Arduino框架下ESP32使用固件自带的SD库的总结
Posted perseverance52
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Arduino框架下ESP32使用固件自带的SD库的总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Arduino框架下ESP32使用固件自带的SD库的总结
- 代码调试还是使用
VSCode PIO方便一些。可以很方便的去查看相关函数的上一层封装。
跟随SD库附带的ReadMe文件认识一下卡的类型

- SD卡与ESP32接线图(VSPI接线)

- 默认使用的是VSPI总线
| SPI | MOSI | MISO | CLK | CS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSPI | 23 | 19 | 18 | 5 |
- SPI通讯
1.GND-for the ground pins.
2.VCC-for the supply voltage.
3.MISO-for the SPI Master Input Slave Output pin.
4.MOSI-for the SPI Master Output Slave Input pin.
5.SCK-for the SPI Serial Clock pin.
6.CS-for the SPI Chip Select pin.
- gnd -用于接地插脚。
- vcc- 电源电压。
- miso-用于SPI主输入从输出引脚。
- mosi -用于SPI主输出从输入引脚。
- sck -用于SPI串行时钟引脚。
- cs -用于SPI芯片选择引脚。
- esp32 Devkeit
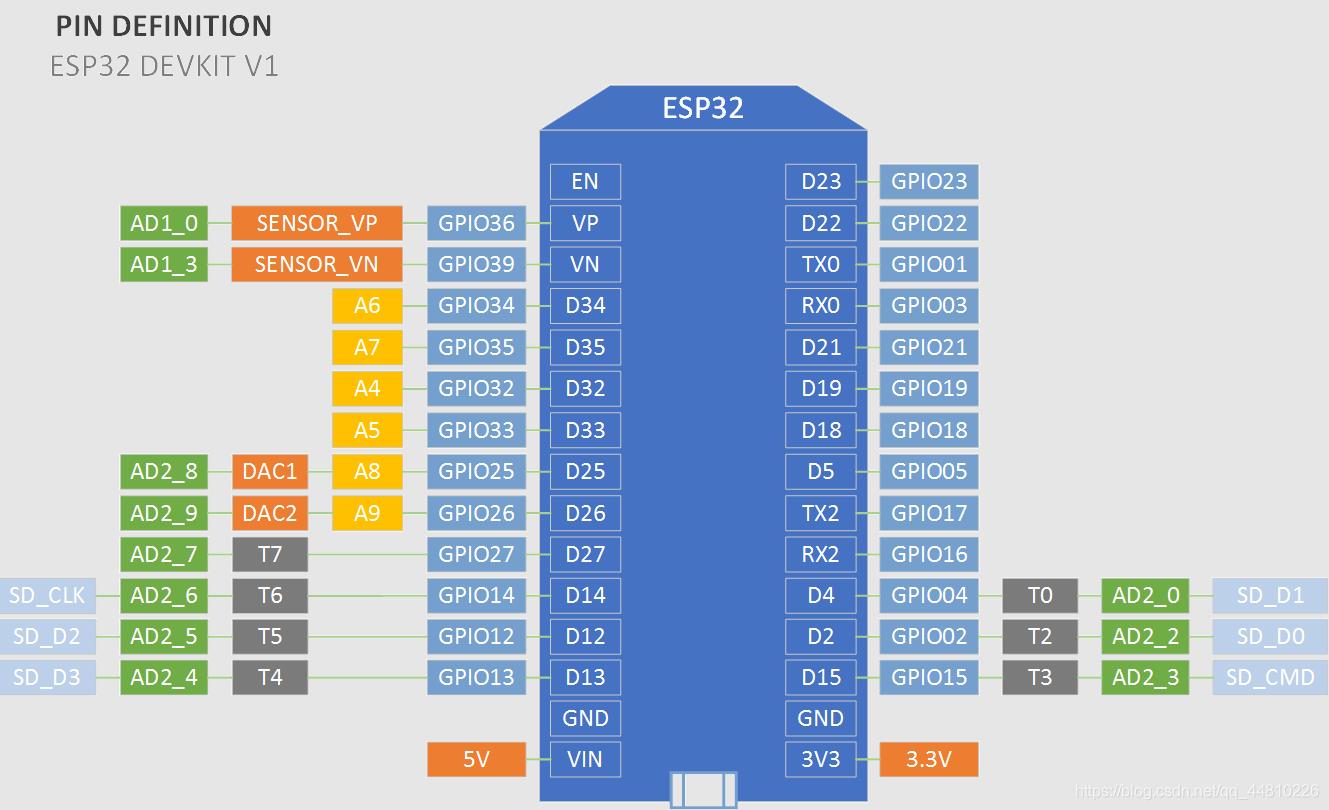
Arduino IDE中SD卡示例位置
-
本实验所使用的模块
-
实例代码
/*
* Connect the SD card to the following pins:
*
* SD Card | ESP32
* D2 -
* D3 SS
* CMD MOSI
* VSS GND
* VDD 3.3V
* CLK SCK
* VSS GND
* D0 MISO
* D1 -
*/
#include "FS.h"
#include "SD.h"
#include "SPI.h"
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels)
Serial.printf("Listing directory: %s\\n", dirname);
File root = fs.open(dirname);
if(!root)
Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
return;
if(!root.isDirectory())
Serial.println("Not a directory");
return;
File file = root.openNextFile();
while(file)
if(file.isDirectory())
Serial.print(" DIR : ");
Serial.println(file.name());
if(levels)
listDir(fs, file.path(), levels -1);
else
Serial.print(" FILE: ");
Serial.print(file.name());
Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
Serial.println(file.size());
file = root.openNextFile();
void createDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path)
Serial.printf("Creating Dir: %s\\n", path);
if(fs.mkdir(path))
Serial.println("Dir created");
else
Serial.println("mkdir failed");
void removeDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * path)
Serial.printf("Removing Dir: %s\\n", path);
if(fs.rmdir(path))
Serial.println("Dir removed");
else
Serial.println("rmdir failed");
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path)
Serial.printf("Reading file: %s\\n", path);
File file = fs.open(path);
if(!file)
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
return;
Serial.print("Read from file: ");
while(file.available())
Serial.write(file.read());
file.close();
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message)
Serial.printf("Writing file: %s\\n", path);
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file)
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
if(file.print(message))
Serial.println("File written");
else
Serial.println("Write failed");
file.close();
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message)
Serial.printf("Appending to file: %s\\n", path);
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
if(!file)
Serial.println("Failed to open file for appending");
return;
if(file.print(message))
Serial.println("Message appended");
else
Serial.println("Append failed");
file.close();
void renameFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path1, const char * path2)
Serial.printf("Renaming file %s to %s\\n", path1, path2);
if (fs.rename(path1, path2))
Serial.println("File renamed");
else
Serial.println("Rename failed");
void deleteFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path)
Serial.printf("Deleting file: %s\\n", path);
if(fs.remove(path))
Serial.println("File deleted");
else
Serial.println("Delete failed");
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path)
File file = fs.open(path);
static uint8_t buf[512];
size_t len = 0;
uint32_t start = millis();
uint32_t end = start;
if(file)
len = file.size();
size_t flen = len;
start = millis();
while(len)
size_t toRead = len;
if(toRead > 512)
toRead = 512;
file.read(buf, toRead);
len -= toRead;
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes read for %u ms\\n", flen, end);
file.close();
else
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file)
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
return;
size_t i;
start = millis();
for(i=0; i<2048; i++)
file.write(buf, 512);
end = millis() - start;
Serial.printf("%u bytes written for %u ms\\n", 2048 * 512, end);
file.close();
void setup()
Serial.begin(115200);
if(!SD.begin())
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
return;
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if(cardType == CARD_NONE)
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
return;
Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
if(cardType == CARD_MMC)
Serial.println("MMC");
else if(cardType == CARD_SD)
Serial.println("SDSC");
else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC)
Serial.println("SDHC");
else
Serial.println("UNKNOWN");
uint64_t cardSize = SD.cardSize() / (1024 * 1024);
Serial.printf("SD Card Size: %lluMB\\n", cardSize);
listDir(SD, "/", 0);
createDir(SD, "/mydir");
listDir(SD, "/", 0);
removeDir(SD, "/mydir");
listDir(SD, "/", 2);
writeFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "Hello ");
appendFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "World!\\n");
readFile(SD, "/hello.txt");
deleteFile(SD, "/foo.txt");
renameFile(SD, "/hello.txt", "/foo.txt");
readFile(SD, "/foo.txt");
testFileIO(SD, "/test.txt");
Serial.printf("Total space: %lluMB\\n", SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
Serial.printf("Used space: %lluMB\\n", SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
void loop()
SD卡初始化
if(!SD.begin())
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
return;
- 自定义
CS引脚
SD.begin(CSpin)
- 默认与microSD通讯时的频率为
10MHz,个人测试推荐使用默认频率比较稳定,容易识别到卡。如果设置到更高频率很大几率识别不到卡。esp32除了默认的SPI1连接的外置flash最高速度可以达到80MHz,其他的两组SPI通讯速度不能设置这么高。
自定义SPI引脚
#define SCK 17 //tx2
#define MISO 19
#define MOSI 23
#define CS 5
SPIClass spi = SPIClass(VSPI);
spi.begin(SCK, MISO, MOSI, CS);
if (!SD.begin(CS,spi,10000000))
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
return;
-
- 采用
128MB容量的MicroSD卡很容易就读到。
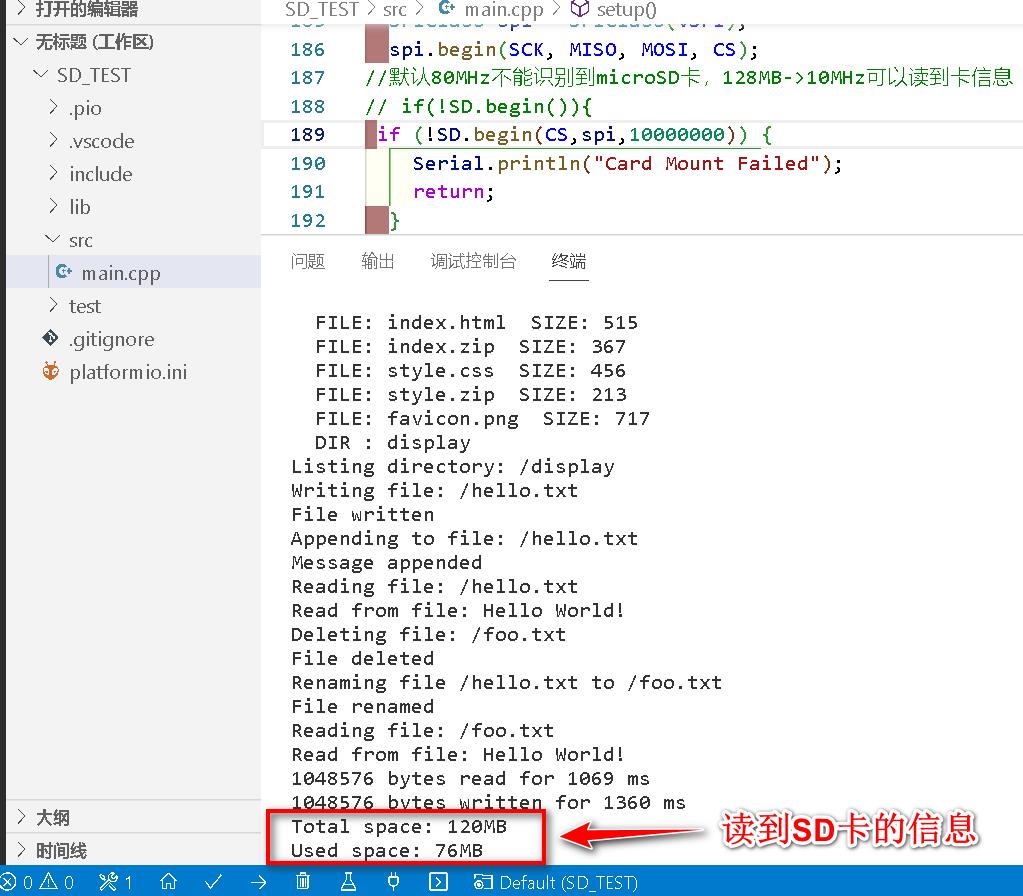
- 采用
2GB的内存卡测试

插卡注意事项
先插卡再给MicroSD卡模块供电,如果是热拔插的情况,在插上Micro SD卡后需要重新给MicroSD卡模块断电重启一下,否则无法读取到卡。这一点很重要。
- 目前发现市面上的有些
MicroSD卡存在读取不到,不能被识别的情况,我在测试手上的3张MicroSD卡时,发现一张1GB容量的卡不管怎么都读不到,不知道是卡本身的原因还是ESP32就是对这类颗粒的存储芯片不兼容,内存卡是好的,通过读卡器,电脑都是可以识别到的,能正常写入和读取的卡。- 容量范围:最大理论支持32GB,目前手上没有这个容量的卡,没法验证和测试。
以上是关于Arduino框架下ESP32使用固件自带的SD库的总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章