如何在android的代码中调用某个组件属性
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何在android的代码中调用某个组件属性相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
现在已经有了一个android工程A。我们想扩展A的功能,但是不想在A的基础上做开发,于是新建了另外一个Android工程B,想在B中引用A。1. 把工程A做成纯Jar包,这样其他的工程就可以直接引用了。
但是,如果在工程A中用了R.java中的引用,则无法打成jar包了。原因是R.java是自动生成的,是动态的,每次编译都是不相同的。如果一定要做成jar包,就不能使用自动生成的R文件,用到资源时候就要写代码去获取。
有时会报错:Conversion to Dalvik format failed with error 1
可能是多层包文件重复导入,冲突。。。
这时可以试试方法2
2.将工程A做成android library project。
设置工程A,右键->Properties->Android,将Is library项选中,然后Apply。设置工程B,右键->Properties->Android,在Library中,点击Add按钮,将A工程加入,然后Apply。此时在B中就引入了A中的资源和代码,这些资源和代码都可以直接调用。需要注意的是,因为A已经不再是一个完整的Android应用,而是一个类库工程,所以有一些内容还需要在B中配置一下。比如A中有lib库引用,则B中也要加入该lib库;比如A中的AndroidManifest.xml文件的内容,在B的AndroidManifest.xml文件中也要相应加上。。。
如果不需要引用A工程的资源文件,同样只需得到jar文件,
设置工程A,右键->Properties->Android,将Is library项选中,然后Apply。在A工程的bin目录下能得到一个jar文件,可以copy到B工程中的libs目录下直接引用。
如果能用jar当然最好,但是jar文件不能把res目录下的资源打包进去,所以才出现lib工程。
创建和使用Android library工程
摘要: 创建library供多个工程共享代码、资源是非常常见的需求,网上这种资料非常少,基本上都是讲创建java工程,然后export,这种方式缺点非常多,大家可以自己google一下。本文着重介绍如何创建Android library,并且在 ...
创建library供多个工程共享代码、资源是非常常见的需求,网上这种资料非常少,基本上都是讲创建java工程,然后export,这种方式缺点非常多,大家可以自己google一下。
本文着重介绍如何创建Android library,并且在工程中使用此library提供的资源,具体步骤如下:
1. 创建一个Android工程,命名为MyLib
2. 进入工程设置选中Is Library
3. 创建另一个Android工程,命名为MyProj
4. 进入工程设置,添加MyLib
5. 在MyProj的AndroidManifest.xml中加入对library中activity的引用
<activity android:name="net.devdiv.mylib.MyLib" />
6. 由于编译后library中的资源和引用它的project资源是合并在一起的,为了避免重名问题,需要对library中资源进行重命名
1). 把main.xml改为mylib.xml,同时修改MyLib.java代码setContentView(R.layout.mylib);
2). strings.xml修改为
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="mylibhello">String fetched from lib!</string>
<string name="mylib_app_name">MyLib</string>
</resources>
7. 在MyProj中引用MyLib的资源
package net.devdiv.myproj;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import net.devdiv.mylib.*;
import android.content.Intent;
public class MyProj extends Activity
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.myprojtext);
tv.setText(R.string.mylibhello);
Intent it = new Intent(this, MyLib.class);
startActivity(it);
参考技术A 静态属性可以通过类名.属性名直接调用。
非静态属性通过创建该组件类的对象,通过对象调用,public访问级别的属性可以通过对象名.属性名任意调用;protect访问级别的在同一个package或子类中可以任意调用;private的属性只能通过对象调用public方法或有限制的protect方法得到,通过方法返回属性值。
如:
class A
private int a = 0;
public String dis = "a的值为:";
public int getA()
return a;
class B
public void printA()
A a = new A();
System.out.print(a.dis+a.getA());
本回答被提问者和网友采纳 参考技术B 一般都是.set后面跟属性
3.React Native在Android中自定义Component和Module
React Native最终展示的UI全是Native的UI,将Native的信息封装成React方便的调用。那么Native是如何封装成React调用的?Native和React是如何交互的?
ViewManager
UI组件:将Native的UI暴露出来供JS调用。
- Native组件封装成JS组件供JS调用。这里的一个问题是怎么将Native中的属性用在JS中,以及属性可以有哪些类型的?可以先思考一下。
下面Native的代码自定义了一个View并定义了一个变化的属性color。
public class MyCustomView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
public MyCustomView(ReactContext context) {
super(context);
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(0xffff0000);
}
// 这里相当于可以改变color属性
public void setColor(int color){
mPaint.setColor(color);
invalidate();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 测试代码,onMeasure中设置的值通过getWidth()/getHeight()拿到的不一样,问题没找到
setMeasuredDimension(300, 300);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight(), mPaint);
}
}创建一个ViewManager。
public class MyCustomViewManager extends SimpleViewManager<MyCustomView> {
protected static final String REACT_CLASS = "MyCustomView";
@Override
public String getName() { // 返回了定义的View Module的名字
return REACT_CLASS;
}
@Override
protected MyCustomView createViewInstance(ThemedReactContext reactContext) {
return new MyCustomView(reactContext); // 创建一个View实例供JS使用。
}
// 设置属性,一定需要加这个注解,不然不认识
@ReactProp(name = "color")
public void setColor(MyCustomView view, String color) {
view.setColor(Color.parseColor(color));
}
}创建一个ReactPackage,并在Application中使用。
public class CustomReactPackage implements ReactPackage {
@Override
public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public List<Class<? extends JavaScriptModule>> createJSModules() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 自定义的ViewManager都可以加在这里。
@Override
public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
return Arrays.<ViewManager>asList(
new MyCustomViewManager()
);
}
}在Application中使用ReactPackage。
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
private final ReactNativeHost mReactNativeHost = new ReactNativeHost(this) {
@Override
public boolean getUseDeveloperSupport() {
return BuildConfig.DEBUG;
}
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new MainReactPackage(), new CustomReactPackage() // 把自定义的ReactPackage加进来
);
}
};
@Override
public ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost() {
return mReactNativeHost;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
SoLoader.init(this, /* native exopackage */ false);
}
}将Native组件封装成JS组件。
import React, {
Component,
PropTypes,
} from 'react';
import {
requireNativeComponent,
View,
UIManager,
} from 'react-native';
const ReactNative = require('ReactNative'); // ReactNative通过import没用
export default class MyCustomView extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
}
render(){
// {...this.props} 一定需要设置,不让你永远也看不到
return(
<RCTMyCustomView
{...this.props}
</RCTMyCustomView>);
}
}
MyCustomView.propTypes = {
color: PropTypes.string, // 设置color属性
...View.propTypes, // 这里一定需要设置,不然会报错。has no propType for native prop。这个被坑了
};
var RCTMyCustomView = requireNativeComponent('MyCustomView', MyCustomView); // 拿到Native组件然后就可以愉快的使用了。(最开始没有设置大小,只是在Native的onMeasure中设置了大小,一直没有View出来,被坑了)
// 一定需要设置大小,不然永远看不到。
<MyCustomView
color='#00ff00'
style={{width:300, height:300}}
/>如果是第一次使用封装UI Component的话,自己一定需要完整的尝试一遍。
- 交互。Native将事件传递给JS、JS将事件传递给Native。想一下这样一个场景,点击了Native以后,JS怎么知道Native被点击了?以及JS能否告诉Native需要干什么?当然需要了,并且React Native已经封装的很好了。
在上面的MyCustomViewManager中实现一些方法就可以了。getCommandsMap()和receiveCommand()用来处理JS向Native发送事件逻辑。getExportedCustomDirectEventTypeConstants()和addEventEmitters()对应了Native向JS发送事件逻辑。
private static final int CHANGE_COLOR = 1;
/**
* 可以接收的JS发过来的事件,返回来的数据是一组对应了方法名以及方法对应的一个ID(这个ID需要唯一区分)的Map。
* 这个在进入App的时候就会运行,得到相应的一组Map。
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public Map<String, Integer> getCommandsMap() {
return MapBuilder.of("changeColor", CHANGE_COLOR);
}
/**
* 接收JS事件以后的处理。JS会通过一些发送发送相应的指令过来,Native会由receiveCommand来处理。
* 事件过来时才会执行。
*/
@Override
public void receiveCommand(MyCustomView root, int commandId, @Nullable ReadableArray args) {
switch (commandId) {
case CHANGE_COLOR:
root.changeColor();
break;
}
}
/**
* 暴露了在JS中定义的方法,例如下面的"onChangeColor"是定义在JS中的方法。
* 这个在进入App的时候就会运行
*
* Returned map should be of the form:
* {
* "onTwirl": {
* "registrationName": "onTwirl"
* }
* }
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getExportedCustomDirectEventTypeConstants() {
return MapBuilder.<String, Object>builder()
.put("changeColor", MapBuilder.of("registrationName", "onChangeColor"))
.build();
}
/**
* 发射入口,相当于将Native的一些事件也注册给JS。
*
* 这个在进入App的时候就会运行。
*/
@Override
protected void addEventEmitters(final ThemedReactContext reactContext, final MyCustomView view) {
super.addEventEmitters(reactContext, view);
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 调用了JS相应的方法。
reactContext.getNativeModule(UIManagerModule.class).getEventDispatcher()
.dispatchEvent(new ClickEvent(view.getId()));
}
});
}在上面的代码中可以看到Native会接受一个1(CHANGE_COLOR)的指令以及会回调一个onChangeColor的方法到JS。那么现在就在JS中实现,把完整的JS代码贴了一遍,注释也写在了里面。
const ReactNative = require('ReactNative');
const CUSTOM_VIEW = "custom_view";
export default class MyCustomView extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this._onChange = this._onChange.bind(this); // 一定需要这样调用才会把属性绑定过来
}
// 把事件给Native
_changeColor() { // is not a function?没有设置this._onChange = this._onChange.bind(this);的时候
let self = this;
UIManager.dispatchViewManagerCommand(
ReactNative.findNodeHandle(self.refs[CUSTOM_VIEW]),
1, // 发送的commandId为1
null
);
}
_onChange() {
if (!this.props.handleClick) {
return;
}
this.props.handleClick();
}
render(){
// 设置ref,没弄明白为什么一定需要设置ref,大概是_changeColor中的findNodeHandle需要
return(
<RCTMyCustomView
ref={CUSTOM_VIEW}
{...this.props}
onChangeColor={() => this._onChange()}>
</RCTMyCustomView>);
}
}
MyCustomView.propTypes = {
handleClick: PropTypes.func,
color: PropTypes.string, // 设置一个属性
...View.propTypes,
};
var RCTMyCustomView = requireNativeComponent('MyCustomView', MyCustomView, {
nativeOnly: {onChangeColor: true}
});注意上面用到了nativeOnly。有时候有一些特殊的属性,想从原生组件中导出,但是又不希望它们成为对应React封装组件的属性。举个例子,Switch组件可能在原生组件上有一个onChange事件,然后在封装类中导出onValueChange回调属性。这个属性在调用的时候会带上Switch的状态作为参数之一。这样的话你可能不希望原生专用的属性出现在API之中,也就不希望把它放到propTypes里。可是如果你不放的话,又会出现一个报错。解决方案就是带上nativeOnly选项。(来自 http://reactnative.cn/docs/0.41/native-component-android.html#content)
现在就可以愉快的调用了。
<MyCustomView
ref='view'
color='#00ff00'
handleSizeClick={() => this._handleSizeClick()}
handleClick={() => this._handleClick()}
style={{width:300, height:300}} />建议初学者好好的实践一遍。
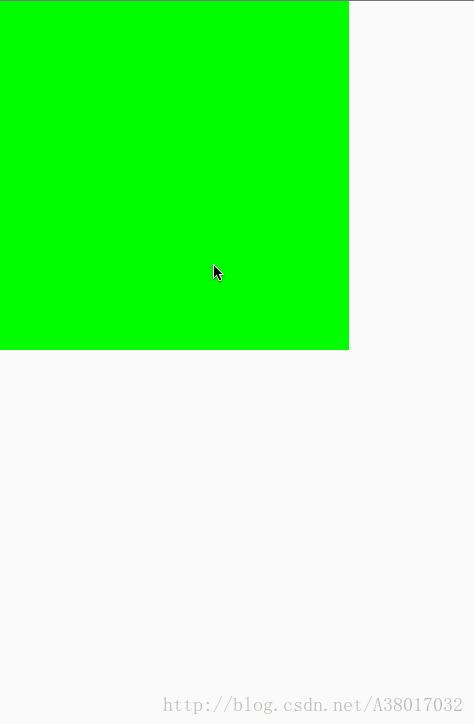
最后的结果
NativeModule
Native模块:定义Native的模块供JS调用。这样的场景会比较的多,比如Toast,在JS中没有Toast这类东西,但是Android/IOS中却很常见。
- JS调用Native组件
封装一个moudle供JS调用。注意里面注释。
@ReactModule(name = "DemoToast")
public class DemoToastModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule {
private static final String DURATION_SHORT_KEY = "SHORT";
private static final String DURATION_LONG_KEY = "LONG";
public DemoToastModule(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
super(reactContext);
}
// Module的名称
@Override
public String getName() {
return "DemoToast";
}
/**
* 这里定义的值可以被JS中引用,JS引用的时候.SHORT就会对应到相应的Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getConstants() {
final Map<String, Object> constants = new HashMap<>();
constants.put(DURATION_SHORT_KEY, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
constants.put(DURATION_LONG_KEY, Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
return constants;
}
/**
* 通过Callback回调到JS
*/
@ReactMethod
public void show(String message, int duration, Callback callback) {
Toast.makeText(getReactApplicationContext(), message, duration).show();
callback.invoke("Egos");
}
}JS将Native module转化成JS组件。
import { NativeModules } from 'react-native';
RCTDemoToast = NativeModules.DemoToast; // 获取到Native Module
var DemoToast = {
/**
* 觉得这里不是很好理解,但是这里对应的那个值(SHORT或者LONG)确实
* 是对应了上面Java代码中的getConstants对应的信息。
*/
SHORT: RCTDemoToast.SHORT,
LONG: RCTDemoToast.LONG,
show(message, duration){
RCTDemoToast.show(message, duration, (msg) => {
var str = msg;
});
}
};
module.exports = DemoToast;- 交互。Native回调信息给JS。
@ReactMethod
public void show(String message, int duration, Callback callback) {
Toast.makeText(getReactApplicationContext(), message, duration).show();
callback.invoke("Egos"); // callback回调信息。注意上面的RCTDemoToast.show方法第三个参数。
}在JS中注册testMethod。Native直接调用JS。
componentWillMount() {
DeviceEventEmitter.addListener('testMethod', (event) => {var s = event;} );
}下面Native代码发送指令就会执行上面代码。
WritableMap params = Arguments.createMap();
params.putString("xixi","Egos");
sendEvent(getReactApplicationContext(), "testMethod", params);
/**
* 也可以直接发送事件给JS代码
*/
private void sendEvent(ReactContext reactContext,
String eventName, @Nullable WritableMap params) {
reactContext.getJSModule(DeviceEventManagerModule.RCTDeviceEventEmitter.class).emit(eventName, params); // 会回调到上面注册的testMethod。
}JavaScriptModule
JS模块:com.facebook.react.CoreModulesPackage中有展示出来一些信息,AppRegistry、RCTEventEmitter(对应了RCTNativeAppEventEmitter)等等。
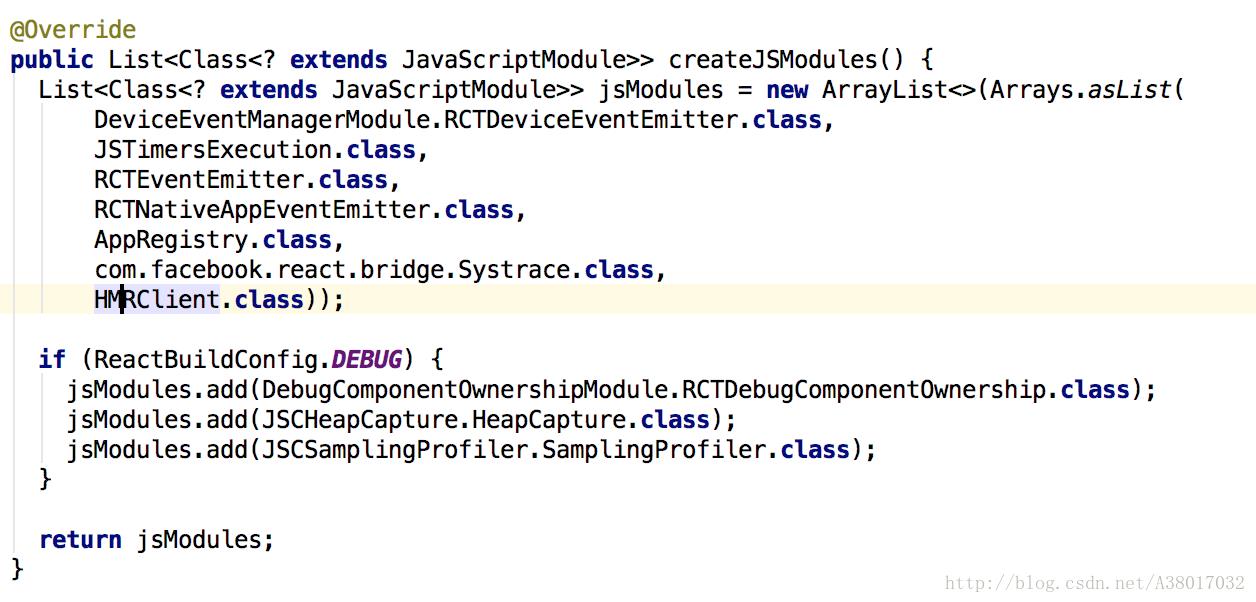
源码中定义的JS Module
相当于执行JS代码的时候会对应去执行Native相应的代码,这部分不是View,不是Native Module。 这部分内容还不是很理解,没有找到合适的例子,后续有问题补充。
思考
- 查看ReactPackage.java这个类,里面的信息说明了UI组件、Native模块、JS模块这三个信息,也就是我们平常定义的这三种信息都需要在这里对应的注册。
public interface ReactPackage {
/**
* @return list of native modules to register with the newly created catalyst instance
*/
List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(ReactApplicationContext reactContext);
/**
* @return list of JS modules to register with the newly created catalyst instance.
*
* IMPORTANT: Note that only modules that needs to be accessible from the native code should be
* listed here. Also listing a native module here doesn't imply that the JS implementation of it
* will be automatically included in the JS bundle.
*/
List<Class<? extends JavaScriptModule>> createJSModules();
/**
* @return a list of view managers that should be registered with {@link UIManagerModule}
*/
List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(ReactApplicationContext reactContext);
}- React Native将很多的Native的UI以及组件都封装成了JS供JS调用,对外暴露的接口应该会越来越全面以及越来越简单,期待未来的发展。
- 最近用React Native写了一点代码,本来准备写写一些控件的使用以及一些坑,但是想想还是算了,每一个控件使用在不同的地方可能就有一些不一样的问题,这些还得花时间慢慢解决。
参考
以上是关于如何在android的代码中调用某个组件属性的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章