180Java用堆实现从列表中获取第k小(或大)的元素
Posted zhangchao19890805
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了180Java用堆实现从列表中获取第k小(或大)的元素相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文讨论的是在不改变用户输入的列表的前提下,按照用户输入的顺序,输出第k个元素。其中k是从0开始计算。
1. 用堆的方法
下面的代码GetKthByHeapUtils.java,用户可以用自定义的排序规则,获取排序中第k个元素。
设计思路:我按照从小到大的排序为例子做讲解。先创建新的列表,容量是 k + 1,取名heap。把列表中的前 k + 1 个元素放入列表heap中,构造最大堆(如果从大到小就是最小堆)。遍历列表中剩余的元素,每个元素和堆顶做对比。如果小于堆顶就和堆顶交换位置,并且调整堆结构;反之就不做操作,直接比对下一个元素。最后直接返回堆顶即可。堆顶就是第k小的元素。
GetKthByHeapUtils.java
package zhangchao.getk;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 根据用户指定的排序规则,获取第k个元素。k从0开始计算。
* @author zhangchao
*/
public class GetKthByHeapUtils
/**
* 创建堆
* @param list 要进行排序的列表
* @param listSize 列表长度
* @param comparator 比较用的函数钩子
* @param <T> list中的元素类型
*/
private static<T> void createHeap(List<T> list, int listSize, Comparator<T> comparator)
// 假设第0个元素已经是堆了,从第1个元素开始加入堆。
for (int i = 1; i < listSize; i++)
int newIndex = i;
while (newIndex > 0)
// int parentIndex = (newIndex - 1) / 2;
int parentIndex = (newIndex - 1) >> 1;
T parent = list.get(parentIndex);
T newNode = list.get(newIndex);
if (comparator.compare(newNode, parent) > 0)
list.set(parentIndex, newNode);
list.set(newIndex, parent);
newIndex = parentIndex;
else
// 小于等于父亲节点,没有上升的需要,不需要再查找上级节点了。
newIndex = -1;
/**
* 从列表中获取,从小到大排序,第k个元素。
* 利用堆来保存前面 K + 1 个元素,并且是最大堆。后面的元素只要小于堆顶元素,就和堆顶元素交换位置,
* 然后调整堆的结构。
* @param list 列表
* @param k 第k个元素,k从0开始计算。
* @param comparator 比较的函数钩子。
* @param <T> 类型。
* @return 从小到大排序,第k个元素。
*/
public static<T> T getKth(List<T> list, int k, Comparator<T> comparator)
if (null == list || list.isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("List is empty!");
if (k < 0)
throw new RuntimeException("K must be greater than or equal to 0 !");
final int size = list.size();
if (k >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("K must be less than the size of list !");
if (0 == k)
T min = list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
T t = list.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(t, min) < 0)
min = t;
return min;
if ((size - 1) == k)
T max = list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
T t = list.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(t, max) > 0)
max = t;
return max;
// 堆的长度
int heapLength = k + 1;
List<T> heap = new ArrayList<>(heapLength);
for (int i = 0; i < heapLength; i++)
heap.add(list.get(i));
// 创建堆
createHeap(heap, heapLength, comparator);
// 从第k+1个元素开始,每个元素和堆顶比较。如果小于堆顶,就和堆顶交换位置,
// 然后调整堆的结构。
for (int i = heapLength; i < size; i++)
T current = list.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(current, heap.get(0)) < 0)
heap.set(0, current);
int currentIndex = 0;
boolean whileFlag = true;
while(whileFlag)
int leftIndex = (currentIndex << 1) + 1;
int rightIndex = (currentIndex << 1) + 2;
if (rightIndex < heapLength)
T left = heap.get(leftIndex);
T right = heap.get(rightIndex);
int maxIndex = rightIndex;
T max = right;
if (comparator.compare(left, right) > 0)
maxIndex = leftIndex;
max = left;
if (comparator.compare(max, current) > 0)
heap.set(currentIndex, max);
heap.set(maxIndex, current);
currentIndex = maxIndex;
else
whileFlag = false;
else if (leftIndex < heapLength)
T left = heap.get(leftIndex);
if (comparator.compare(left, current) > 0)
heap.set(currentIndex, left);
heap.set(leftIndex, current);
currentIndex = leftIndex;
else
whileFlag = false;
else
whileFlag = false;
return heap.get(0);
2. 其他方法
下面是用了另外两个方法来实现功能:
GetKthByListUtils
package zhangchao.getk;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
*
* @author zhangchao
*/
public class GetKthByListUtils
/**
* 复制列表,然后整个列表排序,返回第k个元素。
* @param originList 列表
* @param k 第k个元素,k从0开始计算。
* @param comparator 比较的函数钩子。
* @param <T> 类型。
* @return 从小到大排序,第k个元素。
*/
public static<T> T getKth_sortAll(List<T> originList, int k, Comparator<T> comparator)
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (T t : originList)
list.add(t);
list.sort(comparator);
return list.get(k);
/**
* 前面k+1个元素组成小列表smallList,排序。后面的元素和小列表最后一个元素比较。如果小于smallList最后一个元素,
* 交换位置,重新对smallList排序。
* @param originList 列表
* @param k 第k个元素,k从0开始计算。
* @param comparator 比较的函数钩子。
* @param <T> 类型。
* @return 从小到大排序,第k个元素。
*/
public static<T> T getKth_smallList(final List<T> originList, final int k, Comparator<T> comparator)
if (null == originList || originList.isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("List is empty!");
if (k < 0)
throw new RuntimeException("K must be greater than or equal to 0 !");
final int size = originList.size();
if (k >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("K must be less than the size of list !");
if (0 == k)
T min = originList.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
T t = originList.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(t, min) < 0)
min = t;
return min;
if ((size - 1) == k)
T max = originList.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
T t = originList.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(t, max) > 0)
max = t;
return max;
int smallListSize = k + 1;
List<T> smallList = new ArrayList<>(smallListSize);
for (int i = 0; i < smallListSize; i++)
smallList.add(originList.get(i));
smallList.sort(comparator);
for (int i = smallListSize; i < originList.size(); i++)
T t = originList.get(i);
if (comparator.compare(t, smallList.get(k)) < 0)
smallList.set(k, t);
// smallList.sort(comparator);
for (int smallIndex = 0; smallIndex < k; smallIndex++)
T smallT = smallList.get(smallIndex);
if (comparator.compare(smallT, t) > 0)
smallList.remove(k);
smallList.add(smallIndex, t);
smallIndex = k; // 结束循环。
return smallList.get(k);
3. 对比测试
下面是测试代码,统一用了长度为10000的列表做测试。
package zhangchao.getk;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GetKMain
public static void main(String[] args)
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
list.add(i);
Collections.shuffle(list);
Comparator<Integer> comparator = ((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
long t1, t2;
final int k = 9000;
t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer k1 = GetKthByHeapUtils.getKth(list, k, comparator);
t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("heap k1=" + k1 + " time=" + (t2 - t1));
t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer k2 = GetKthByListUtils.getKth_sortAll(list, k, comparator);
t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("sort all k2=" + k2 + " time=" + (t2 - t1));
t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer k3 = GetKthByListUtils.getKth_smallList(list, k, comparator);
t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("small list k3=" + k3 + " time=" + (t2 - t1));
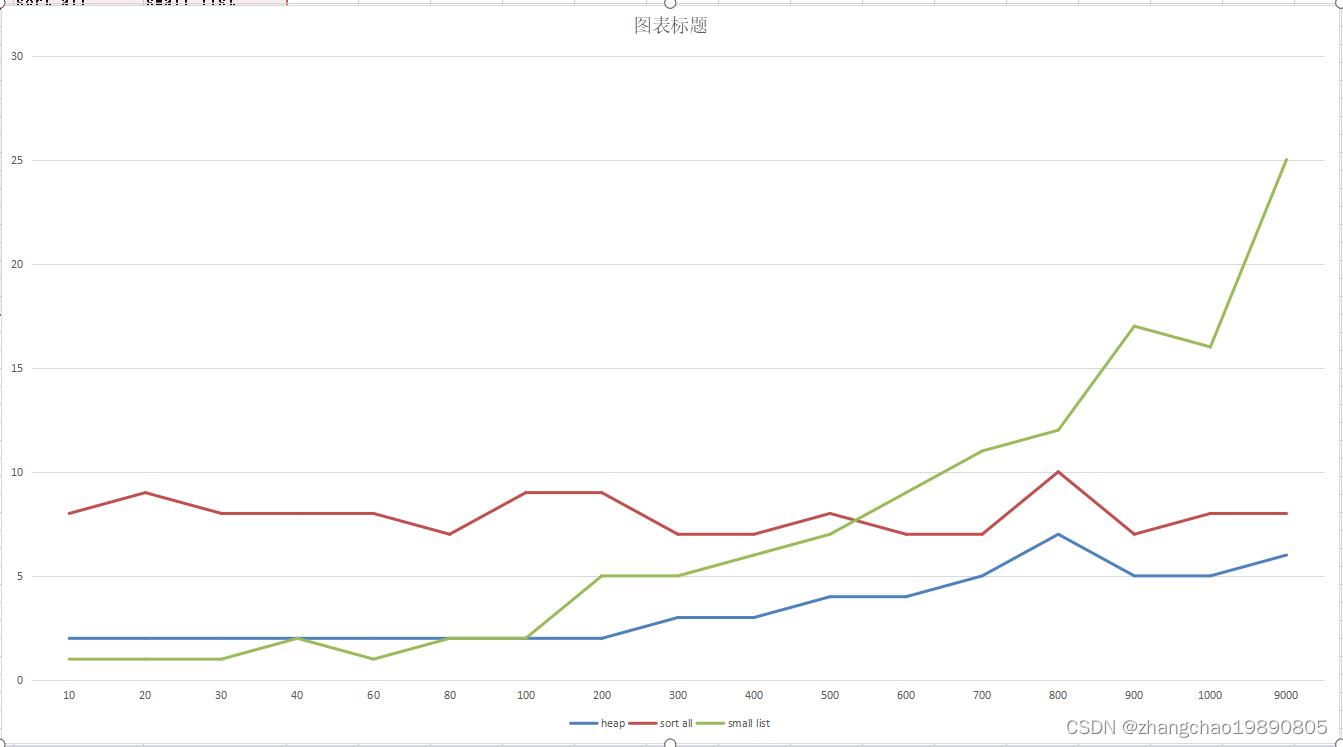
下面是统计折线图。横轴是k的取值,纵轴是耗时(单位:毫秒)。蓝色、红色、绿色分别代码代码中 heap、sort all、small list 三种代码实现。
以上是关于180Java用堆实现从列表中获取第k小(或大)的元素的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章