算法系列实战篇:Diffie-Hellman算法实现通信秘钥流程
Posted 善良勤劳勇敢而又聪明的老杨
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了算法系列实战篇:Diffie-Hellman算法实现通信秘钥流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
热门系列:
目录
2.4 通过B的公钥材料Y生成A的通信秘钥SecretKey
1、Diffie-Hellman算法简介
Diffie-Hellman算法(以下简称为:DH算法),是最早的密钥交换算法之一,它使得通信的双方能在非安全的信道中安全的交换密钥,用于加密后续的通信消息。
起基本流程原理如下:
假定小明和小红期望在一个不安全的网络中协商一个共同的密钥,那么进行如下步骤:
两人先说好大素数(质数)p和它的原始根g。
小明随机产生一个数a,并计算
A = p^a mod g, 发送给小红。小红随机产生一个数b,并计算
B = p^b mod g,发送给小明。此时, 小明手握小红发过来的B,结合自己产生的a开始这样计算:
B^a mod p = (p^b mod g)^a mod p = p^ab mod g小红也拿到了小明发来的A,同时结合自己的b,也开始计算:
A^b mod p = (p^a mod g)^b mod p = p^ab mod g这样小明和小红都得到了相同的密钥。
流程图如下:

2、使用DH算法生成通信秘钥加解密
以下会分为2端,发送端 A 和接收端 B ,后续以 A 和 B 简称描述。
以下代码内常量参数,先贴出来:
private static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "DH";
private static final String SECRET_ALGORITHM = "AES";
private static final int KEY_SIZE=512;
private static String ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM_MODE = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
private static String ENCRYPT_IV_PARAMETER_SPEC = "A-16-Byte-String";
//B的公钥材料
private static PublicKey receivePublicKey;
//B的私钥材料
private static PrivateKey receivePrivateKey;
//A的公钥材料
private static PublicKey senderPublicKey;
//A的私钥材料
private static PrivateKey senderPrivateKey;
//A的通信秘钥SecretKey
private static SecretKey senderSecretKey;
//B的通信秘钥SecretKey
private static SecretKey receiveSecretKey;2.1 A向B请求获取秘钥组成参数
该环节主要为了获取B的大素数(质数)p 和 它的原始根g,供后续使用。
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class DHEncryptParamBean
private String P;
private String G;
private int god;
/**
* @Description 从B获取大素数(质数)p 和 它的原始根g,并生成A的公私钥材料
* @return DHEncryptParamBean
**/
public static DHEncryptParamBean getParam() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException
DHEncryptParamBean resultBean = new DHEncryptParamBean("0", "0", 0);
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEY_SIZE);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
receivePublicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
receivePrivateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
byte[] encodedKey = receivePublicKey.getEncoded();
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(encodedKey);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec);
DHParameterSpec params = ((DHPublicKey) publicKey).getParams();
resultBean.setP(params.getP().toString(10));
resultBean.setG(params.getG().toString(10));
resultBean.setGod(KEY_SIZE);
return resultBean;
2.2 生成A的公私钥材料
/**
* @Description 生成的A的公私钥材料
* @return String
**/
public static void getPublicKey () throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
KeyPairGenerator senderPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
senderPairGenerator.initialize(KEY_SIZE);
KeyPair senderPair = senderPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
//生成的A的公私钥材料,后面会用于生成 加解密秘钥secretKey
senderPublicKey = senderPair.getPublic();
senderPrivateKey = senderPair.getPrivate();
2.3 A向B请求获取B的公钥材料
/**
* @Description 通过A的公钥材料,生成B的通信秘钥SecretKey
* @return byte []
**/
public static BigInteger getReceivePublicKey()
try
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(senderPublicKey.getEncoded());
DHPublicKey senderDHPublicKey = (DHPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec);
//生成B公私钥
KeyAgreement keyAgreement = KeyAgreement.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
keyAgreement.init(receivePrivateKey);
keyAgreement.doPhase(senderDHPublicKey, true);
receiveSecretKey = keyAgreement.generateSecret(SECRET_ALGORITHM);
BigInteger y = ((DHPublicKey)receivePublicKey).getY();
return y;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
2.4 通过B的公钥材料Y生成A的通信秘钥SecretKey
/**
* @Description 通过B的公钥材料Y,生成A的通信秘钥SecretKey
* @return
**/
public static void getSenderSecretKey(BigInteger revicePublicKeyY,DHEncryptParamBean paramBean)
try
BigInteger p = new BigInteger(paramBean.getP(),10);
BigInteger g = new BigInteger(paramBean.getG(),10);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
DHPublicKeySpec reviceDHPublicSpec = new DHPublicKeySpec(revicePublicKeyY, p, g);
DHPublicKey reviceDHPublicKey = (DHPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(reviceDHPublicSpec);
KeyAgreement keyAgreement = KeyAgreement.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
keyAgreement.init(senderPrivateKey);
keyAgreement.doPhase(reviceDHPublicKey, true);
senderSecretKey = keyAgreement.generateSecret(SECRET_ALGORITHM);
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidKeyException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidKeySpecException e)
e.printStackTrace();
2.5 加密请求参数
/**
* @Description 加密请求参数
* @Param [secretKey]
* @return java.lang.String
**/
public static String encrptyParam(SecretKey secretKey)
try
//加密发送端请求参数,通过AES加密
Cipher aesCipher = Cipher.getInstance(ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM_MODE);
aesCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new IvParameterSpec(ENCRYPT_IV_PARAMETER_SPEC.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
//请求参数原文
Map<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("name","jack");
//加密参数
String originalBody = JSON.toJSONString(paramMap);
byte[] encryptBody = aesCipher.doFinal(originalBody.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byte[] base64Body = Base64.getEncoder().encode(encryptBody);
String encryptParam = new String(base64Body, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
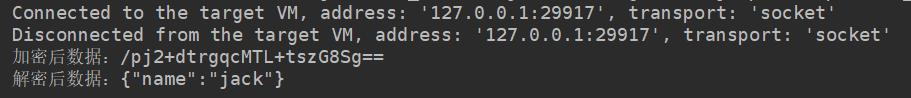
System.out.println("加密后数据:"+encryptParam);
return encryptParam;
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidKeyException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (NoSuchPaddingException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (BadPaddingException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
2.6 解密请求参数
/**
* @Description 解密请求参数
* @Param [secretKey]
* @return java.lang.String
**/
private static String decryptParam(SecretKey secretKey,String encryptParam)
try
Cipher deAesCipher = Cipher.getInstance(ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM_MODE);
deAesCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new IvParameterSpec(ENCRYPT_IV_PARAMETER_SPEC.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
byte[] decodedBase64Body = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptParam.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byte[] realBody = deAesCipher.doFinal(decodedBase64Body);
String deStr = new String(realBody, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("解密后数据:"+deStr);
return deStr;
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (NoSuchPaddingException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidKeyException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (BadPaddingException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
2.7 全流程演示
public static void main(String[] args)
try
//2.1 从B获取大素数(质数)p 和 它的原始根g,并生成B的公私钥材料
DHEncryptParamBean paramBean = getParam();
//2.2 获取A的公私钥材料
getPublicKey();
//2.3 通过A的公钥材料,生成B的通信秘钥SecretKey
BigInteger receivePublicKeyY = getReceivePublicKey();
//2.4 通过B的公钥材料Y,生成A的通信秘钥SecretKey
getSenderSecretKey(receivePublicKeyY,paramBean);
//2.5 A使用获取的SecretKey加密参数
String encryptParam = encrptyParam(senderSecretKey);
//2.6 B使用获取的SecretKey解密参数
String decryptParam = decryptParam(receiveSecretKey,encryptParam);
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (InvalidKeySpecException e)
e.printStackTrace();
请求完成结果如下:
3、总结
此实践内容中,有几个需要注意的点:
1、使用AES加解密时,需要将加解密的内容通过Base64先解密/后加密处理,关键代码如下:
//加密参数
String originalBody = JSON.toJSONString(paramMap);
byte[] encryptBody = aesCipher.doFinal(originalBody.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//这一步Base64加密要有,否则会报错
byte[] base64Body = Base64.getEncoder().encode(encryptBody);
String encryptParam = new String(base64Body, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
//解密参数
//对应上一步加密中的Base64解密,必须有否则会报错
byte[] decodedBase64Body = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptParam.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byte[] realBody = deAesCipher.doFinal(decodedBase64Body);
String deStr = new String(realBody, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);否则,会报出如下错误:
javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException: Input length must be multiple of 16 when decrypting with padded cipher

2、keyAgreement.generateSecret(SECRET_ALGORITHM)这句代码可能会报错,报错内容如下:
java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: Unsupported secret key algorithm: AES

可在运行时,在JVM参数上,加上:-Djdk.crypto.KeyAgreement.legacyKDF=true ,即可解决!

当然,还有很多其他的解决方式。例如,我接来下用的一种,比如在获取SecretKey是做如下处理:
byte[] secretKey = keyAgreement.generateSecret();
BigInteger secretBig = new BigInteger(1, secretKey);
byte[] secretTmpByte = secretBig.toString(10).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
secretKey = Arrays.copyOfRange(secretTmpByte, 0, 32);
//如果此处获取通信秘钥如此处理,那B也需要以同样方式处理,才可保证通讯秘钥一致,即receiveSecretKey
senderSecretKey = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey, SECRET_ALGORITHM);另外,在网上还有这种方式:
直接代码中配置
System.getProperties().setProperty("jdk.crypto.KeyAgreement.legacyKDF", "true");至此,DH加密梳理演示,就算完成啦。最后,有一点建议,就是请求过程中的这些秘钥材料、SecretKey都可以使用一个缓存存储起来使用,定制一个失效时间。
如有不足,也欢迎各位朋友下方留言探讨~~~~~
以上是关于算法系列实战篇:Diffie-Hellman算法实现通信秘钥流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
#私藏项目实操分享#Java技术开发专题系列之Guava RateLimiter针对于限流器的入门到实战(含源码分析介绍)