使用Pytorch实现Transformer,如何巧妙的使用或者停用 optimizer.zero_grad()来训练大模型?
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用Pytorch实现Transformer,如何巧妙的使用或者停用 optimizer.zero_grad()来训练大模型?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A optimizer.zero_grad()意思是把梯度置零,也就是把loss关于weight的导数变成0.pytorch对于每个batch大都执行了这样的操作:
optimizer.zero_grad() ## 梯度清零preds = model(inputs) ## inference
loss = criterion(preds, targets) ## 求解loss
loss.backward() ## 反向传播求解梯度
optimizer.step() ## 更新权重参数
1,由于pytorch的动态计算图,当我们使用loss.backward()和opimizer.step()进行梯度下降更新参数的时候,梯度并不会自动清零。并且这两个操作是独立操作。
2,backward():反向传播求解梯度。
3,step():更新权重参数。 参考技术B optimizer.zero_grad()意思是把梯度置零,也就是把loss关于weight的导数变成0.
pytorch对于每个batch大都执行了这样的操作:
optimizer.zero_grad() ## 梯度清零preds = model(inputs) ## inference
loss = criterion(preds, targets) ## 求解loss
loss.backward() ## 反向传播求解梯度
optimizer.step() ## 更新权重参数
1,由于pytorch的动态计算图,当我们使用loss.backward()和opimizer.step()进行梯度下降更新参数的时候,梯度并不会自动清零。并且这两个操作是独立操作。
2,backward():反向传播求解梯度。
3,step():更新权重参数。
Swin Transformer模型——pytorch实现
论文传送门:Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows
前置文章:ViT模型——pytorch实现
Swin Transformer的特点:
相较于ViT:
①采用逐渐递增的下采样倍数,获得具有层次的特征图(hierarchical feature maps),便于进行检测和分割任务;
②引入W-MSA(Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention)和SW-MSA(Shifted Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention),减少了计算量。
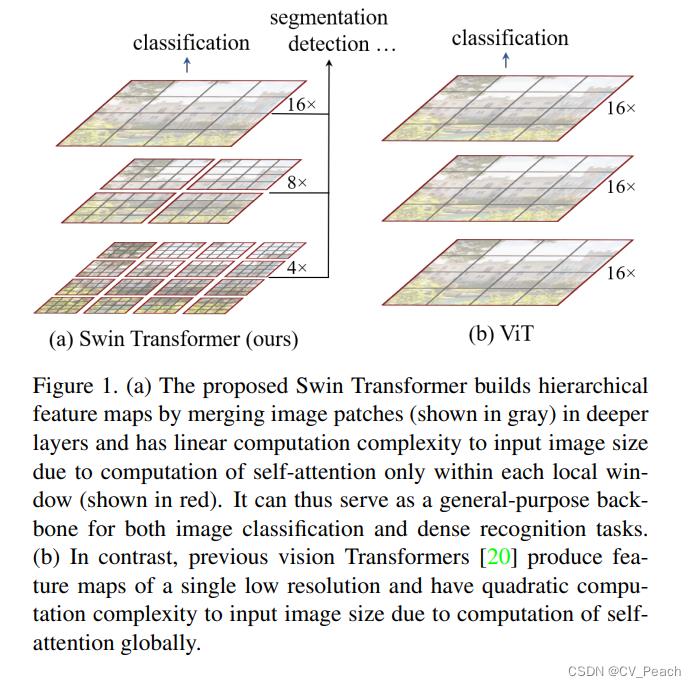
W-MSA和SW-MSA:
W-MSA是将特征图划分成一个个Window,然后在每个Window中进行Patch的划分和Attention的计算,这样可以减少计算量,但同时也使得不同Window之间无法进行信息交互;
因此,作者又提出SW-MSA,即偏移的W-MSA,具体做法为将原本划分Windows的网格向右、向下平移window_size//2长度,然后通过平移拼接将小块的Window拼接成整块Window,从而保证与W-MSA的Windows数量相同,同时生成mask,将原本不相邻的区域的tokens(patches)设为-100,在Attention计算时,与attention(
Q
K
T
QK^T
QKT)相加,使得不相邻的区域的attention经过softmax后趋近于0,避免不相邻区域的干扰,经过Attention后再将拼接的Windows拆分,反向平移还原回原特征图。
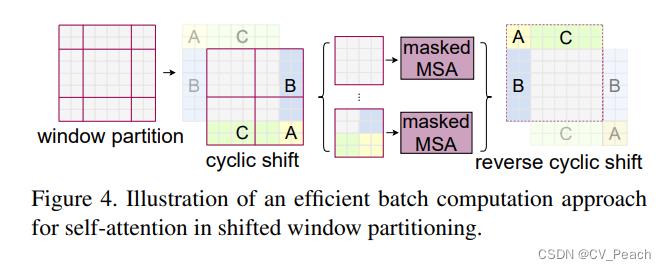
Relative Position Bias:
在Attention计算中,引入一个偏置项B,B从一个可训练的矩阵(relative positon bias matrix)中取,索引为每个token(patch)的相对位置索引(经过一些变换)。
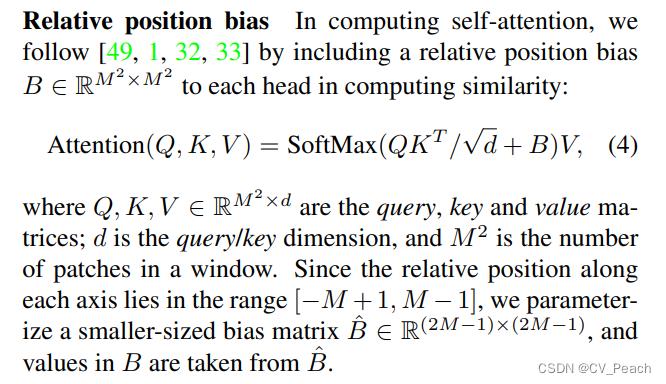
Swin Transformer的结构:
①Patch Partition:将输入图片用4x4的窗口划分,并在Channel通道堆叠,代码中使用Conv2d实现;
②Linear Embedding:将H和W维度展平;
(代码中将Patch Partition和Linear Embedding通过一个Patch Embedding实现)
③Swin Transformer Block:成对出现,整个结构与ViT中的Transformer Block相同,只是把MSA替换成了W-MSA和SW-MSA,第奇数个Block使用W-MSA,第偶数个Block使用SW-MSA(二者交替使用);
④Patch Merging:下采样方法,类似focus,每次Patch Merging先使高H、宽W减半,通道C翻4倍,然后通过一个Linear将C减半,即最后C为原来的2倍;
Stage:Linear Embedding/Patch Merging + L * Swin Transformer Block
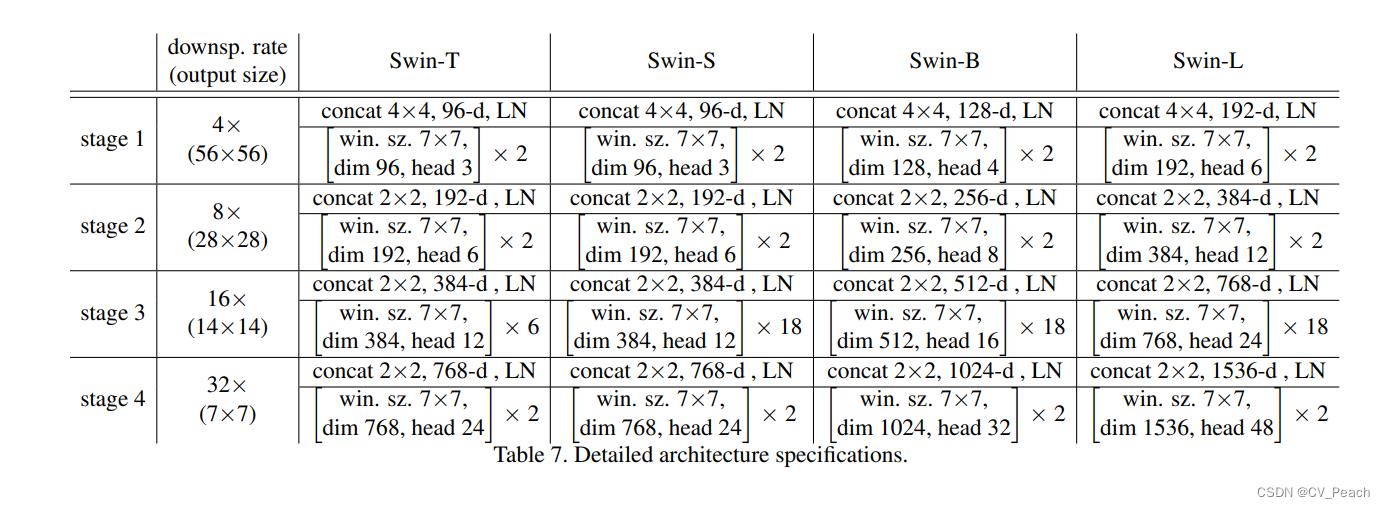
不同规模的Swin Transformer模型:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from einops import rearrange
def drop_path_f(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path_f(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class PatchEmbedding(nn.Module): # Patch Partition + Linear Embedding
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_channels=3, emb_dim=96):
super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, emb_dim, patch_size, patch_size) # 4x4卷积实现Patch Partition
def forward(self, x):
# (B,C,H,W)
x = self.conv(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
x = rearrange(x, "B C H W -> B (H W) C") # Linear Embedding
return x, H, W
class MLP(nn.Module): # MLP
def __init__(self, in_dim, hidden_dim=None, drop_ratio=0.):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
if hidden_dim is None:
hidden_dim = in_dim * 4 # linear的hidden_dims默认为in_dims的4倍
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, in_dim)
self.gelu = nn.GELU()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
# Linear + GELU + Dropout + Linear + Dropout
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.gelu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x
class WindowMultiHeadSelfAttention(nn.Module): # W-MSA / SW-MSA
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads,
attn_drop_ratio=0., proj_drop_ratio=0.):
super(WindowMultiHeadSelfAttention, self).__init__()
self.window_size = window_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop_ratio)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop_ratio)
# 创建Relative position bias matrix,其参数可训练,根据Relative position index取其中的值作为B
self.relative_position_bias_matrix = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((2 * window_size - 1) ** 2, num_heads))
# 使用register_buffer,使得relative_position_index可以随model.state_dict()保存,并可以随model.cuda()加载至GPU
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", self._get_relative_position_index())
def _get_relative_position_index(self): # 创建Relative position index
coords = torch.flatten(
torch.stack(
torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(self.window_size), torch.arange(self.window_size)], indexing="ij"), dim=0
), 1
)
relative_coords = coords[:, :, None] - coords[:, None, :]
relative_coords += self.window_size - 1
relative_coords[0, :, :] *= 2 * self.window_size - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(0)
return relative_position_index.view(-1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
qkv = self.qkv(x)
qkv = rearrange(qkv, "B P (C H d) -> C B H P d", C=3, H=self.num_heads, d=self.head_dim)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
k = rearrange(k, "B H P d -> B H d P")
# Attention(Q, K, V ) = softmax(QKT/dk)V (T表示转置)
attn = torch.matmul(q, k) * self.head_dim ** -0.5 # QKT/dk
bias = self.relative_position_bias_matrix[self.relative_position_index]
bias = rearrange(bias, "(P1 P2) H -> 1 H P1 P2", P1=self.window_size ** 2, P2=self.window_size ** 2)
attn += bias # QKT/dk + B
if mask is not None:
# 如果mask不为None,对attn进行加和,使得在原图上不相邻的token对应的attn-100,经过softmax后趋近于0
attn = rearrange(attn, "(B NW) H P1 P2 -> B NW H P1 P2", NW=mask.shape[0])
mask = rearrange(mask, "NW P1 P2 -> 1 NW 1 P1 P2")
attn += mask
attn = rearrange(attn, "B NW H P1 P2 -> (B NW) H P1 P2")
attn = F.softmax(attn) # softmax(QKT/dk + B)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = torch.matmul(attn, v) # softmax(QKT/dk + B)V
x = rearrange(x, "B H P d -> B P (H d)")
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module): # Swin Transformer Block
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=7, shift=True,
attn_drop_ratio=0., proj_drop_ratio=0., drop_path_ratio=0.):
super(SwinTransformerBlock, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = window_size // 2 if shift else 0. # 不进行shift时,shift_size取0
self.layernorm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.attn = WindowMultiHeadSelfAttention(dim, self.window_size, self.num_heads,
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio,
proj_drop_ratio=proj_drop_ratio)
self.droppath = DropPath(drop_path_ratio) if drop_path_ratio > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.layernorm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.mlp = MLP(dim)
def _create_mask(self, H, W, device): # 创建mask
mask = torch.zeros((1, 1, H, W), device=device)
slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
count = 0
for h in slices:
for w in slices:
mask[:, :, h, w] = count
count += 1
mask = rearrange(mask, "1 1 (H Hs) (W Ws) -> (H W) (Hs Ws)", Hs=self.window_size, Ws=self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask.unsqueeze(1) - mask.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.)) # 在原图上不相邻的token,mask为-100.
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.)) # 在原图上相邻的token,mask为0.
return attn_mask
def forward(self, input: tuple):
x, H, W = input
shortcut = x
x = self.layernorm1(x)
x = rearrange(x, "B (H W) C -> B C H W", H=H, W=W)
if self.shift_size > 0.: # 如果偏移量shift_size>0.,则对x进行偏移,同时创建对应的mask
x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(2, 3))
mask = self._create_mask(H, W, device=x.device)
else:
mask = None
num_windows = (x.shape[2] // self.window_size, x.shape[3] // self.window_size)
# x = rearrange(x, "B C (H Hs) (W Ws) -> (B H W) C Hs Ws", Hs=self.window_size, Ws=self.window_size)
x = rearrange(x, "B C (H Hs) (W Ws) -> (B H W) (Hs Ws) C", Hs=self.window_size, Ws=self.window_size)
x = self.attn(x, mask)
# x = rearrange(x, "(B H W) C Hs Ws -> B C (H Hs) (W Ws)", Hs=self.window_size, Ws=self.window_size)
x = rearrange(x, "(B H W) (Hs Ws) C -> B C (H Hs) (W Ws)", H=num_windows[0], W=num_windows[1],
Hs=self.window_size, Ws=self.window_size)
if self.shift_size > 0.: # 如果偏移量shift_size>0.,则将偏移过的x调整回原来的位置
x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(2, 3))
x = rearrange(x, "B C H W -> B (H W) C", H=H, W=W)
x = shortcut + self.droppath(x) # 残差连接
shortcut = x
x = self.layernorm2(x)
x = self.mlp(x)
x = shortcut + self.droppath(x) # 残差连接
return x, H, W
class PatchMerging(nn.Module): # Patch Merging
def __init__(self, dim):
super(PatchMerging, self).__init__()
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(4 * dim)
self.linear = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
def forward(self, input: tuple):
# (B,L,C) --> (B,C,H,W) --> (B,4*C,H/2,W/2) --> (B,L/4,4*C) --> (B,L/4,2*C)
x, H, W = input
x = rearrange(x, "B (H W) C -> B C H W", H=H, W=W)
x = torch.cat([x[:, :, 0::2, 0::2], x[:, :, 1::2, 0::2], x[:, :, 0::2, 1::2], x[:, :, 1::2, 1::2]], dim=1)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
x = rearrange(x, "B C H W -> B (H W) C")
x = self.layernorm(x)
x = self.linear(x)
return x, H, W
class SwinHead(nn.Module): # Swin Head,分类任务的Head
def __init__(self, dim, num_classes):
super(SwinHead, self).__init__()
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.mlphead = nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layernorm(x)
x = rearrange(x, "B L C -> B C L")
x = self.avgpool(x)
return self.mlphead(x.squeeze())
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module): # Swin Transformer
def __init__(self, dims=(96, 192, 384, 768), num_blocks=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24),
num_classes=1000,
pos_drop_ratio=0., attn_drop_ratio=0., proj_drop_ratio=0., drop_path_ratio_max=0.1):
super(SwinTransformer, self).__init__()
self.patchembedding = PatchEmbedding(emb_dim=dims[0])
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(pos_drop_ratio)
# #drop path ratio从0递增至drop_path_ratio_max
drop_path_ratio = [i.item() for i in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_ratio_max, sum(num_blocks))]
self.blocks1 = nn.Sequential(
*[SwinTransformerBlock(dims[0], num_heads[0], shift=(i % 2 != 0),
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio,
proj_drop_ratio=proj_drop_ratio,
drop_path_ratio=drop_path_ratio[i + sum(num_blocks[:0])])
for以上是关于使用Pytorch实现Transformer,如何巧妙的使用或者停用 optimizer.zero_grad()来训练大模型?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章