Spark Streaming源码解读之数据清理内幕彻底解密
Posted snail_gesture
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spark Streaming源码解读之数据清理内幕彻底解密相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本篇博客的主要目的是:
1. 理清楚Spark Streaming中数据清理的流程
组织思路如下:
a) 背景
b) 如何研究Spark Streaming数据清理?
c) 源码解析
一:背景
Spark Streaming数据清理的工作无论是在实际开发中,还是自己动手实践中都是会面临的,Spark Streaming中Batch Durations中会不断的产生RDD,这样会不断的有内存对象生成,其中包含元数据和数据本身。由此Spark Streaming本身会有一套产生元数据以及数据的清理机制。
二:如何研究Spark Streaming数据清理?
- 操作DStream的时候会产生元数据,所以要解决RDD的数据清理工作就一定要从DStream入手。因为DStream是RDD的模板,DStream之间有依赖关系。
DStream的操作产生了RDD,接收数据也靠DStream,数据的输入,数据的计算,输出整个生命周期都是由DStream构建的。由此,DStream负责RDD的整个生命周期。因此研究的入口的是DStream。 - 基于Kafka数据来源,通过Direct的方式访问Kafka,DStream随着时间的进行,会不断的在自己的内存数据结构中维护一个HashMap,HashMap维护的就是时间窗口,以及时间窗口下的RDD.按照Batch Duration来存储RDD以及删除RDD.
- Spark Streaming本身是一直在运行的,在自己计算的时候会不断的产生RDD,例如每秒Batch Duration都会产生RDD,除此之外可能还有累加器,广播变量。由于不断的产生这些对象,因此Spark Streaming有自己的一套对象,元数据以及数据的清理机制。
- Spark Streaming对RDD的管理就相当于JVM的GC.
三:源码解析
generatedRDDs:安照Batch Duration的方式来存储RDD以及删除RDD。
// RDDs generated, marked as private[streaming] so that testsuites can access it
@transient
private[streaming] var generatedRDDs = new HashMap[Time, RDD[T]] ()
我们在实际开发中,可能手动缓存,即使不缓存的话,它在内存generatorRDD中也有对象,如何释放他们?不仅仅是RDD本身,也包括数据源(数据来源)和元数据(metada),因此释放RDD的时候这三方面都需要考虑。
释放跟时钟Click有关系,因为数据是周期性产生,所以肯定是周期性释放。
因此下一步就需要找JobGenerator
- RecurringTimer: 消息循环器将消息不断的发送给EventLoop
private val timer = new RecurringTimer(clock, ssc.graph.batchDuration.milliseconds,
longTime => eventLoop.post(GenerateJobs(new Time(longTime))), "JobGenerator")
2. eventLoop:onReceive接收到消息。
/** Start generation of jobs */
def start(): Unit = synchronized
if (eventLoop != null) return // generator has already been started
// Call checkpointWriter here to initialize it before eventLoop uses it to avoid a deadlock.
// See SPARK-10125
checkpointWriter
eventLoop = new EventLoop[JobGeneratorEvent]("JobGenerator")
override protected def onReceive(event: JobGeneratorEvent): Unit = processEvent(event)
override protected def onError(e: Throwable): Unit =
jobScheduler.reportError("Error in job generator", e)
3. processEvent:中就会接收到ClearMetadata和ClearCheckpointData。
/** Processes all events */
private def processEvent(event: JobGeneratorEvent)
logDebug("Got event " + event)
event match
case GenerateJobs(time) => generateJobs(time)
case ClearMetadata(time) => clearMetadata(time)
case DoCheckpoint(time, clearCheckpointDataLater) =>
doCheckpoint(time, clearCheckpointDataLater)
case ClearCheckpointData(time) => clearCheckpointData(time)
4. clearMetadata:清楚元数据信息。
/** Clear DStream metadata for the given `time`. */
private def clearMetadata(time: Time)
ssc.graph.clearMetadata(time)
// If checkpointing is enabled, then checkpoint,
// else mark batch to be fully processed
if (shouldCheckpoint)
eventLoop.post(DoCheckpoint(time, clearCheckpointDataLater = true))
else
// If checkpointing is not enabled, then delete metadata information about
// received blocks (block data not saved in any case). Otherwise, wait for
// checkpointing of this batch to complete.
val maxRememberDuration = graph.getMaxInputStreamRememberDuration()
jobScheduler.receiverTracker.cleanupOldBlocksAndBatches(time - maxRememberDuration)
jobScheduler.inputInfoTracker.cleanup(time - maxRememberDuration)
markBatchFullyProcessed(time)
5. DStreamGraph:首先会清理outputDStream,其实就是forEachDStream
def clearMetadata(time: Time)
logDebug("Clearing metadata for time " + time)
this.synchronized
outputStreams.foreach(_.clearMetadata(time))
logDebug("Cleared old metadata for time " + time)
6. DStream.clearMetadata:除了清除RDD,也可以清除metadata元数据。如果想RDD跨Batch Duration的话可以设置rememberDuration时间. rememberDuration一般都是Batch Duration的倍数。
/**
* Clear metadata that are older than `rememberDuration` of this DStream.
* This is an internal method that should not be called directly. This default
* implementation clears the old generated RDDs. Subclasses of DStream may override
* this to clear their own metadata along with the generated RDDs.
*/
private[streaming] def clearMetadata(time: Time)
val unpersistData = ssc.conf.getBoolean("spark.streaming.unpersist", true)
// rememberDuration记忆周期 查看下RDD是否是oldRDD
val oldRDDs = generatedRDDs.filter(_._1 <= (time - rememberDuration))
logDebug("Clearing references to old RDDs: [" +
oldRDDs.map(x => s"$x._1 -> $x._2.id").mkString(", ") + "]")
//从generatedRDDs中将key清理掉。
generatedRDDs --= oldRDDs.keys
if (unpersistData)
logDebug("Unpersisting old RDDs: " + oldRDDs.values.map(_.id).mkString(", "))
oldRDDs.values.foreach rdd =>
rdd.unpersist(false)
// Explicitly remove blocks of BlockRDD
rdd match
case b: BlockRDD[_] =>
logInfo("Removing blocks of RDD " + b + " of time " + time)
b.removeBlocks() //清理掉RDD的数据
case _ =>
logDebug("Cleared " + oldRDDs.size + " RDDs that were older than " +
(time - rememberDuration) + ": " + oldRDDs.keys.mkString(", "))
//依赖的DStream也需要清理掉。
dependencies.foreach(_.clearMetadata(time))
7. 在BlockRDD中,BlockManagerMaster根据blockId将Block删除。删除Block的操作是不可逆的。
/**
* Remove the data blocks that this BlockRDD is made from. NOTE: This is an
* irreversible operation, as the data in the blocks cannot be recovered back
* once removed. Use it with caution.
*/
private[spark] def removeBlocks()
blockIds.foreach blockId =>
sparkContext.env.blockManager.master.removeBlock(blockId)
_isValid = false
回到上面JobGenerator中的processEvent
1. clearCheckpoint:清除缓存数据。
/** Clear DStream checkpoint data for the given `time`. */
private def clearCheckpointData(time: Time)
ssc.graph.clearCheckpointData(time)
// All the checkpoint information about which batches have been processed, etc have
// been saved to checkpoints, so its safe to delete block metadata and data WAL files
val maxRememberDuration = graph.getMaxInputStreamRememberDuration()
jobScheduler.receiverTracker.cleanupOldBlocksAndBatches(time - maxRememberDuration)
jobScheduler.inputInfoTracker.cleanup(time - maxRememberDuration)
markBatchFullyProcessed(time)
2. clearCheckpointData:
def clearCheckpointData(time: Time)
logInfo("Clearing checkpoint data for time " + time)
this.synchronized
outputStreams.foreach(_.clearCheckpointData(time))
logInfo("Cleared checkpoint data for time " + time)
3. ClearCheckpointData: 和清除元数据信息一样,还是清除DStream依赖的缓存数据。
private[streaming] def clearCheckpointData(time: Time)
logDebug("Clearing checkpoint data")
checkpointData.cleanup(time)
dependencies.foreach(_.clearCheckpointData(time))
logDebug("Cleared checkpoint data")
4. DStreamCheckpointData:清除缓存的数据
/**
* Cleanup old checkpoint data. This gets called after a checkpoint of `time` has been
* written to the checkpoint directory.
*/
def cleanup(time: Time)
// Get the time of the oldest checkpointed RDD that was written as part of the
// checkpoint of `time`
timeToOldestCheckpointFileTime.remove(time) match
case Some(lastCheckpointFileTime) =>
// Find all the checkpointed RDDs (i.e. files) that are older than `lastCheckpointFileTime`
// This is because checkpointed RDDs older than this are not going to be needed
// even after master fails, as the checkpoint data of `time` does not refer to those files
val filesToDelete = timeToCheckpointFile.filter(_._1 < lastCheckpointFileTime)
logDebug("Files to delete:\\n" + filesToDelete.mkString(","))
filesToDelete.foreach
case (time, file) =>
try
val path = new Path(file)
if (fileSystem == null)
fileSystem = path.getFileSystem(dstream.ssc.sparkContext.hadoopConfiguration)
fileSystem.delete(path, true)
timeToCheckpointFile -= time
logInfo("Deleted checkpoint file '" + file + "' for time " + time)
catch
case e: Exception =>
logWarning("Error deleting old checkpoint file '" + file + "' for time " + time, e)
fileSystem = null
case None =>
logDebug("Nothing to delete")
至此我们也知道了清理的过程,全流程如下:
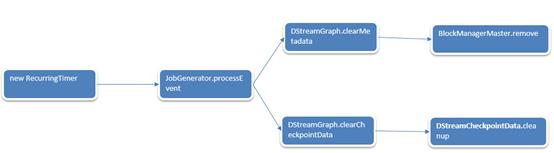
但是清理是什么时候被触发的?
1. 在最终提交Job的时候,是交给JobHandler去执行的。
private class JobHandler(job: Job) extends Runnable with Logging
import JobScheduler._
def run()
try
val formattedTime = UIUtils.formatBatchTime(
job.time.milliseconds, ssc.graph.batchDuration.milliseconds, showYYYYMMSS = false)
val batchUrl = s"/streaming/batch/?id=$job.time.milliseconds"
val batchLinkText = s"[output operation $job.outputOpId, batch time $formattedTime]"
ssc.sc.setJobDescription(
s"""Streaming job from <a href="$batchUrl">$batchLinkText</a>""")
ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(BATCH_TIME_PROPERTY_KEY, job.time.milliseconds.toString)
ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(OUTPUT_OP_ID_PROPERTY_KEY, job.outputOpId.toString)
// We need to assign `eventLoop` to a temp variable. Otherwise, because
// `JobScheduler.stop(false)` may set `eventLoop` to null when this method is running, then
// it's possible that when `post` is called, `eventLoop` happens to null.
var _eventLoop = eventLoop
if (_eventLoop != null)
_eventLoop.post(JobStarted(job, clock.getTimeMillis()))
// Disable checks for existing output directories in jobs launched by the streaming
// scheduler, since we may need to write output to an existing directory during checkpoint
// recovery; see SPARK-4835 for more details.
PairRDDFunctions.disableOutputSpecValidation.withValue(true)
job.run()
_eventLoop = eventLoop
if (_eventLoop != null)
//当Job完成的时候,eventLoop会发消息初始化onReceive
_eventLoop.post(JobCompleted(job, clock.getTimeMillis()))
else
// JobScheduler has been stopped.
finally
ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(JobScheduler.BATCH_TIME_PROPERTY_KEY, null)
ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(JobScheduler.OUTPUT_OP_ID_PROPERTY_KEY, null)
2. OnReceive初始化接收到消息JobCompleted.
def start(): Unit = synchronized
if (eventLoop != null) return // scheduler has already been started
logDebug("Starting JobScheduler")
eventLoop = new EventLoop[JobSchedulerEvent]("JobScheduler")
override protected def onReceive(event: JobSchedulerEvent): Unit = processEvent(event)
override protected def onError(e: Throwable): Unit = reportError("Error in job scheduler", e)
eventLoop.start()
3. processEvent:
private def processEvent(event: JobSchedulerEvent)
try
event match
case JobStarted(job, startTime) => handleJobStart(job, startTime)
case JobCompleted(job, completedTime) => handleJobCompletion(job, completedTime)
case ErrorReported(m, e) => handleError(m, e)
catch
case e: Throwable =>
reportError("Error in job scheduler", e)
4. 调用JobGenerator的onBatchCompletion方法清楚元数据。
private def handleJobCompletion(job: Job, completedTime: Long)
val jobSet = jobSets.get(job.time)
jobSet.handleJobCompletion(job)
job.setEndTime(completedTime)
listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerOutputOperationCompleted(job.toOutputOperationInfo))
logInfo("Finished job " + job.id + " from job set of time " + jobSet.time)
if (jobSet.hasCompleted)
jobSets.remove(jobSet.time)
jobGenerator.onBatchCompletion(jobSet.time)
logInfo("Total delay: %.3f s for time %s (execution: %.3f s)".format(
jobSet.totalDelay / 1000.0, jobSet.time.toString,
jobSet.processingDelay / 1000.0
))
listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerBatchCompleted(jobSet.toBatchInfo))
job.result match
case Failure(e) =>
reportError("Error running job " + job, e)
case _ =>
触发流程如下:
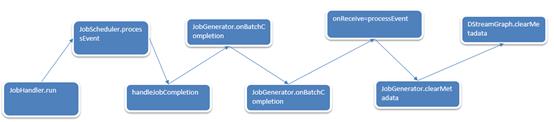
以上是关于Spark Streaming源码解读之数据清理内幕彻底解密的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章