Linear
)
ForEach(this.scanData,(item: any) =>
Column()
Image($r(app.media.icon))
.width(28)
.height(28)
.backgroundColor(#fff)
.borderRadius(19)
Text(item.name)
.fontColor(#fff)
.margin(top: 5)
.fontSize(10)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
.position(x: item.x, y: item.y)
.scale(x: this.w, y: this.h)
.animation(
duration: 1000,
iterations: 1,
curve: Curve.Friction
)
.opacity(this.opt)
)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100%)
.height(100%)
.backgroundColor(0x111111)
来看看最终完整的效果

git地址
https://gitee.com/yango520/yg-radar
总结
通过这个雷达demo,特别是第三种方法,可以学到了颜色渐变属性中的三种渐变,线性渐变,径向渐变,和角度渐变。也可以学习属性动画的实现。
更多原创内容请关注:中软国际 HarmonyOS 技术团队
入门到精通、技巧到案例,系统化分享HarmonyOS开发技术,欢迎投稿和订阅,让我们一起携手前行共建鸿蒙生态。
https://ost.51cto.com/#bkwz
以上是关于#打卡不停更# HarmonyOS 基于ArkUI(ETS) 实现雷达扫描的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章