C语言如何对链表的数进行排序?
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C语言如何对链表的数进行排序?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>structnodeintsnum,grad;structnode*next;;intmain(void)structnode*p=NULL,*q=NULL,*t=NULL,*head,*p1=NULL,*q1=NULL,*head1;head=NULL;intn... #include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>struct node int snum, grad; struct node*next;;int main(void) struct node*p=NULL, *q=NULL, *t=NULL, *head,*p1=NULL,*q1=NULL,*head1; head = NULL; int n, m,num1,num2; scanf_s("%d%d", &n,&m); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf_s("%d%d", &num1,&num2); p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); p->snum = num1; p->grad = num2; p->next = NULL; if (head == NULL) head = p; else q->next = p; q = p; head1 = NULL; for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) scanf_s("%d%d", &num1, &num2); p1 = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); p1->snum = num1; p1->grad = num2; p1->next = NULL; if (head1 == NULL) head1 = p1; else q1->next = p1; q1 = p1; p->next = head1; t = head; printf("\n\n\n\n"); while (t != NULL) printf("%d %d\n", t->snum, t->grad); t = t->next; return 0;本人愚笨,实在不知道如何对其排序,希望大佬指点一二 ; 展开
参考技术A 同学,给你一段代码,里面涵盖了链表的冒泡排序!#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef
struct
node
int
data;/*data代表成绩分数*/
struct
node
*next;
LNode,*LinkList;
LinkList
Creat(void)/*创建链表,结束标志为当输入的数据为0!*/
LinkList
H,p1,p2;
int
n;
n=0;
p1=p2=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
printf("输入数据:");
scanf("%d",&p1->data);
H=NULL;
while(p1->data!=0)
n=n+1;
if(n==1)
H=p1;
else
p2->next=p1;
p2=p1;
p1=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
scanf("%d",&p1->data);
p2->next=NULL;
return(H);
LinkList
Sort(LinkList
SL)/*递增排序函数:入口参数:链表的头指针,此为链表中的排序函数*/
LinkList
p,q;
int
temp;
for(p=SL;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
for(q=p->next;q!=NULL;q=q->next)
if(p->data>q->data)
temp=q->data;
q->data=p->data;
p->data=temp;
return
SL;
int
main()
LinkList
L,S,K;
L=Creat();
printf("初始化的单链表数据序列为:\n");
for(S=L;S!=NULL;S=S->next)
printf("%d
",S->data);
Sort(L);
printf("\n按递增顺序排序后的序列为:\n");
for(K=L;K!=NULL;K=K->next)
printf("%d==>",K->data);
return
0;
链表相关面试题:返回一个链表的深度拷贝,对链表进行插入排序,删除链表中重复的结点
一、返回一个链表的深度拷贝。
题目描述:
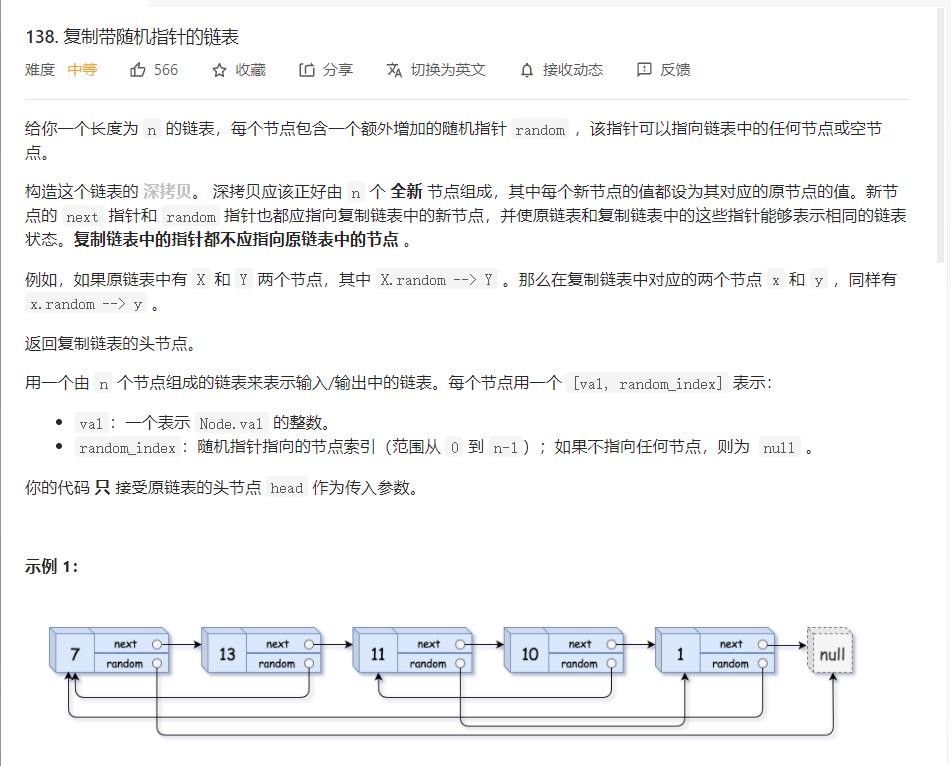
解题思路:
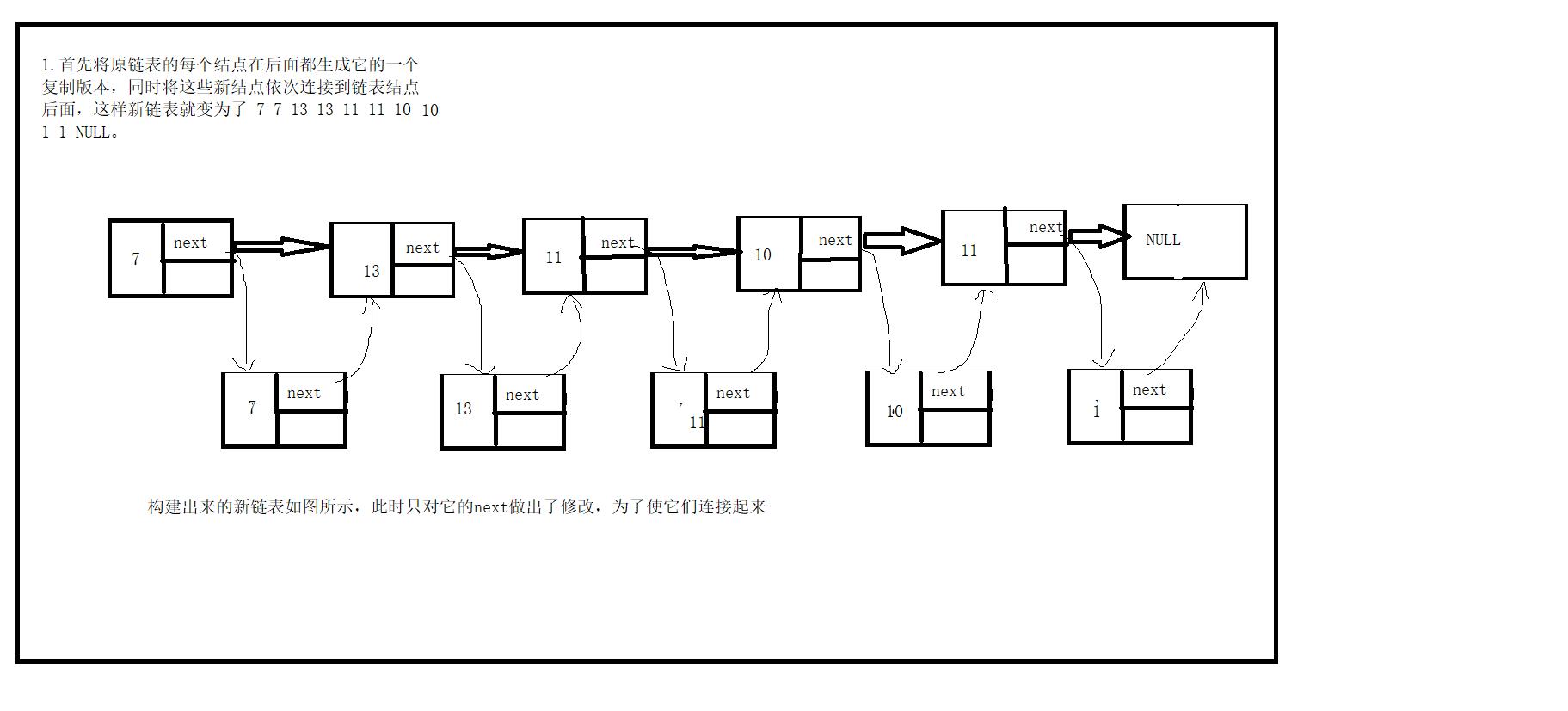
1.首先将原链表的每个结点在后面都生成它的一个复制版本,同时将这些新结点依次连接到链表结点后面,这样新链表就变为了 7 7 13 13 11 11 10 1 1 NULL。
2.依次对它的random指针域赋值,在cur->random不为空的情况下,将 newnode->random=cur->random->next;
3.解链,将新复制出来的结点从链表中解出来,同时将解下来的结点连接起来,构成的便是复制出来的链表。核心:更改next指针指向。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct Node*cur=head;
struct Node*newnode=NULL;
//构建同等链表,并将其插入
while(cur)
{
newnode=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newnode->next=newnode->random=NULL;
newnode->val=cur->val;
newnode->next=cur->next;
cur->next=newnode;
cur=newnode->next;
}
//将random指针指向改变,
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
newnode=cur->next;
if(cur->random)
{
newnode->random=cur->random->next;//指向cur->random->next.这是因为使其刚好指向的是复制的那个结点,而不是原结点
}
cur=newnode->next;
}
//拆链
cur=head;
struct Node*newhead=cur->next;
newnode=cur->next;
while(newnode)
{
cur->next=newnode->next;
cur=newnode;
newnode=cur->next;
}
return newhead;
}
二、对链表进行插入排序
题目描述:
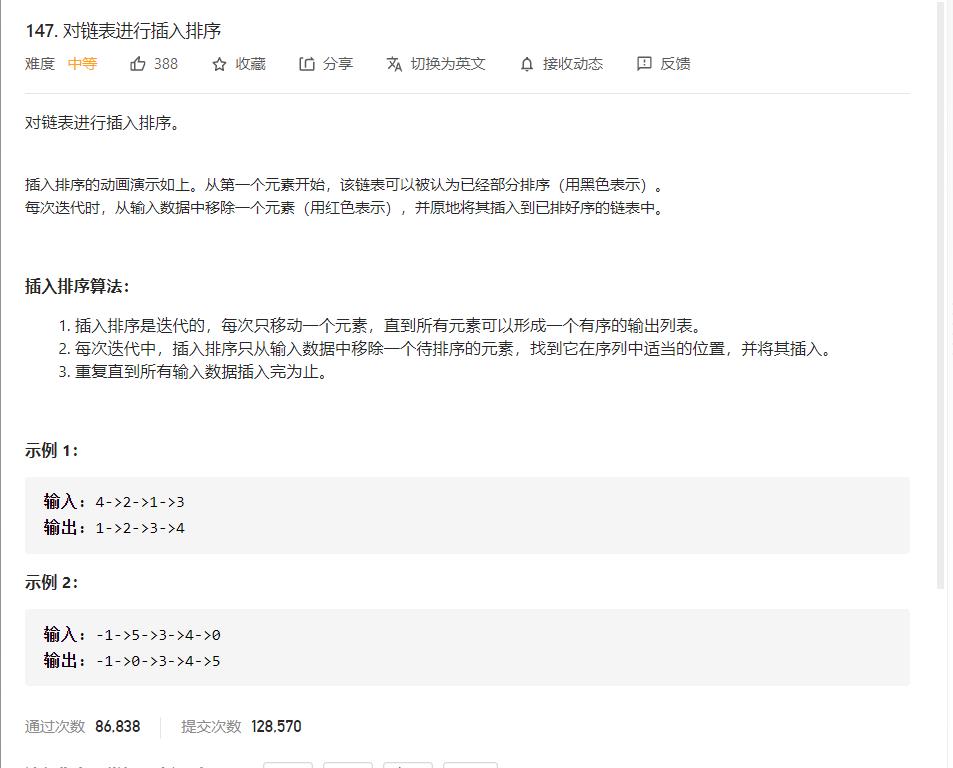
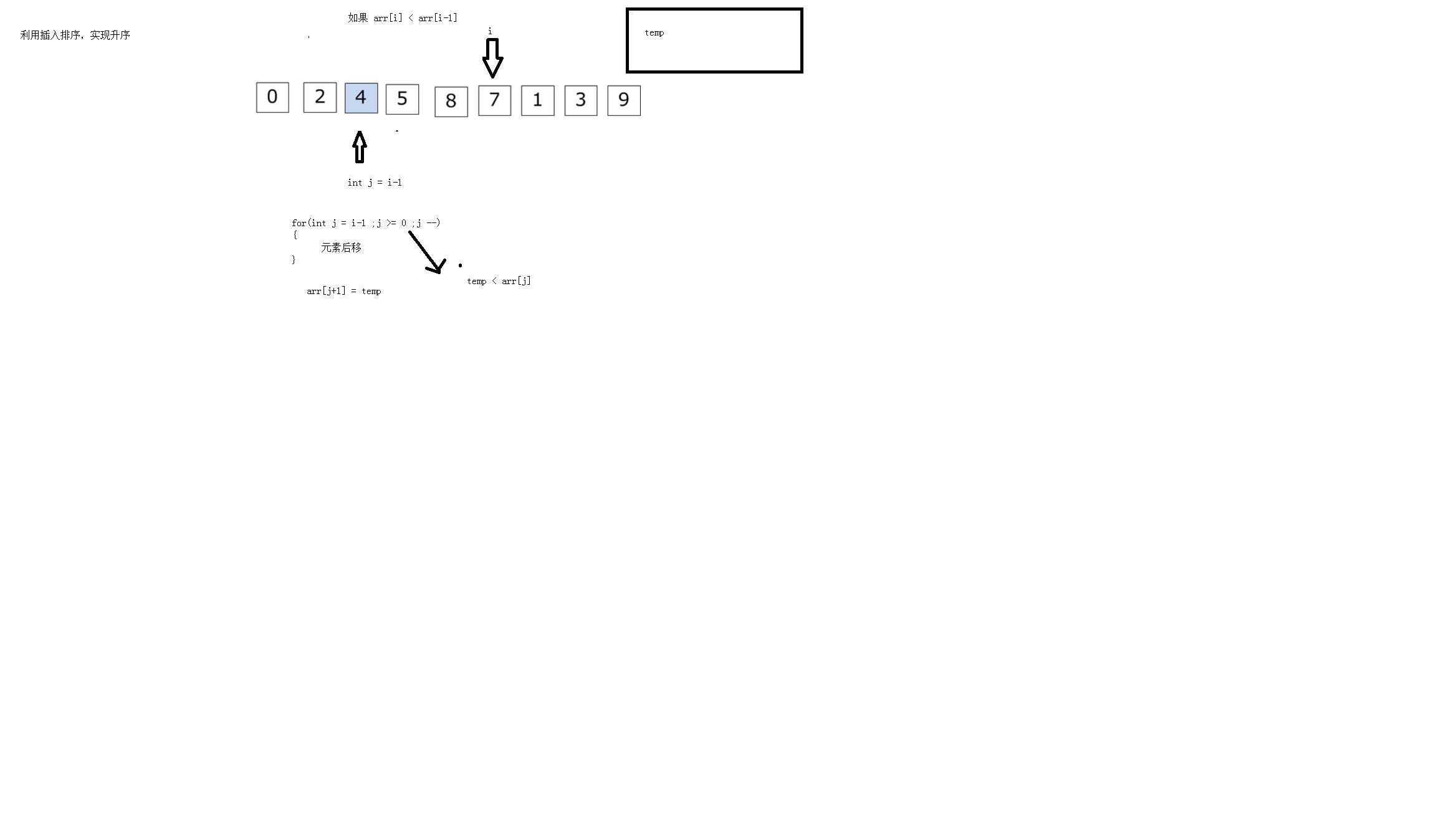
首先我们对插入排序进行了解:
这里给出的是数组插入排序,思想是一样的。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
//方法:将其实位置至于数组的第二个元素,让他与前面的元素进行比较,若小于,将其置于temp变量中,然后根据条件依次后移前面排序好
//的数组其他元素,依次执行
void sort(int* arr, int len)
{
int temp;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
int j = i-1;
if (arr[i] > arr[i - 1])
{
int j = i - 1;
temp = arr[i];
for( ; j>=0&&temp>arr[j] ; j--)
{
arr[j +1] = arr[j];
}
//在结束循环时会执行--操作,所以指针指向所需插入的前一个元素
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
void test01()
{
int a[] = { 1,4,2,0,9,5 };
int len = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
sort(a, len);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%d\\n", a[i]);
}
}
int main(void)
{
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
这里呈现的是链表插入排序的代码
struct ListNode* insertionSortList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode*phead=NULL;//记录的是插入排序后链表的第一个有效元素
struct ListNode*cur=head;//记录的是当前指向元素
struct ListNode*pos=NULL;//pos此时记录的是大于cur的第一个结点
struct ListNode*pre=NULL;//pre此时记录的插入的有效结点
while(cur!=NULL)
{
head=cur->next;
pos=phead;
pre=NULL;
while(pos)
{
if(cur->val<=pos->val)
{
break;
}
pre=pos;
pos=pos->next;
}
if(pos==phead)
{
cur->next=phead;
phead=cur;
}
else
{
cur->next=pos;
pre->next=cur;
}
cur=head;
}
return phead;
}
三、删除链表中重复的结点
题目描述:
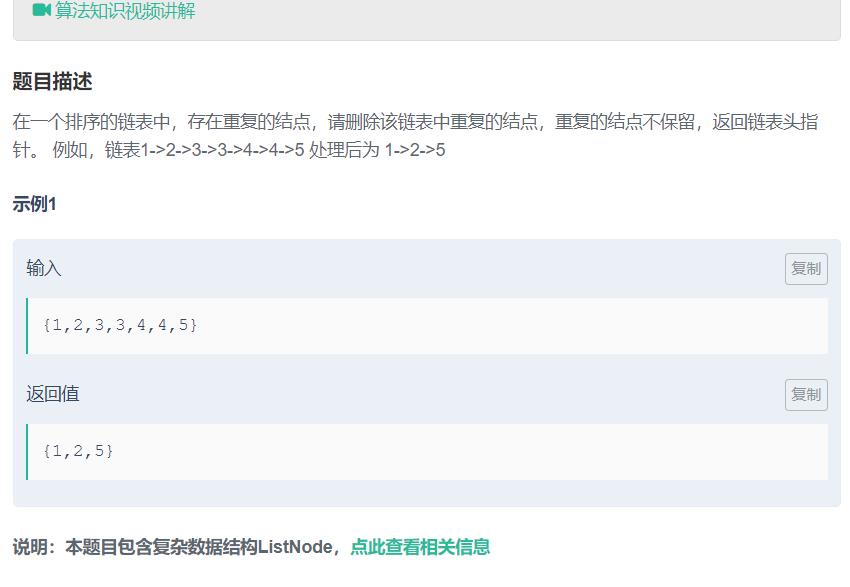
解题思路:

class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead==NULL||pHead->next==NULL)
{
return pHead;
}//如果只有一个元素,则必不可能有重复元素
struct ListNode* prev=NULL;//记录的是链表的尾元素,尾结点,同时prev还充当着判断链表头结点是否为空(类似于链表中都是一个元素)。
struct ListNode* cur=pHead;
struct ListNode* pnext=pHead->next;
while(next)
{
if(cur->val==pnext->val)
{
while(pnext && cur->val==pnext->val)//确定删除的区间cur--del
{
pnext=pnext->next;
}
while(cur!=pnext)
{
struct ListNode* del=cur;
cur=cur->next;
free(del);
}
if(prev==NULL)//此步是为了确定链表是否有首元素,
//同时记录了链表的尾结点,其实最好放在else后面,
//因为当链表中没有重复结点的话,此时pHead会为空。
{
pHead=cur;
}
else
{
prev->next=cur;//此时cur记录的是pnext的值,类似于1 2 3 3 4 4 5此时你在将3删除干净后将链表组合为 1 2 4 4 5
}
if(pnext)
{
pnext=pnext->next;
}
}
else
{
prev=cur;
cur=pnext;
pnext=pnext->next;
}
}
return pHead;
}
};
共同进步!!
以上是关于C语言如何对链表的数进行排序?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章