解析vue-router到html5的pushState replaceState是如何实现页面不刷新而时时刷新数据的
Posted 浪里个浪里个浪里个浪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了解析vue-router到html5的pushState replaceState是如何实现页面不刷新而时时刷新数据的相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
首先我们知道vue是单页面应用,一般情况下是不回去刷新页面,应为刷新页面vuex的数据就会不见,那一般url变更的时候,如指定location.href history.push replace 等等页面就会刷新,那么vue页面在实现页面跳转的时候改变了浏览器的url 是怎么实现页面没有刷新而数据刷新的呢
可以去看一下vue-router的源码 有这么一段代码:
export class html5History extends History
...
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function)
const current: fromRoute = this
this.transitionTo(location, route =>
pushState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath))
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
, onAbort)
replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function)
const current: fromRoute = this
this.transitionTo(location, route =>
replaceState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath))
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
, onAbort)
...
在看看里面的
export function pushState (url?: string, replace?: boolean)
saveScrollPosition()
// try...catch the pushState call to get around Safari
// DOM Exception 18 where it limits to 100 pushState calls
const history = window.history
try
if (replace)
history.replaceState( key: _key , '', url)
else
_key = genKey()
history.pushState( key: _key , '', url)
catch (e)
window.location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url)
清楚了吧,就是用的html5的history新增的方法:pushState和replaceState。
先说一下history的作用是保存当前窗口访问过的所有url的地址,可以通过history.back history.go(-1) 来访问历史记录的URL. history.forward() 来跳转到下一个URL
1.history.pushState()
他的作用就是在当前窗口访问的历史URL中在增加一条URL
pushState()他不会触发页面刷新,只是history的对象发生了变化,并且执行这句话之后浏览器地址栏也会变化,只是改变了地址栏,页面不回变化。
他有三个参数
window.history.pushStat(stata,title,url)
state:一个与添加的记录相关联的状态对象,主要用于popstate事件。该事件触发时,该对象会传入回调函数。也就是说,浏览器会将这个对象序列化以后保留在本地,重新载入这个页面的时候,可以拿到这个对象。如果不需要这个对象,此处可以填null。
title:新页面的标题。但是,现在所有浏览器都忽视这个参数,所以这里可以填空字符串。
url:新的网址,必须与当前页面处在同一个域。浏览器的地址栏将显示这个网址。
2.history.replaceState()
History.replaceState()方法用来修改 History 对象的当前记录,其他都与pushState()方法一样,替换当前浏览器的地址,页面不刷新
如果URL为 : https://blog.csdn.net/yexudeng/art/det
history.pushState(page: 1, 'title 1', '?page=1')
//https://blog.csdn.net/yexudeng/art/det?page=1
pushState() 方法新增一条历史记录
replaceState() 替换当前的历史记录
3.popState事件
同一域名下,当浏览器的地址发生改变时就会触发popstate事件
但是仅仅只有pushState和replaceState方法并不会触发该事件,用户必须点机浏览器的前进或者倒退按钮才会触发事件 或者调用history.back forword go这些方法才会触发。
注册事件:
window.onpopstate = function (event)
console.log('location: ' + document.location);
console.log('state: ' + JSON.stringify(event.state));
;
// 或者
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(event)
console.log('location: ' + document.location);
console.log('state: ' + JSON.stringify(event.state));
);
注意页面初始化第一次加载的时候不会出发popstate事件
vue-router 源码解析最简版
前端路由和后端路由
后端路由: 输入url -> 请求发送到服务器 -> 服务器解析请求的路径 -> 拿到对应页面 -> 返回出去 前端路由: 输入url -> js解析地址 -> 找到对应地址的页面 -> 执行页面生成的js -> 看到页面
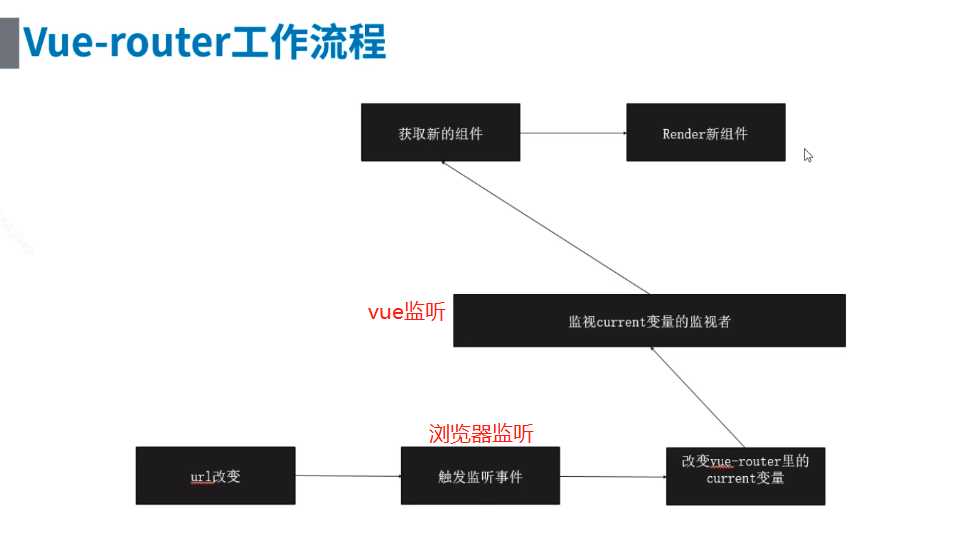

1、Hash 和 History

vue插件的基础知识 -- 如何检测vue外部的对象,插件等。。。
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command // (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias. import Vue from ‘vue‘ import App from ‘./App‘ import router from ‘./router‘ import { create } from ‘domain‘ Vue.config.productionTip = false var test = { //独立于vue外的对象 testa: 1 } setTimeout(() => { //独立于vue外的操作 test.testa = 3333333; }, 2000); function f1(){ console.log(‘f1-----------‘) } f1.install = function(vue){ console.log(‘添加了install属性,,执行install中方法,,不再打印f1-----------‘) console.log(vue) //打印的是vue这个类,和import一样的类 //全局混入vue实例 console.log(vue.util); //vue一系列api vue.util.defineReactive(test, ‘testa‘); console.log(‘util.extend----‘, vue.util.extend); console.log(‘extend------‘, vue.extend) vue.mixin({ data(){ return { c: ‘this is mixin in c‘, } }, //定义一些公共方法 methods: { golableMethod(){ console.log(‘调用了mixin混入的全局方法--golableMethod‘) } }, beforeCreate: function(){ //为什么在beforeCreate中注入,,因为created时data已经生成,再注入已经晚了 this.test = test //这样就可以监听vue外的对象 }, //最关键的还是混入生命周期 created: function(){ console.log(‘i am mixin混入的created‘) //打印了三个 i am mixin混入的created //1、new Vue({}) 2、app.vue 3、HelloWorld.vue console.log(this) //this指的是当前组件 } }) } f1.c = function(){console.log(‘f1的c方法,,,‘)} /** * vue.use() ---把给vue的东西执行一遍 * 如果给的是个方法,那么他会直接执行这个方法 * 如果给的给的东西里面有个install属性,那么会执行install * 为什么不直接调用要执行的方法,而要使用install, ==》因为install方法中可以传递vue参数,, */ Vue.use(f1) /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, router, components: { App }, template: ‘<App/>‘ }) /** * vue的工具属性 * vue.util = { * warn: function(){}, * extend: function(){}, * mergeOptions: function(){}, * defineReactive: function(){} * } */ /** * vue.util.extend 和 vue.extend 区别 * vue.util.extend --- 拷贝 * vue.extend --- 可以在任何地方拿到任何组件 */
2、路由原理
class HistoryRoute{ constructor(){ this.current = null; } } class vueRouter { constructor(options){ this.mode = options.mode || ‘hash‘; this.routes = options.routes || []; this.history = new HistoryRoute; this.routesMap = this.createMap(this.routes) this.init() } init(){ if(this.mode == ‘hash‘){ location.hash ? ‘‘ : location.hash = ‘/‘; window.addEventListener(‘load‘, ()=>{ this.history.current = location.hash.slice(1); }) window.addEventListener(‘hashchange‘, ()=>{ this.history.current = location.hash.slice(1); }) }else{ location.pathname ? ‘‘ : location.pathname = ‘/‘; window.addEventListener(‘load‘, ()=>{ this.history.current = location.pathname; }) window.addEventListener(‘popstate‘, ()=>{ this.history.current = location.pathname; }) } } createMap(routes){ return routes.reduce((memo, current)=>{ memo[current.path] = current.component; return memo; },{}) } } vueRouter.install = function(Vue){ Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate(){ if(this.$options && this.$options.router){ this._root = this; this._router = this.$options.router; Vue.util.defineReactive(this, ‘current‘, this._router.history) }else { this._root = this.$parent._root } } }) Vue.component(‘router-view‘, { render(h){ let current = this._self._root._router.history.current; console.log(current) let routesMap = this._self._root._router.routesMap; console.log(routesMap) return h(routesMap[current]) } }) } export default vueRouter
以上是关于解析vue-router到html5的pushState replaceState是如何实现页面不刷新而时时刷新数据的的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章