C#如何封装字段
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C#如何封装字段相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在C#中选择 重构--〉封装字段只能一次封装一个字段 如何一起封装多个字段?????
我是说在将多个字段 封装成属性 能不能一起封装??
2.静态字段和静态方法:(static关键字修饰的字段和方法)静态字段不需要实例化对象即可通过类名访问,最大的作用在可以在同一个类的不同对象实例之间共享数据(参考代码中只能创建一个对象的类的实现机制)。静态方法是不需要实例化对象即可访问的方法,不需要想内存申请存储空间,可以用来只有计算之类的功能函数的类!
3.封装字段还可以控制字段的属性是只读、只写或是可读写。
把字段声明为私有的,然后用两个public方法来代替get,set块也可以不过这样不太完美
首先
private string name;
public string name
getreturn name;
setname=value;
这样看起来美观、程序的可读性好、结构清楚、它有保护数据的作用
再次当我们需要它的时候可以直接调用就行了,而两个public需要调用两次,额外给程序增加了负担,写多了程序就会混乱。最重要的是:这是面向对象的思想!!
namespace CSCONSOLE
partial class Test
/// <summary>
/// 字段封装:选中变量右键选择 重构 封装字段 可以根据IDE的向导完成(或者ctrl+R+E),也可以手工输入如下代码段
/// </summary>
private int integer;
public int Integer
get return integer;
set integer = value;
private string str;
public string Str
get return str;
set str = value;
example2:
private string FLAG;
public string flag
set
FLAG = value;
get
return FLAG;
定义一个变量FLAG,再定义一个公共成员变量flag(可以在别的类中对flag进行赋值,如obj.flag="aa"),set将"aa"赋给value,再将value赋值给变量FLAG,FLAG="aa",再用get返回给flag. 参考技术A 好像是一次只能封装一个,但可以用快捷键,很快的,不再需要鼠标!
ctrl+R,ctrl+e,然后2次回车,可明显提高速度本回答被提问者采纳 参考技术B 只能一次封装一个。
你可以用动软代码生成器,可以针对数据库的字段生成这些代码。
http://www.maticsoft.com/ 参考技术C String CString LPSTR LPCSTR 都是字符串相关的类,具体用法看书去。 参考技术D 只能一次封装一个
C# PropertyGrid 简单使用
目录
一、 导入数据
propertyGrid1.SelectedObject = new Level1();
- 显示Level1类中所有 public 属性 Get Set 封装的字段。
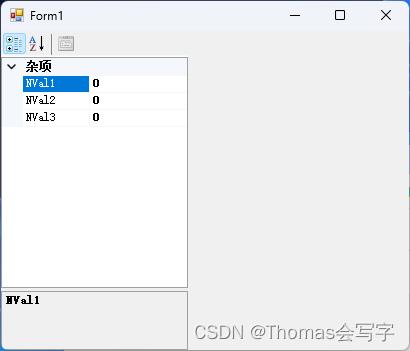
propertyGrid1.SelectedObject = new Level1();
public class Level1
private int nVal1;
private int nVal2;
private int nVal3;
public int NVal1 get => nVal1; set => nVal1 = value;
public int NVal2 get => nVal2; set => nVal2 = value;
public int NVal3 get => nVal3; set => nVal3 = value;
propertyGrid1.SelectedObjects = new object[] new Level1(), new Level2() ;
- 显示Level2 和 Level2 中所有公共属性
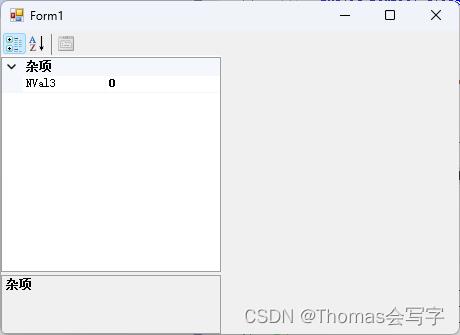
propertyGrid1.SelectedObjects = new object[] new Level1(), new Level2() ;
public class Level1
private int nVal1;
private int nVal2;
private int nVal3;
public int NVal1 get => nVal1; set => nVal1 = value;
public int NVal2 get => nVal2; set => nVal2 = value;
public int NVal3 get => nVal3; set => nVal3 = value;
public class Level2
private int nVal3;
private int nVal4;
private int nVal5;
public int NVal3 get => nVal3; set => nVal3 = value;
public int NVal4 get => nVal4; set => nVal4 = value;
public int NVal5 get => nVal5; set => nVal5 = value;
二、 PropertyGrid 的简单属性配置
- BackColor 更改其背景色。
- HelpBackColor 更改助窗口背景色。
- HelpForeColor 更改助窗口字体颜色。
- HelpVisible 显示隐藏帮助窗口。
- ToolbarVisible 显示隐藏工具栏。
- LargeButtons 显示大型工具栏按钮。
- PropertySort 按字母顺序对属性进行排序。
- BackColor 更改拆分器颜色。
- LineColor 更改网格线和边框。
三、 设置字段属性
- DescriptionAttribute - 设置属性在属性下方的说明帮助窗格中显示的属性的文本。 这是为具有焦点的活动属性提供帮助文本的有用方法。 将此属性应用于 MaxRepeatRate 该属性。
- CategoryAttribute 设置属性在网格中所属的类别。 当需要按类别名称分组的属性时,这非常有用。 如果属性未指定类别,则会将其分配给 Misc 类别。 将此属性应用于所有属性。
- BrowsableAttribute – 指示属性是否显示在网格中。 如果要从网格中隐藏属性,这非常有用。 默认情况下,公共属性始终显示在网格中。 将此属性应用于 SettingsChanged 该属性。
- ReadOnlyAttribute – 指示属性是否为只读。 如果要使属性在网格中不可编辑,这非常有用。 默认情况下,具有 get 和 set 访问器函数的公共属性在网格中可编辑。 将此属性应用于 AppVersion 该属性。
- DefaultValueAttribute – 标识属性的默认值。 如果想要为属性提供默认值,然后确定该属性的值是否不同于默认值,则这非常有用。 将此属性应用于所有属性。
- DefaultPropertyAttribute – 标识类的默认属性。 类的默认属性在网格中选择类时首先获取焦点。 将此属性应用于 AppSettings 类。
- DisplayNameAttribute - 实际显示的名称
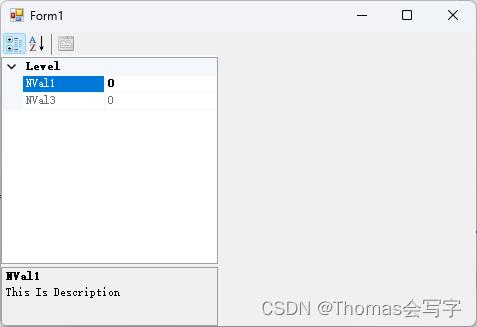
[DefaultProperty("NVal1")]
public class Level1
private int nVal1;
private int nVal2;
private int nVal3;
[Category("Level"), DefaultValue("123"), ReadOnly(false), Browsable(true), Description("This Is Description")]
public int NVal1 get => nVal1; set => nVal1 = value;
[Category("Level"),Browsable(false)]
public int NVal2 get => nVal2; set => nVal2 = value;
[Category("Level"), DefaultValue("456"), ReadOnly(true)]
public int NVal3 get => nVal3; set => nVal3 = value;
四、 字段的下拉框
常用属性 PropertyGrid 中已经封装了下拉框属性
字符串:
1. 通过继承重写 StringConverter 函数
/* 创建从类型转换器类继承的类。
* 由于属性 DefaultFileName 属于 String 类型
* 因此可以从 StringConverter 继承。
* 如果属性类型的类型转换器不存在,则可以从
* TypeConverter 继承;在这种情况下,不需要这样做。
*/
public class MyStringConverter : StringConverter
//重写 GetStandardValuesSupported 方法并返回 true 以指示此对象支持可从列表中选择的标准值集。
public override bool GetStandardValuesSupported( ITypeDescriptorContext context)
return true;
/* 重写 GetStandardValues 方法,并返回用标准值填充的 StandardValuesCollection 。
* 创建 StandardValuesCollection 的一种方法是在构造函数中提供值数组。
* 对于选项窗口应用程序,可以使用填充有建议的默认文件名的 字符串 数组。
*/
public override StandardValuesCollection GetStandardValues(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
return new StandardValuesCollection(new string[]"Str2", "Str3", "Str4");
/* (可选) 如果希望用户能够键入不在下拉列表中的值,
* 请重写 GetStandardValuesExclusive 方法并返回 false。
* 这基本上将下拉列表样式更改为组合框样式。
*/
public override bool GetStandardValuesExclusive(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
return false;
2. 通过Enum.ToString()实现,将String[] 变为 Enum,通过 Enum 实现下拉框
public class Level1
private bool bVal = true;
private Size sizeVal = new Size(100,200);
private Font fontVal= new Font("宋体", 9, FontStyle.Regular);
private Color colVal = Color.Red;
private EnumVal eVal = EnumVal.E02;
private String sVal = "Str1";
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框")]
public bool BVal get => bVal; set => bVal = value;
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框")]
public Size SizeVal get => sizeVal; set => sizeVal = value;
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框")]
public Font FontVal get => fontVal; set => fontVal = value;
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框")]
public Color ColVal get => colVal; set => colVal = value;
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框")]
public EnumVal EVal get => eVal; set => eVal = value;
[CategoryAttribute("下拉框"), TypeConverter(typeof(MyStringConverter))]
public string SVal get => sVal; set => sVal = value;
五、 多级展开

public class Level1
private SpellingOptions spell = new SpellingOptions();
/* 6. 将 TypeConverterAttribute 应用于示例中的类 SpellingOptions 目标类。
*/
[TypeConverterAttribute(typeof(SpellingOptionsConverter))]
public SpellingOptions Spell get => spell; set => spell = value;
public class SpellingOptions
private bool spellCheckWhileTyping = true;
private bool spellCheckCAPS = false;
private bool suggestCorrections = true;
[DefaultValueAttribute(true)]
public bool SpellCheckWhileTyping
get return spellCheckWhileTyping;
set spellCheckWhileTyping = value;
[DefaultValueAttribute(false)]
public bool SpellCheckCAPS
get return spellCheckCAPS;
set spellCheckCAPS = value;
[DefaultValueAttribute(true)]
public bool SuggestCorrections
get return suggestCorrections;
set suggestCorrections = value;
/* 1. 创建继承自 ExpandableObjectConverter 的类。
* 若要获取 PropertyGrid 以展开 SpellingOptions 该属性,需要创建 TypeConverter。
* TypeConverter 提供了一种从一种类型转换为另一种类型的方法。
* PropertyGrid 使用 TypeConverter 将对象类型转换为字符串,该字符串用于在网格中显示对象值。
* 在编辑期间, TypeConverter 将从 String 转换回对象类型。
* .NET Framework提供了 ExpandableObjectConverter 类,以便更轻松地执行此操作。
*/
public class SpellingOptionsConverter : ExpandableObjectConverter
/* 2. 如果参数与使用此类型的SpellingOptions转换器的类相同,
* 则重写 CanConvertTo 方法并返回 truedestinationType;
* 否则,返回基类 CanConvertTo 方法的值。
*/
public override bool CanConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, System.Type destinationType)
if (destinationType == typeof(SpellingOptions))
return true;
return base.CanConvertTo(context, destinationType);
/* 3. 重写 ConvertTo 方法,并确保 destinationType 参数是 字符串 ,
* 并且该值与使用此类型转换器 SpellingOptions 的类(示例中的类) 的类型相同。
* 如果任一情况为 false,则返回基类 ConvertTo 方法的值;
* 否则返回值对象的字符串表示形式。 字符串表示形式需要用唯一分隔符分隔类的每个属性。
* 由于整个字符串将显示在 PropertyGrid 中,
* 因此你需要选择一个不减去可读性的分隔符;逗号通常效果良好。
*/
public override object ConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
CultureInfo culture,
object value,
System.Type destinationType)
if (destinationType == typeof(System.String) &&
value is SpellingOptions)
SpellingOptions so = (SpellingOptions)value;
return "Typing:" + so.SpellCheckWhileTyping +
", CAPS: " + so.SpellCheckCAPS +
", Suggest: " + so.SuggestCorrections;
return base.ConvertTo(context, culture, value, destinationType);
/* 4. (可选) 可以通过指定类型转换器可以从字符串转换来启用对网格中
* 对象的字符串表示形式的编辑。 为此,请先重写 CanConvertFrom 方法,
* 如果源 Type 参数的类型为 String,则返回 true;否则,
* 返回基类 CanConvertFrom 方法的值。
*/
public override bool CanConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
System.Type sourceType)
if (sourceType == typeof(string))
return true;
return base.CanConvertFrom(context, sourceType);
/* 5. 若要启用对对象的基类的编辑,
* 还需要重写 ConvertFrom 方法,并确保值参数为 String。
* 如果不是 String,则返回基类 ConvertFrom 方法的值;
* 否则,请根据值参数返回类的新实例, (SpellingOptions 示例中的类) 。
* 需要从值参数分析类的每个属性的值。
* 了解在 ConvertTo 方法中创建的带分隔符的字符串的格式将有助于执行分析。
*/
public override object ConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value)
if (value is string)
try
string s = (string)value;
int colon = s.IndexOf(':');
int comma = s.IndexOf(',');
if (colon != -1 && comma != -1)
string checkWhileTyping = s.Substring(colon + 1,
(comma - colon - 1));
colon = s.IndexOf(':', comma + 1);
comma = s.IndexOf(',', comma + 1);
string checkCaps = s.Substring(colon + 1,
(comma - colon - 1));
colon = s.IndexOf(':', comma + 1);
string suggCorr = s.Substring(colon + 1);
SpellingOptions so = new SpellingOptions();
so.SpellCheckWhileTyping = Boolean.Parse(checkWhileTyping);
so.SpellCheckCAPS = Boolean.Parse(checkCaps);
so.SuggestCorrections = Boolean.Parse(suggCorr);
return so;
catch
throw new ArgumentException( "Can not convert '" + (string)value + "' to type SpellingOptions");
return base.ConvertFrom(context, culture, value);
六、 显示内容的排序
6.1 属性排序
- PropertyGrid 默认支持的排序方式
- 自定义顺序的排序方式
- 根据字段封装顺序的排序方式


6.1.1 自定义排序
[TypeConverter(typeof(PropertySorter))]
public class Level1
int n01 = 1;
int n02 = 2;
int n03 = 3;
int n04 = 4;
int n05 = 5;
int n06 = 6;
[PropertyOrder(1)]
public int N01 get => n01; set => n01 = value;
[PropertyOrder(2)]
public int N04 get => n04; set => n04 = value;
[PropertyOrder(3)]
public int N02 get => n02; set => n02 = value;
[PropertyOrder(4)]
public int N05 get => n05; set => n05 = value;
[PropertyOrder(5)]
public int N03 get => n03; set => n03 = value;
[PropertyOrder(6)]
public int N06 get => n06; set => n06 = value;
public class PropertySorter : ExpandableObjectConverter
public override bool GetPropertiesSupported(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
return true;
public override PropertyDescriptorCollection GetProperties(ITypeDescriptorContext context, object value, Attribute[] attributes)
//
// This override returns a list of properties in order
//
PropertyDescriptorCollection pdc = TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(value, attributes);
ArrayList orderedProperties = new ArrayList();
foreach (PropertyDescriptor pd in pdc)
Attribute attribute = pd.Attributes[typeof(PropertyOrderAttribute)];
if (attribute != null)
//
// If the attribute is found, then create an pair object to hold it
//
PropertyOrderAttribute poa = (PropertyOrderAttribute)attribute;
orderedProperties.Add(new PropertyOrderPair(pd.Name, poa.Order));
else
//
// If no order attribute is specifed then given it an order of 0
//
orderedProperties.Add(new PropertyOrderPair(pd.Name, 0));
//
// Perform the actual order using the value PropertyOrderPair classes
// implementation of IComparable to sort
//
orderedProperties.Sort();
//
// Build a string list of the ordered names
//
ArrayList propertyNames = new ArrayList();
foreach (PropertyOrderPair pop in orderedProperties)
propertyNames.Add(pop.Name);
//
// Pass in the ordered list for the PropertyDescriptorCollection to sort by
//
return pdc.Sort((string[])propertyNames.ToArray(typeof(string)));
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class PropertyOrderAttribute : Attribute
//
// Simple attribute to allow the order of a property to be specified
//
private int _order;
public PropertyOrderAttribute(int order)
_order = order;
public int Order
get
return _order;
public class PropertyOrderPair : IComparable
private int _order;
private string _name;
public string Name
get
return _name;
public PropertyOrderPair(string name, int order)
_order = order;
_name = name;
public int CompareTo(object obj)
//
// Sort the pair objects by ordering by order value
// Equal values get the same rank
//
int otherOrder = ((PropertyOrderPair)obj)._order;
if (otherOrder == _order)
//
// If order not specified, sort by name
//
string otherName = ((PropertyOrderPair)obj)._name;
return string.Compare(_name, otherName);
else if (otherOrder > _order)
return -1;
return 1;
6.1.2 根据字段封装顺序
[TypeConverter(typeof(PropertySorter))]
public class Level1
int n01 = 1;
int n02 = 2;
int n03 = 3;
int n04 = 4;
int n05 = 5;
int n06 = 6;
public int N01 get => n01; set => n01 = value;
public int N04 get => n04; set => n04 = value;
public int N02 get => n02; set => n02 = value;
public int N05 get => n05; set => n05 = value;
public int N03 get => n03; set => n03 = value;
public int N06 get => n06; set => n06 = value;
public class PropertySorter : ExpandableObjectConverter
public override bool GetPropertiesSupported(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
return true;
public override PropertyDescriptorCollection GetProperties(ITypeDescriptorContext context, object value, Attribute[] attributes)
PropertyDescriptorCollection pdc = TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(value, attributes);
ArrayList propertyNames = new ArrayList();
foreach (PropertyDescriptor pd in pdc)
propertyNames.Add(pd.Name);
return pdc.Sort((string[])propertyNames.ToArray(typeof(string)));
6.2 类别排序
1. PropertyGrid.PropertySort = CategorizedAlphabetical
2. 数据类中添加类别排序List
private List<String> categorys = new List<string>() ... ;3. 添加 PropertyGrid 的 Paint 事件
private void propertyGrid1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
var categorysinfo = propertyGrid1.SelectedObject.GetType().GetField("categorys", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance);
if (categorysinfo != null)
var categorys = categorysinfo.GetValue(propertyGrid1.SelectedObject) as List<String>;
propertyGrid1.CollapseAllGridItems();
GridItemCollection currentPropEntries = typeof(PropertyGrid).GetField("currentPropEntries", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance).GetValue(propertyGrid1) as GridItemCollection;
var newarray = currentPropEntries.Cast<GridItem>().OrderBy((t) => categorys.IndexOf(t.Label)).ToArray();
currentPropEntries.GetType().GetField("entries", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance).SetValue(currentPropEntries, newarray);
propertyGrid1.ExpandAllGridItems();
object obj = propertyGrid1.Tag;
if (obj != null)
propertyGrid1.PropertySort = (PropertySort)obj;
propertyGrid1.Paint -= new PaintEventHandler(propertyGrid1_Paint);
propertyGrid1.CollapseAllGridItems();
七、 闪屏问题
Form.DoubleBuffered = true; 或者 SetStyle(ControlStyles.OptimizedDoubleBuffer, true);
八、 主要参考
充分利用 .NET Framework PropertyGrid 控件 | Microsoft Learn
c# PropertyGrid 自定义属性排序_楚楚3107的博客-CSDN博客
PropertyGrid控件 分类(Category)及属性(Property)排序_propertygrid 排序_衣舞晨风的博客-CSDN博客
以上是关于C#如何封装字段的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章