leetcode链表
Posted 芋泥*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了leetcode链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
1. 倒数第k个节点
OJ:倒数第k个节点
描述
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
示例1
输入:1,1,2,3,4,5
返回值:5
解题思路
- 思路1
倒数第k个 = 链表长度 - k;
先求出链表的长度,如果k>链表长度,则不存在这个节点,返回null;否则循环到第k个返回。
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k)
int length = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null)
length ++;
node = node.next;
if(k >length)
return null;
// k = k % length;
int index = length - k;
node = head;
for(int i = 0;i < index;i++)
node = node.next;
return node;
- 思路2
双指针法
(1)fir先走k步,若fir走到空,则说明k>链表长度,直接返回null;
(2)fir与ser一起走,当fir走到null时,ser正好到倒数第k个节点。
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k)
if(head == null || k <= 0)
return null;
ListNode fir = head,ser = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
if(fir == null)
return null;
fir = fir.next;
while (fir != null)
fir = fir.next;
ser = ser.next;
return ser;
2. 合并两个有序链表
OJ:合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
解题思路
- 思路1
拼接法
(1)创建一个新的链表,头节点newHead(不存储数据),tail指向新链表的最后一个
(2)判断list1与list2哪个的头节点数据小,将小的那个拼接到新节点的后面,tail后移,list1或list2后移。直到list1与list2其中一个为空。
(3)将剩下没拼接完的拼接到tail后面。
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = newHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null)
if(list1.val <= list2.val)
tail.next = list1;
tail = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
else
tail.next = list2;
tail = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
if(list1 != null)
tail.next = list1;
if(list2 != null)
tail.next = list2;
return newHead.next;
- 思路2
递归法
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
if(list1 == null)
return list2;
if(list2 == null)
return list1;
if(list1.val <= list2.val)
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
else
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
3. 链表分割
OJ:链表分割
现有一链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
解题思路
(1)创建两个新的链表,一个链表的头节点为smallHead,存储小于x的节点,smallTail指向smallHead这个链表的最后一个;另一个链bigHead,存储大于等于x的节点,bigTail指向bigHead这个链表的最后一个。
(2)如果当前节点的值小于x,拼接到smallTail后面,smallTail后移;比x大,拼接到bigTail后面,bigTail后移;一直遍历到pHead链表的最后。
(3)将bigTail的next置空,将两个链表拼接,即将bigHead.next拼接到smallTail后面,返回smallHead.next。
import java.util.*;
public class Partition
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x)
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
// write code here
ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(-101);
ListNode smallTail = smallHead;
ListNode bigHead = new ListNode(-101);
ListNode bigTail = bigHead;
while (pHead != null)
if (pHead.val < x)
smallTail.next = pHead;
smallTail = pHead;
else
bigTail.next = pHead;
bigTail = pHead;
pHead = pHead.next;
bigTail.next = null;
smallTail.next = bigHead.next;
return smallHead.next;
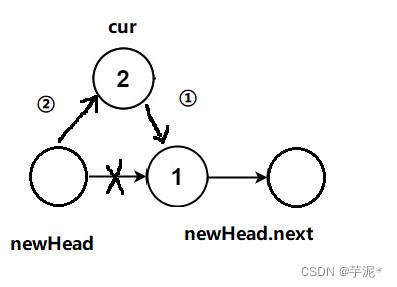
4. 反转链表
OJ:反转链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例1:
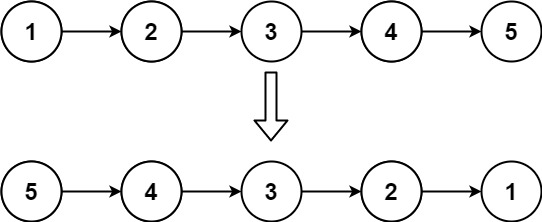
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
解决思路
创建一个新链表,存放反转后的节点
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head)
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode newhead = new ListNode();
while(head != null)
ListNode cur = new ListNode(head.val);
cur.next = newhead.next;
newhead.next = cur;
head = head.next;
return newhead.next;
5. 链表的回文结构
OJ:链表的回文结构
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。
给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
【测试样例】
1->2->2->1
返回:true
解题思路
- 思路1:
借助赋值空间,因为题目说了链表节点个数不超过900,因此辅助空间大小是固定的,故空间复杂也是O(1)
(1)遍历链表,将链表中节点的值域放到数组中
(2)检测数组是否为回文结构
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A)
int[] array = new int[900];
ListNode cur = A;
int size = 0;
while(cur != null)
array[size++] = cur.val;
cur = cur.next;
// 判断是否为回文结构
int left = 0;
int right = size-1;
while(left < right)
if(array[left] != array[right])
return false;
left++;
right--;
return true;
- 思路2
(1)找到链表的中间节点,然后从中间节点位置断开链表,形成两个链表A和B
(2) 对后半部分B进行逆置
(3)从前往后遍历A和B,检测A和B中节点的值域是否都相同,相同就是回文结构,否则就不是
(4) 再对后半部分进行逆置,将A和B拼接会之前的原链表
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A)
// write code here
// ListNode node2 = middleNode(A);
ListNode node = reverseList(A);
while(A != null && node != null)
if(node.val != A.val)
return false;
node = node.next;
A = A.next;
return true;
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head)
ListNode low = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null)
low = low.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
return low;
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head)
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(head.val);
while (head.next != null)
ListNode cur = new ListNode(head.next.val);
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
head = head.next;
return newHead;
6. 相交链表
OJ:相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点
headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回null。图示两个链表在节点
c1开始相交:
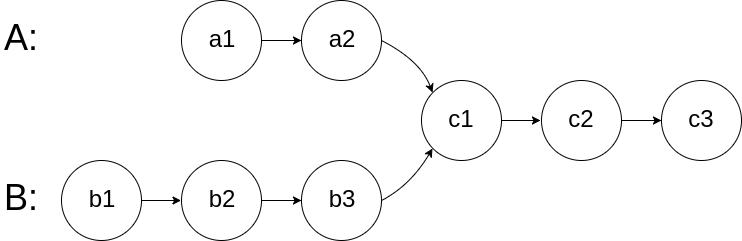
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
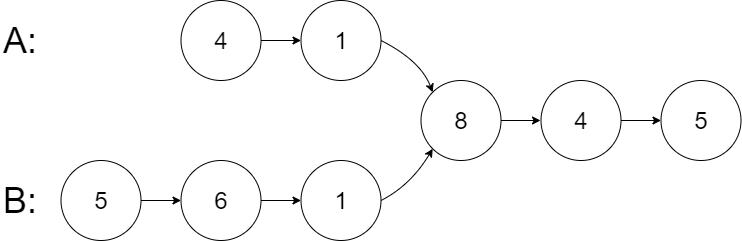
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8' 解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。 — 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
解题思路
- 思路1
路程相同的原理,引入两个引用listA和listB,若这两个链表有交点 listA走到终点后倒过头从B链表开始走 listB走到终点后倒过头来从A链表开始走。
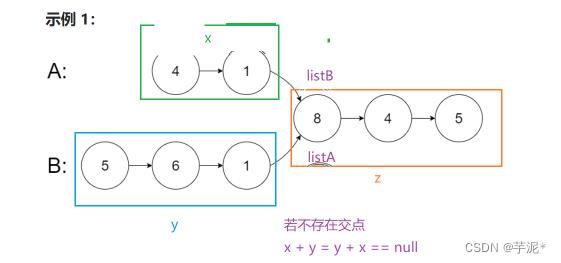
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
ListNode listA = headA;
ListNode listB = headB;
while(listA != listB)
listA = listA == null ? headB : listA.next;
listB = listB == null ? headA : listB.next;
return listA;
- 思路2
(1)如果两个链表有一个为空,则一定不会相交
(2)如果两个链表都不为空
a. 找到两个链表的最后一个节点,找的过程中记录链表的长度
b. 如果最后一个节点相同则相交,否则不相交
(3)如果相交,找交点
a. 让长的链表先往后走两个链表差值步
b. 两个同时往后走,相遇时机为交点
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
// 如果两个链表有一个为空,则一定不会相交
if(null == headA || null == headB)
return null;
// 找到两个链表的最后一个节点,找的过程中统计链表的长度
ListNode curA = headA;
int sizeA = 1; // 从1开始是因为cur在最后一个节点时循环进不去
while(null != curA.next)
curA = curA.next;
++sizeA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int sizeB = 1;
while(null != curB.next)
curB = curB.next;
sizeB++;
// 如果两个链表最后一个节点不同,则一定不相交,否则相交
if(curA != curB)
return null;
// 让长的链表从头先走两个链表差值步,然后两个引用同时往后走
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
int gap = sizeA - sizeB;
if(gap > 0)
// curA长
while(0 != gap)
curA = curA.next;
--gap;
else
// curB长
while(0 != gap)
curB = curB.next;
++gap;
// curA和curB同时往后移动,相遇的时候即为交点
while(curA != curB)
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
return curA;
趁热打铁:
[JavaScript 刷题] 链表 - 相交链表, leetcode 160
[JavaScript 刷题] 链表 - 相交链表, leetcode 160
github repo 地址: https://github.com/GoldenaArcher/js_leetcode,Github 的目录 大概 会更新的更勤快一些。
题目地址:160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
题目
如下:
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists
headAandheadB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, returnnull.For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node
c1:
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal- The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is 0 if there is no intersected node.listA- The first linked list.listB- The second linked list.skipA- The number of nodes to skip ahead in listA (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.skipB- The number of nodes to skip ahead in listB (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
解题思路
这道题有两种解决方法,第一个是使用 Hashmap,将所有出现在 listA 或者是 listB 的 LinkedList Node 存到 Map 中,再遍历另一个 LinkedList 即可,这种做法的时间复杂度为
O
(
m
+
n
)
O(m + n)
O(m+n),空间复杂度为
O
(
m
,
n
)
O(m, n)
O(m,n)。
另外一种做法则是不需要使用额外的空间去存储出现过的结点,依旧以上图为例,这时候的 list1 如下:
list2 如下:
只要将 list1 和 list2 拼接起来如下:
list2 拼接 list1 如下:
二者如果有公用的结点,在便利的时候一定会出现当下 list1 的结点与 list2 的结点一样的情况。
如果二者没有公用结点,那么在条件 list1.node === list2.node 不触发的情况下,循环结束之后 list1 和 list2 都会指向 null。
使用 JavaScript 解题
哈希表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val)
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
*
*/
/**
* @param ListNode headA
* @param ListNode headB
* @return ListNode
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB)
const set = new Set();
while (headA !== null && headA.val !== null)
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
while (headB !== null && headB.val !== null)
if (set.has(headB)) return headB;
headB = headB.next;
return null;
;
双指针
当 l1 和 l2 遍历完了 headA + headB 之后,二者会双双指向 null,触发 null === null 的条件。
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB)
let l1 = headA,
l2 = headB;
while (l1