Mac 安装 Python 看这里就够了,Python2Python3 再也不懵了
Posted DevOps前进四
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Mac 安装 Python 看这里就够了,Python2Python3 再也不懵了相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Mac 安装 Python2、Python3 。
零、基础准备
- 官网
- https://www.python.org/
- 下载入口
- https://www.python.org/downloads/
- https://www.python.org/downloads/macos/
一、安装包下载及安装
安装包下载的页面路径是:官网>>> Downloads>>> macOS
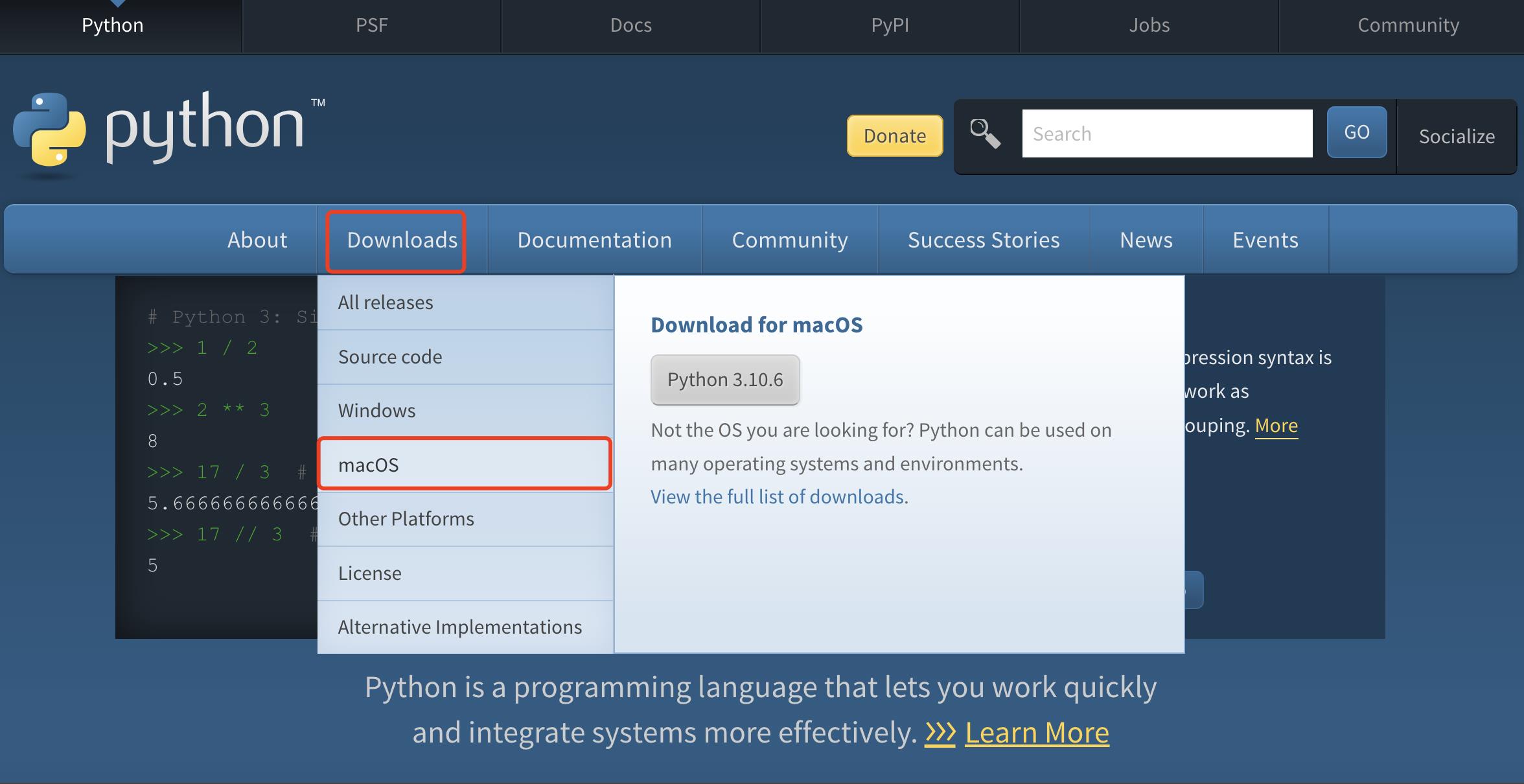
其他平台根据请自己的实际情况选择
安装包下载的页面路径也可以是:官网>>> Downloads(点击)

进入到版本选择页面

最上面是最新的 Release 版本,分别是2.x的最新版本和3.x的最新版。
可以下载最新的 Release 版本进行安装,也可以通过搜索选择自己想要的版本进行安装。
通过搜索找到「2.7.16」
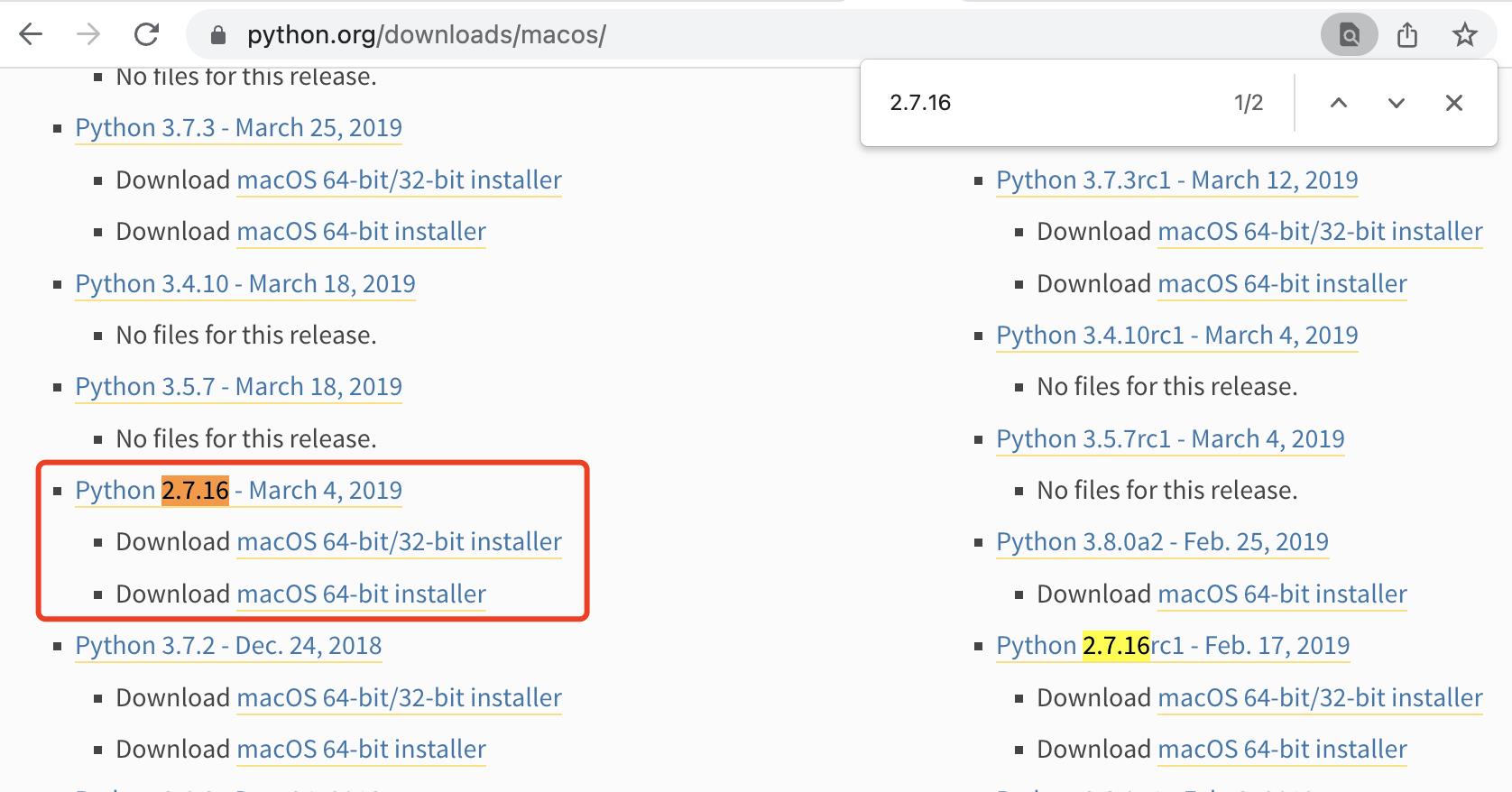
通过搜索找到「3.9.9」

强烈推荐下载最新的 Release 版进行安装
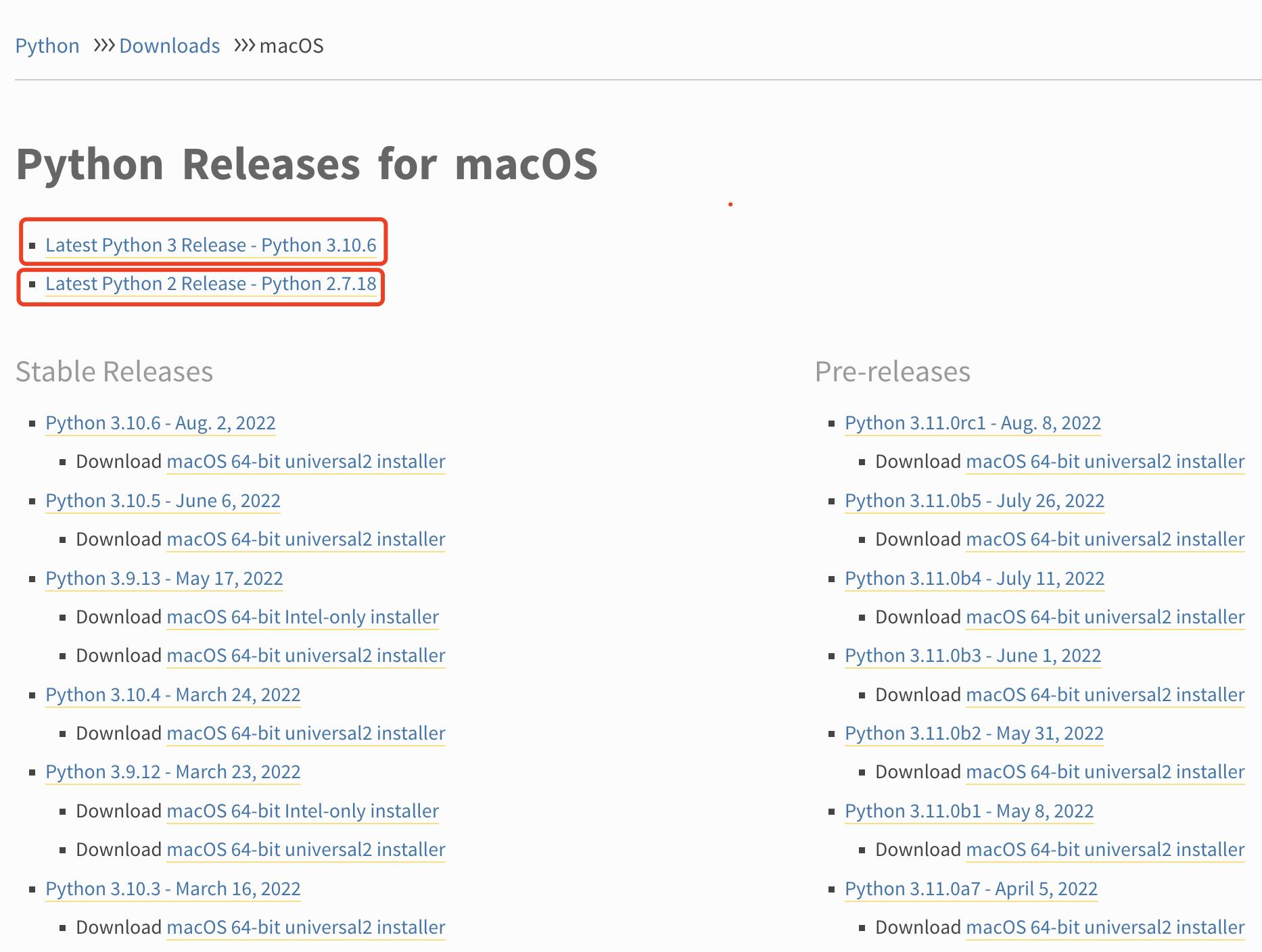
点击对应的链接分别下载即可(下载的过程中注意操作系统的架构和位数)。

👆下载「2.7.18」

👆下载「3.10.6」

👆下载好的安装包
使用下载好的安装包一直「下一步」即可安装对应版本的 python。
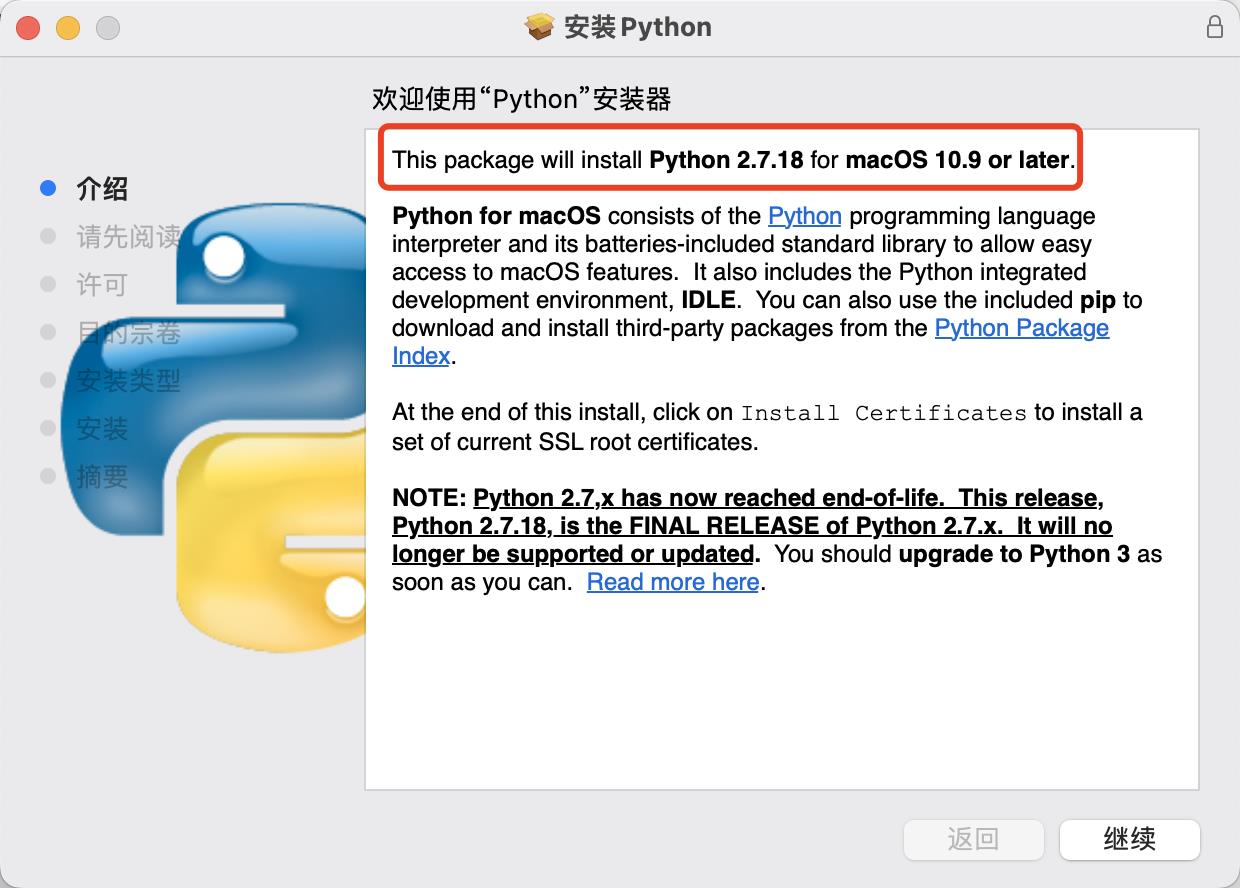

二、安装确认
1、Python2
- 查看版本号
$ python -V
Python 2.7.18
- 帮助命令
$ python -h
usage: /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/Resources/Python.app/Contents/MacOS/Python [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ...
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about comparing bytearray with unicode
(-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .py[co] files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : debug output from parser; also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : optimize generated bytecode slightly; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : remove doc-strings in addition to the -O optimizations
-R : use a pseudo-random salt to make hash() values of various types be
unpredictable between separate invocations of the interpreter, as
a defense against denial-of-service attacks
-Q arg : division options: -Qold (default), -Qwarn, -Qwarnall, -Qnew
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-t : issue warnings about inconsistent tab usage (-tt: issue errors)
-u : unbuffered binary stdout and stderr; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
see man page for details on internal buffering relating to '-u'
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-3 : warn about Python 3.x incompatibilities that 2to3 cannot trivially fix
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ':'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>:<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>/pythonX.X.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', the effect is the same
as specifying the -R option: a random value is used to seed the hashes of
str, bytes and datetime objects. It can also be set to an integer
in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a predictable seed.
2、Python3
- 查看版本号
$ python3 -V
Python 3.10.6
- 帮助命令
$ python3 -h
usage: /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3 [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ...
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about str(bytes_instance), str(bytearray_instance)
and comparing bytes/bytearray with str. (-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .pyc files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : turn on parser debugging output (for experts only, only works on
debug builds); also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also -? or --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-I : isolate Python from the user's environment (implies -E and -s)
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : remove assert and __debug__-dependent statements; add .opt-1 before
.pyc extension; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : do -O changes and also discard docstrings; add .opt-2 before
.pyc extension
-q : don't print version and copyright messages on interactive startup
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-u : force the stdout and stderr streams to be unbuffered;
this option has no effect on stdin; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
when given twice, print more information about the build
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-X opt : set implementation-specific option. The following options are available:
-X faulthandler: enable faulthandler
-X showrefcount: output the total reference count and number of used
memory blocks when the program finishes or after each statement in the
interactive interpreter. This only works on debug builds
-X tracemalloc: start tracing Python memory allocations using the
tracemalloc module. By default, only the most recent frame is stored in a
traceback of a trace. Use -X tracemalloc=NFRAME to start tracing with a
traceback limit of NFRAME frames
-X importtime: show how long each import takes. It shows module name,
cumulative time (including nested imports) and self time (excluding
nested imports). Note that its output may be broken in multi-threaded
application. Typical usage is python3 -X importtime -c 'import asyncio'
-X dev: enable CPython's "development mode", introducing additional runtime
checks which are too expensive to be enabled by default. Effect of the
developer mode:
* Add default warning filter, as -W default
* Install debug hooks on memory allocators: see the PyMem_SetupDebugHooks()
C function
* Enable the faulthandler module to dump the Python traceback on a crash
* Enable asyncio debug mode
* Set the dev_mode attribute of sys.flags to True
* io.IOBase destructor logs close() exceptions
-X utf8: enable UTF-8 mode for operating system interfaces, overriding the default
locale-aware mode. -X utf8=0 explicitly disables UTF-8 mode (even when it would
otherwise activate automatically)
-X pycache_prefix=PATH: enable writing .pyc files to a parallel tree rooted at the
given directory instead of to the code tree
-X warn_default_encoding: enable opt-in EncodingWarning for 'encoding=None'
--check-hash-based-pycs always|default|never:
control how Python invalidates hash-based .pyc files
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ':'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>:<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>/lib/pythonX.X.
PYTHONPLATLIBDIR : override sys.platlibdir.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONUTF8: if set to 1, enable the UTF-8 mode.
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONFAULTHANDLER: dump the Python traceback on fatal errors.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', a random value is used
to seed the hashes of str and bytes objects. It can also be set to an
integer in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a
predictable seed.
PYTHONMALLOC: set the Python memory allocators and/or install debug hooks
on Python memory allocators. Use PYTHONMALLOC=debug to install debug
hooks.
PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the locale
coercion behavior. Use PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE=warn to request display of
locale coercion and locale compatibility warnings on stderr.
PYTHONBREAKPOINT: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the default
debugger. It can be set to the callable of your debugger of choice.
PYTHONDEVMODE: enable the development mode.
PYTHONPYCACHEPREFIX: root directory for bytecode cache (pyc) files.
PYTHONWARNDEFAULTENCODING: enable opt-in EncodingWarning for 'encoding=None'.
三、其他
除了使用python、python3命令来调用对应版本的 python 外,还可以使用如下的命令来调用对应版本的 python。
$ python2 -V
Python 2.7.18
$ python2.7 -V
Python 2.7.18
$ python3.10 -V
Python 3.10.6
这些都可以可以在 /usr/local/bin 这个目录下看到相关命令对应的「软连接」。
$ pwd
/usr/local/bin
$ ls -l | grep python
python -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python
python-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python-config
python2 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2
python2-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2-config
python2.7 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2.7
python2.7-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/python2.7-config
python3 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3
python3-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3-config
python3-intel64 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3-intel64
python3.10 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10
python3.10-config -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10-config
python3.10-intel64 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/bin/python3.10-intel64
pythonw -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw
pythonw2 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw2
pythonw2.7 -> ../../../Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin/pythonw2.7
PS:python2和python3的兼容性一直被广大开发者诟病。
Python 安装环境搭建看这一篇就够了(Windows+Mac+Linux)
Windows
1. 下载Python安装包
访问Python官网(www.python.org),点击页面上的“Downloads”,选择你的操作系统:
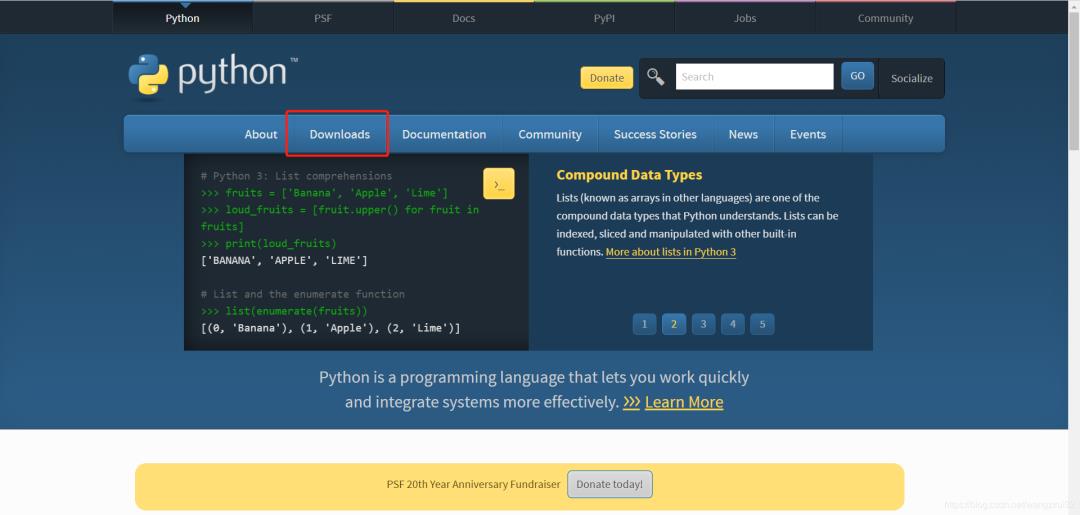
笔者的电脑是Windows 10系统,所以进入了Windows的下载页面,我们要下载Python的最新版,因此点击下载区域的“Latest Python 3 Release - Python 3.9.5“,如图:
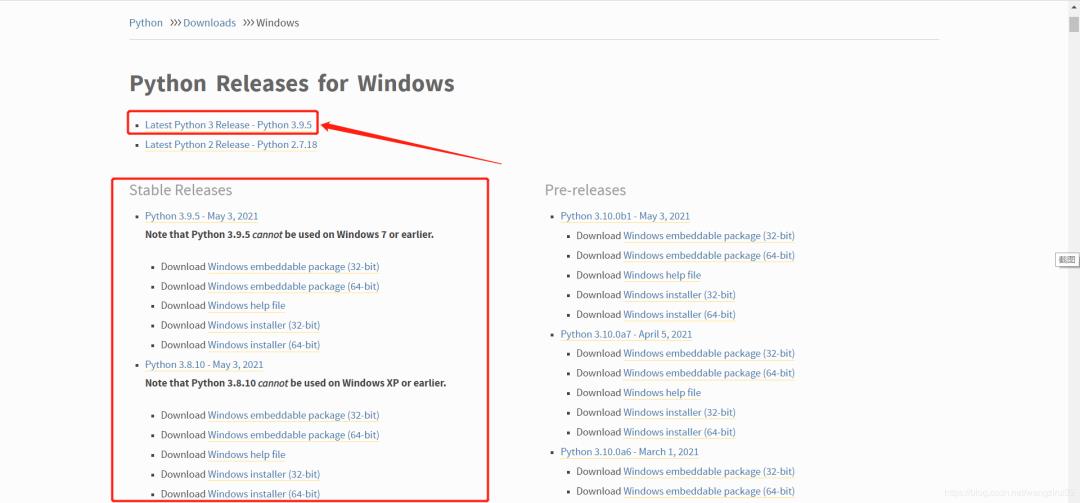
当然,如果要下载指定版本,你也可以在“Stable Releases”中找到需求版本。
进入了Python3.9.5的安装包下载页面,翻滚到最底部,找到下载表格:
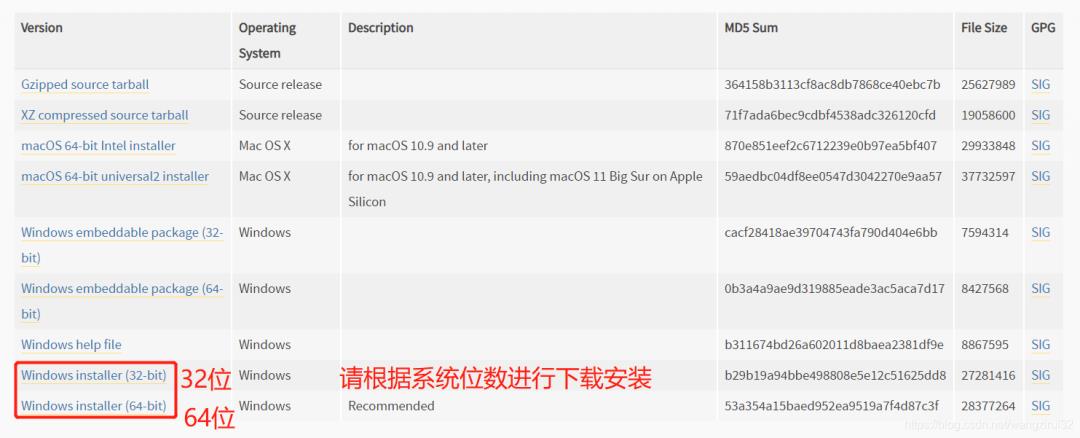
根据系统位数选择安装包并下载。
2. 运行Python安装包
打开下载的安装包exe,如图:
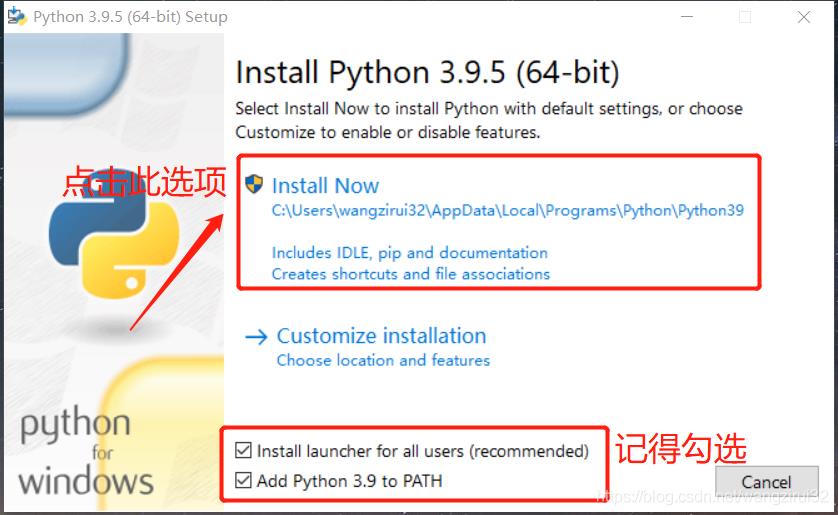
等待进度条,安装完毕后,退出页面:
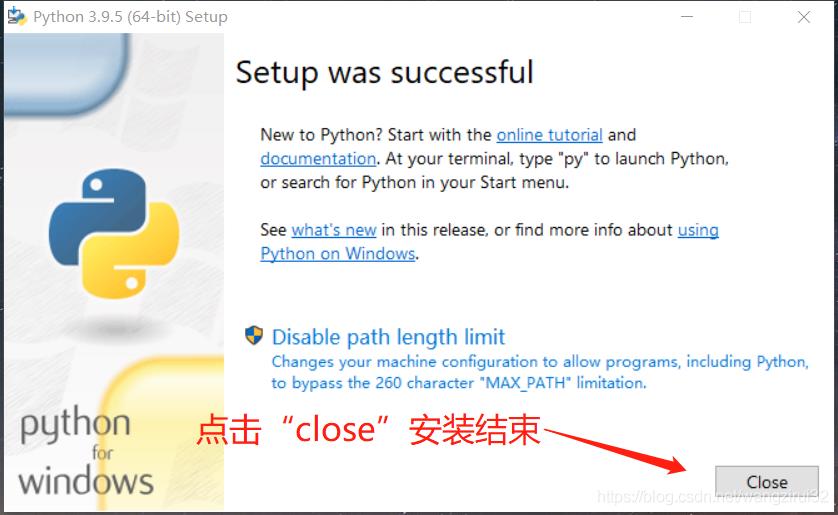
3. IDLE编辑器使用
IDLE是Python自带的集成开发环境,首先在开始菜单中搜索“IDLE”,打开搜索到的程序:
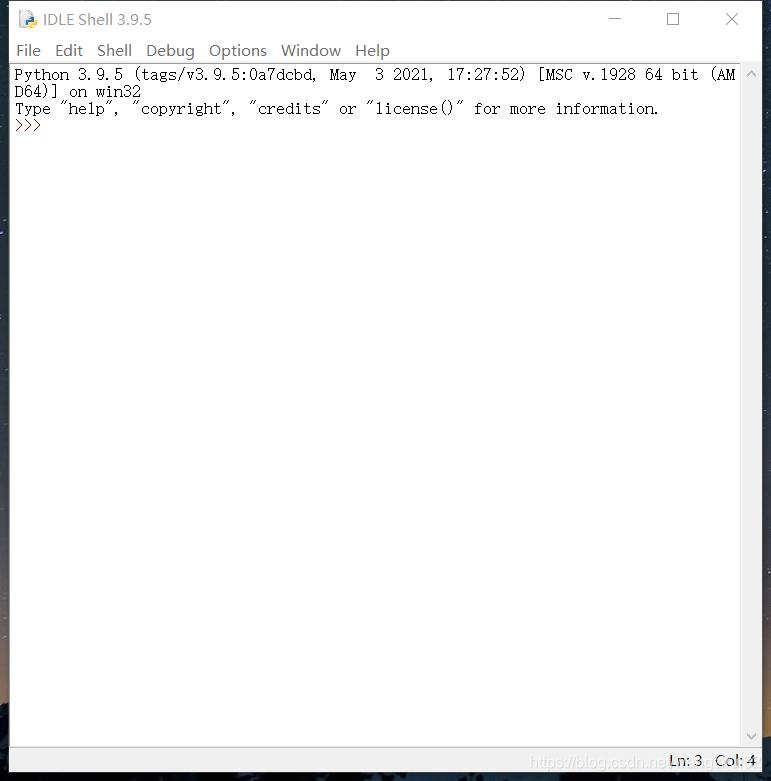
键入指令:
>>> print("Hello, world !")
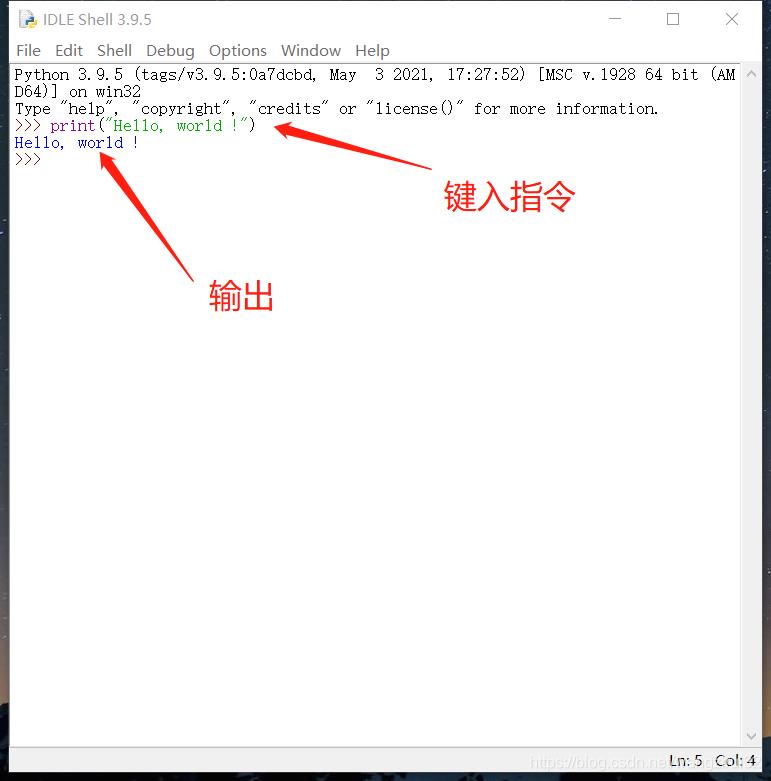
接下来学习如何新建,保存和运行一个Python程序。
点击菜单栏中的“File” --> “New File”,新建文件并写入代码:
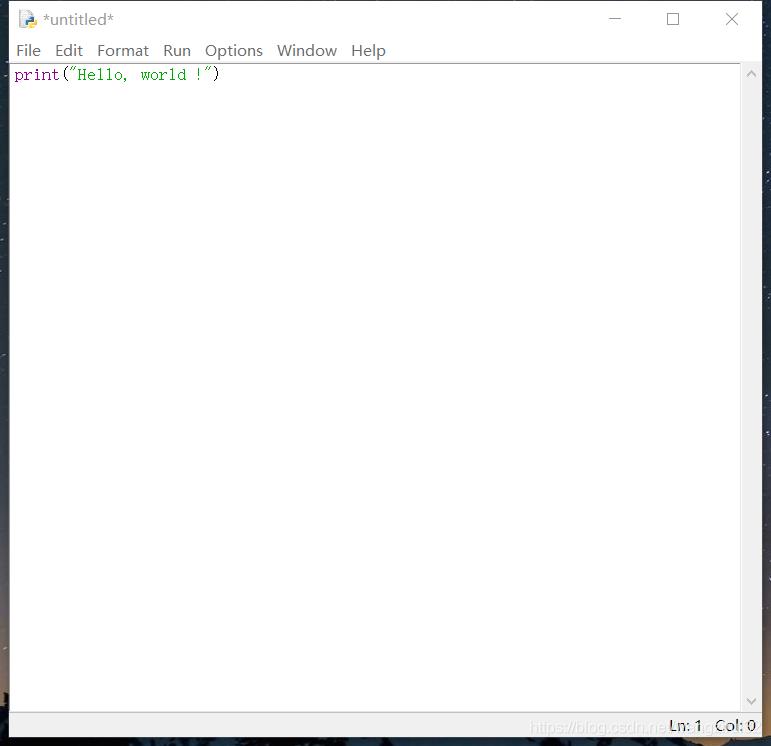
再次点击“FIie” --> “Save”,保存Python文件。
然后,点击“Run” --> “Run Module”, 运行程序:
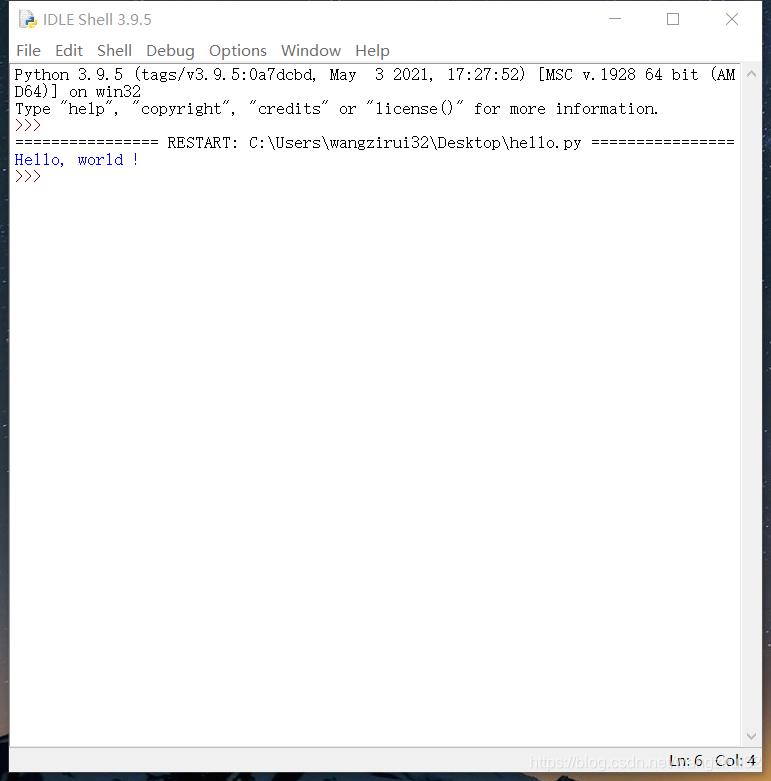
作者:wangzirui32 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wangzirui32/article/details/117156716
Mac
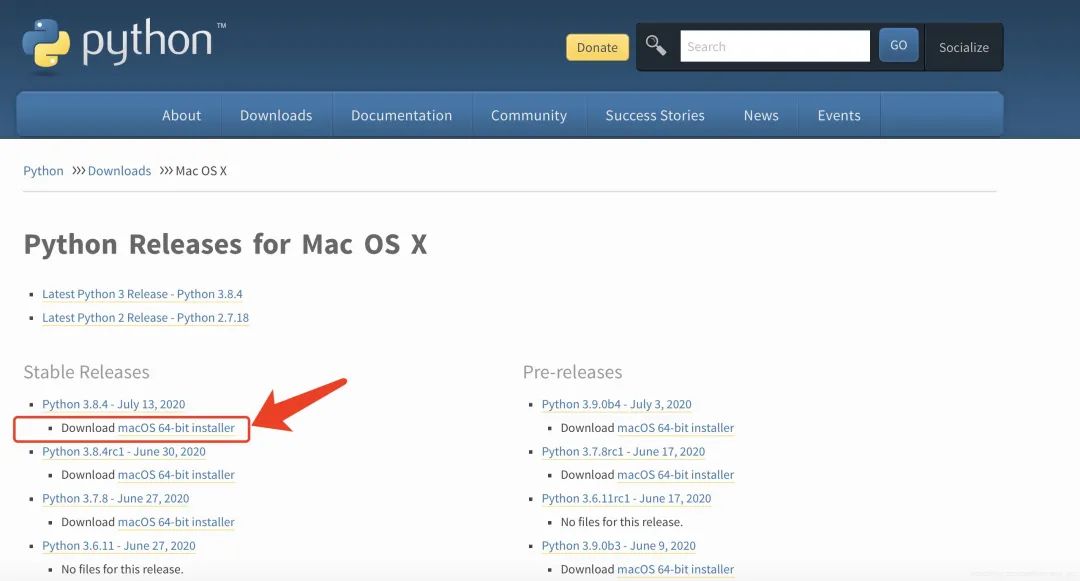
1. 下载安装文件
访问Python官网(www.python.org),选取稳定版本,如:macOS 64-bit installer点击下载。
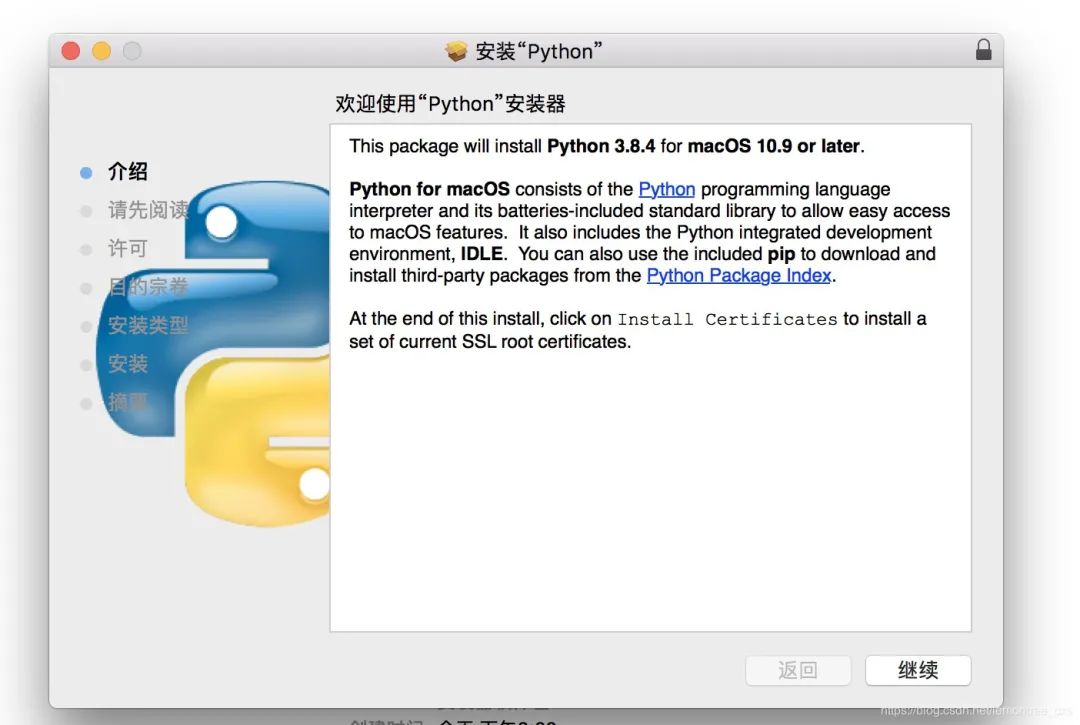
2. 安装文件
打开下载的安装文件,按照提示信息点击“继续”安装,直至安装完成。

3. 配置mac默认版本是python3
打开终端,输入命令which python3,查看python3的安装目录
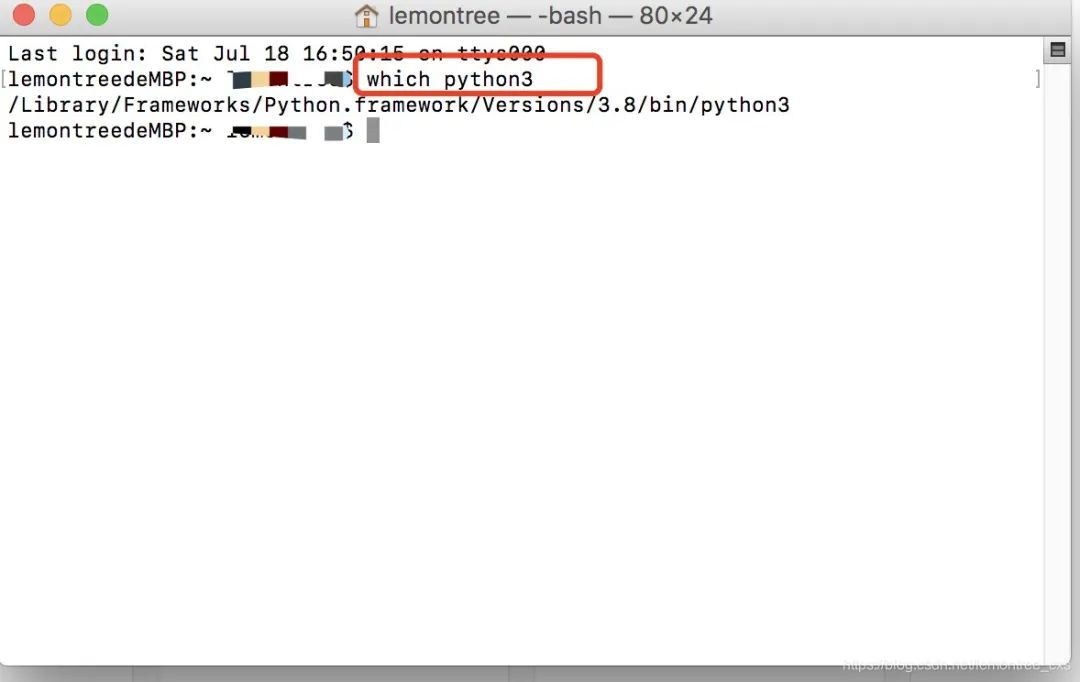
将路径配入环境变量。
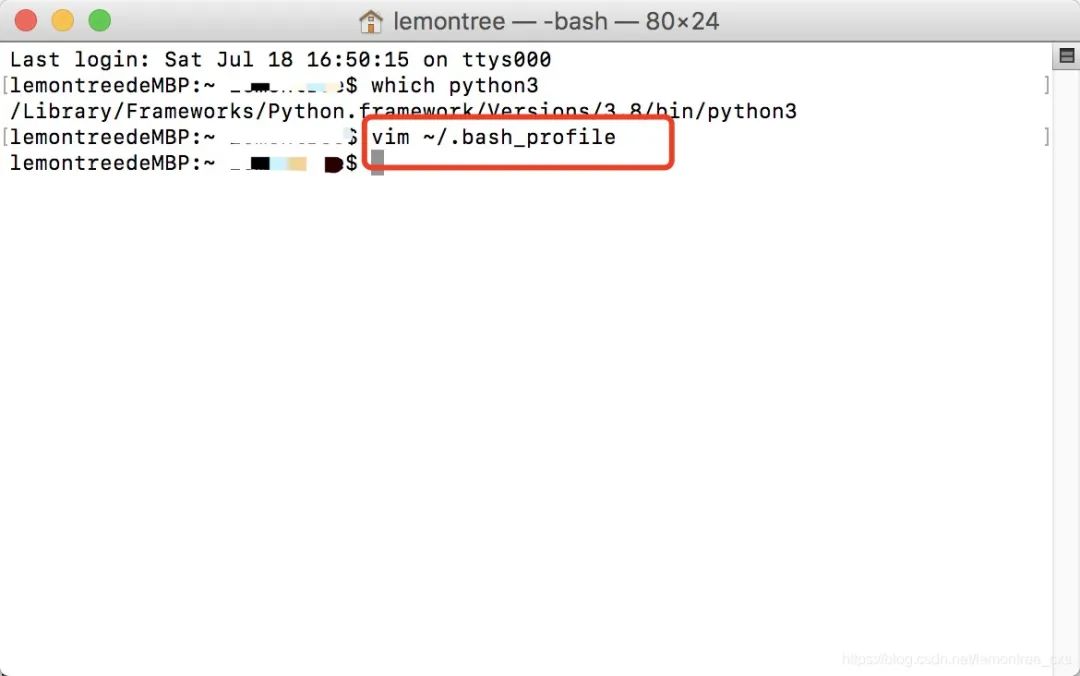
在文件最后加上alias python="/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.8/bin/python3",保存并退出
在终端输入source ~/.bash_profile使其生效,查看当前python版本:
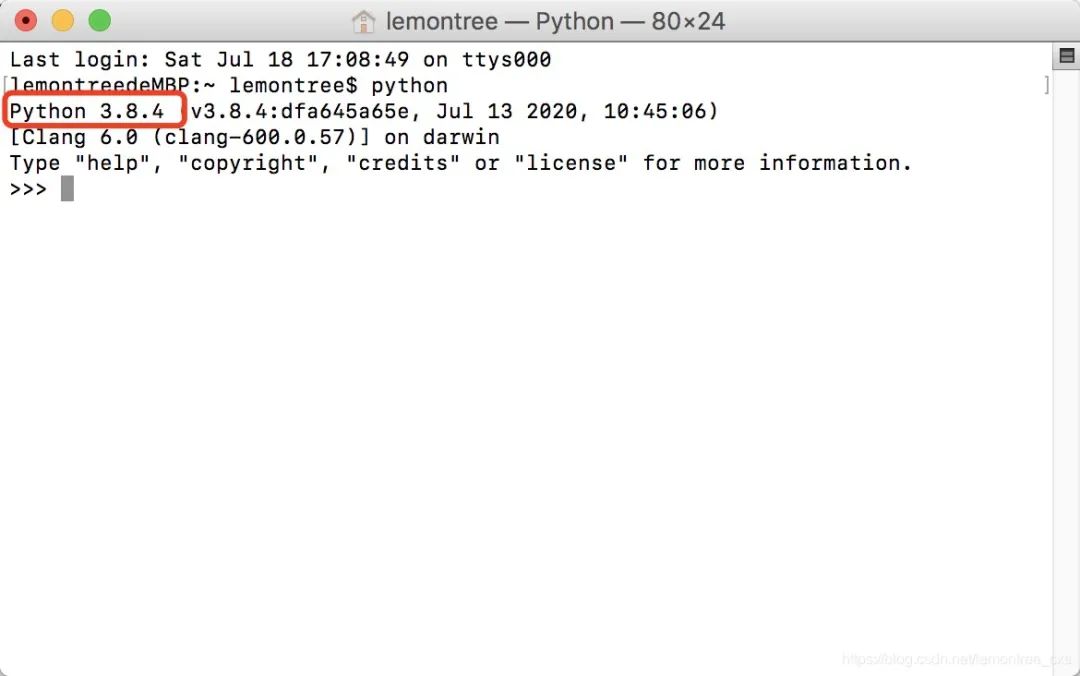
作者:lemon柚子 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lemontree_cxs/article/details/107431120
Linux
Linux,centos系统本身默认安装有python2.x,版本x根据不同版本系统有所不同,可通过 python --V 或 python --version 查看系统自带的python版本
有一些系统命令时需要用到python2,不能卸载
1. 安装依赖包
1)首先安装gcc编译器,gcc有些系统版本已经默认安装,通过 gcc --version 查看,没安装的先安装gcc,yum -y install gcc
2)安装其它依赖包,(注:不要缺少,否则有可能安装python出错,python3.7.0以下的版本可不装 libffi-devel )
yum-yinstallzlib-develbzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel libffi-devel
2. 下载python3.7.3源码,根据需求下载
1)去python官网下载源码包
https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.7.2/Python-3.7.2.tgz
2)下载
3)解压Python-3.7.2.tgz
tar -zvxf Python-3.7.2.tgz
3. 建立一个空文件夹,用于存放python3程序
mkdir/usr/local/python3 //做完了需要每次新建单个文件夹 mkdir usr 建完之后 cd usr 到usr文件夹继续建剩下,步骤一致
4. 执行配置文件,编译,编译安装
cd Python-3.7.2 先进去桌面已经解压文件
在执行下面这段 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python3 &&make &&make install
安装完成没有提示错误便安装成功了
5. 建立软连接
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/python3.7/usr/bin/python3
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/pip3.7/usr/bin/pip3
6. 测试一下python3是否可以用
如果Python3 查看不到Python3.7.2版本,需要添加系统变量
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:/usr/local/python3/bin 这个只是当前窗口临时查看
复制代码
7. 添加永久系统变量
通过修改profile文件:
执行 vim /etc/profile
/export PATH //找到设置PATH的行,添加
export PATH=/usr/local/python37/bin:$PATH
:wq //保存文件并退出vi
生效方法:
系统重启
要想马上生效还要运行
# source /etc/profile
不然只能在下次重进此用户时生效。
有效期限:永久有效 用户局限:对所有用户
到这里,就可以执行查看到Python 3.7.2版本!
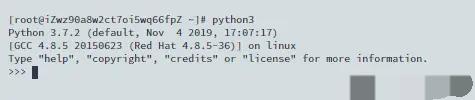
作者:灰太狼的精神 原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903987146145800
< END >

微信扫码关注,了解更多内容
以上是关于Mac 安装 Python 看这里就够了,Python2Python3 再也不懵了的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Python 安装环境搭建看这一篇就够了(Windows+Mac+Linux)