SpringBoot 常用读取配置文件的 3 种方法!
Posted 小二上酒8
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot 常用读取配置文件的 3 种方法!相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们在SpringBoot框架进行项目开发中该如何优雅的读取配置呢?或者说对于一些List或者Map应该如何配置呢?
本篇主要解决如下几个问题:
1、Spring Boot有哪些常用的读取配置文件方式?
1)使用 @Value 读取配置文件
2) 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 读取配置文件
3)使用 Environment 读取配置文件
2、一些复杂的数据结构,如List、Map,如何配置?如何读取呢?
前言
Spring Boot默认的配置文件有两种格式: application.properties 和 application.yml。 查找顺序是首先从application.properties 查找,
如果找不到,再查找 application.yml。优先级:application.properties > application.yml。
以yml中rabbitmq的配置为例,配置文件如下:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
password: root
port: 5672
username: root
一、使用 @Value 读取配置文件
这种方法适用于对象的参数比较少的情况
我们可以直接在对象的属性上使用 @Value 注解,同时以 $ 的形式传入配置文件中对应的属性。同时需要在该类的上方使用 @Configuration 注解,将该类作为配置
文件加入,在启动项目的时候实现注入。
@Configuration
public class RabbitmqProperties
@Value("$rabbitmq.host")
private String rabbitmqHost;
@Value("$rabbitmq.port")
private String rabbitmqPort;
@Value("$rabbitmq.username")
private String rabbitmqUsername;
@Value("$rabbitmq.password")
private String rabbitmqPassword;
如果哪里需要用到,通过 @Autowired 注入进去就可以获取属性值了
@Component
public class PropertiesTest
@Autowired
private RabbitmqProperties rabbitmqProperties;
二、使用 @ConfigurationProperties 读取配置文件
如果对象的参数比较多情况下,推荐使用 @ConfigurationProperties 会更简单一些,不需要在每一个字段的上面的使用@Value注解。
@ConfigurationProperties注解声明当前类为配置读取类
prefix="rabbitmq" 表示读取前缀为rabbitmq的属性
示例如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "rabbitmq")
public class RabbitmqProperties
private String host;
private String port;
private String username;
private String password;
这里有一点需要注意: 必须保证属性名称和字段一模一样,且类需要提供字段的setter方法
注意 如果仅仅只是使用了 @ConfigurationProperties 注解是没有效果的,它并不会将这个配置注入容器中,它还需要和注入容器的注解一起使用。
这里有两种方法实现将它注入到容器中
1、类上添加@Configuration注解
除了@Configuration,也可以是@Controller、@RestController、@Service、@Componet等注解,加入到Ioc容器里。
@Setter
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "rabbitmq")
public class RabbitmqProperties
private String host;
private String port;
private String username;
private String password;
同样哪里需要用到,通过 @Autowired 注入进去就可以获取属性值了
2、使用@EnableConfigurationProperties注解
通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解可以将指定的配置读取类的对象加载到Spring容器,也就是说,在其他配置类上使用一个@EnableConfigurationProperties注解,
来将配置文件的参数和RabbitmqProperties类的属性绑定。这样就不需要在RabbitmqProperties类上使用@Configuration注解了
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RabbitmqProperties.class)
public class RabbitmqConfig
@Autowired
private RabbitmqProperties prop;
@Bean
public Rabbitmq rabbitmq()
Rabbitmq mq = new Rabbitmq();
mq.setHost(prop.getHost());
mq.setPort(prop.getPort());
mq.setUsername(prop.getUsername());
mq.setPassword(prop.getPassword());
return mq;
3、使用@ConfigurationPropertiesScan扫描
在 Spring Boot 2.2.0.RELEASE 中提供了一个扫描注解@ConfigurationPropertiesScan。它可以扫描特定包下所有的被@ConfigurationProperties标记的配置类,
并将它们进行IoC注入。
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication
public static void main(String[] args)
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
三、使用 Environment 读取配置文件
Environment 是 SpringCore 中的一个用于读取配置文件的类,将此类使用 @Autowired 注入到类中就可以使用它的getProperty方法来获取某个配置项的值。
如下代码所示:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication implements InitializingBean
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
public static void main(String[] args)
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet()
String username = environment.getProperty("rabbitmq.username");
System.out.println("rabbitmq当前用户名为: " + username);
四、常用的几种数据结构配置读取
比如我们常见的字符串、整数、List、Map如何配置和读取呢?这里以之前自己开发的一个项目中用到复杂的配置数据来做示例之前有发布一个基于
Spring Cache实现二级缓存(Caffeine+Redis) 的项目,里面的配置就比较复杂。
这里展示配置示例:
application.yml
# 二级缓存配置
l2cache:
config:
# 是否存储空值,默认true,防止缓存穿透
allowNullValues: true
# 组合缓存配置
composite:
# 是否全部启用一级缓存,默认false
l1AllOpen: false
# 是否手动启用一级缓存,默认false
l1Manual: true
# 手动配置走一级缓存的缓存key集合,针对单个key维度
l1ManualKeySet:
- userCache:user01
- userCache:user02
- userCache:user03
- userCache:user04
# 一级缓存
caffeine:
# 缓存刷新调度线程池的大小
refreshPoolSize: 2
# 写入后过期时间(秒)
expireAfterWrite: 180
# 访问后过期时间(秒)
expireAfterAccess: 180
# 初始化大小
initialCapacity: 100
# 最大缓存对象个数,超过此数量时之前放入的缓存将失效
maximumSize: 300
# 二级缓存
redis:
# 全局过期时间,单位毫秒,默认不过期
defaultExpiration: 300000
# 每个cacheName的过期时间,单位毫秒
expires: userCache: 300000,goodsCache: 50000
# 缓存更新时通知其他节点的topic名称 默认 cache:redis:caffeine:topic
topic: cache:redis:caffeine:topic
配置实体类
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "l2cache")
public class L2CacheProperties
/**
* 缓存配置
*/
private L2CacheConfig config;
L2CacheConfig
/**
* 缓存配置
*
* @author xub
* @date 2022/9/20 下午6:02
*/
@Data
public class L2CacheConfig
/** 是否存储空值,设置为true时,可防止缓存穿透 */
private boolean allowNullValues = true;
/** 组合缓存配置 */
private final Composite composite = new Composite();
/** 一级缓存配置 */
private final Caffeine caffeine = new Caffeine();
/** 二级缓存配置 */
private final Redis redis = new Redis();
/**
* 组合缓存配置
*/
@Data
public static class Composite
/** 是否全部启用一级缓存,默认false*/
private boolean l1AllOpen = false;
/** 是否手动启用一级缓存,默认false */
private boolean l1Manual = false;
/** 手动配置走一级缓存的缓存key集合,针对单个key维度*/
private Set<String> l1ManualKeySet = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 一级缓存配置
*/
@Data
public static class Caffeine
/** 缓存刷新调度线程池的大小 默认为 CPU数 * 2 */
private Integer refreshPoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/** 写入后过期时间,单位秒 */
private long expireAfterWrite;
/** 写入后刷新时间,单位秒 */
private long refreshAfterWrite;
/** 初始化大小 */
private int initialCapacity;
/** 最大缓存对象个数,超过此数量时之前放入的缓存将失效 */
private long maximumSize;
/**
* 二级缓存配置
*/
@Data
public static class Redis
/** 全局过期时间,单位毫秒,默认不过期 */
private long defaultExpiration = 0;
/** 每个cacheName的过期时间,单位毫秒,优先级比defaultExpiration高 */
private Map<String, Long> expires = new HashMap<>();
/** 缓存更新时通知其他节点的topic名称 */
private String topic = "cache:redis:caffeine:topic";
Configuration类
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(L2CacheProperties.class)
public class CacheRedisCaffeineAutoConfiguration
@Autowired
private L2CacheProperties l2CacheProperties;
@Bean
public RedisCaffeineCacheManager cacheManager()
return new RedisCaffeineCacheManager(l2CacheProperties.getConfig());
测试
项目启动后,进行Debug打断点,看有木有注入到L2CacheProperties实体中
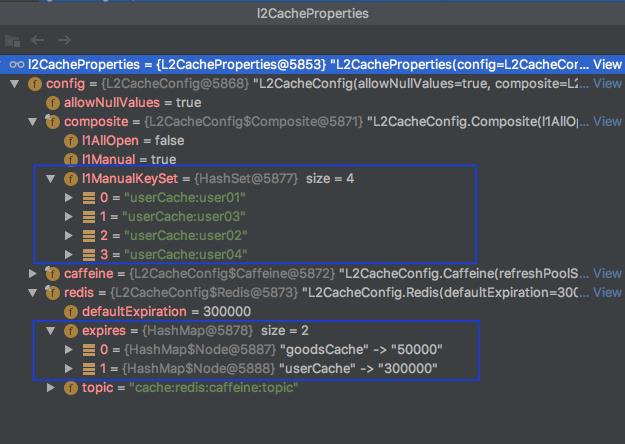
通过上面截图就可以看出,所有application.yml配置数据,都已经在L2CacheProperties实体中,说明配置成功,获取也成功了。
Springboot-读取核心配置文件及自定义配置文件
读取核心配置文件
核心配置文件是指在resources根目录下的application.properties或application.yml配置文件,读取这两个配置文件的方法有两种,都比较简单。
核心配置文件application.properties内容如下:
server.port=9090 test.msg=Hello World Springboot!
-
使用
@Value方式(常用)
1 @RestController 2 public class WebController { 3 4 @Value("${test.msg}") 5 private String msg; 6 7 @RequestMapping(value = "index", method = RequestMethod.GET) 8 public String index() { 9 return "The Way 1 : " +msg; 10 } 11 }
注意:在@Value的${}中包含的是核心配置文件中的键名。在Controller类上加@RestController表示将此类中的所有视图都以JSON方式显示,类似于在视图方法上加@ResponseBody。
访问:http://localhost:9090/index 时将得到The Way 1 : Hello World Springboot!
-
使用
Environment方式
@RestController public class WebController { @Autowired private Environment env; @RequestMapping(value = "index2", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String index2() { return "The Way 2 : " + env.getProperty("test.msg"); } }
注意:这种方式是依赖注入Evnironment来完成,在创建的成员变量private Environment env上加上@Autowired注解即可完成依赖注入,然后使用env.getProperty("键名")即可读取出对应的值。
访问:http://localhost:9090/index2 时将得到The Way 2 : Hello World Springboot!
读取自定义配置文件
-
通过
@ConfigurationProperties注解,通过getter、setter方法注入及获取配置
为了不破坏核心文件的原生态,但又需要有自定义的配置信息存在,一般情况下会选择自定义配置文件来放这些自定义信息,这里在resources/config目录下创建配置文件my-web.properties
resources/config/my-web.properties内容如下:
web.name=isea533
web.jdbc.username=root
web.jdbc.password=root
创建管理配置的实体类:
@ConfigurationProperties(locations = "classpath:config/my-web.properties", prefix = "web") @Component public class MyWebConfig{ private String name; private Jdbc jdbc; class Jdbc { private String username; private String password; //getter... } public Integer gePort(){ return this.port; } public Jdbc getJdbc() { return this.jdbc; } }
注意:
-
在
@ConfigurationProperties注释中有两个属性:locations:指定配置文件的所在位置prefix:指定配置文件中键名称的前缀(我这里配置文件中所有键名都是以web.开头)
-
使用
@Component是让该类能够在其他地方被依赖使用,即使用@Autowired注释来创建实例。
-
通过
@PropertySource注解,然后使用@Value逐个注入配置
1 @Configuration 2 @PropertySource("classpath:test.properties") 3 public class ELConfig { 4 5 @Value("${book.name}") 6 private String bookName; 7 8 //PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer这个bean,这个bean主要用于解决@value中使用的${…}占位符。假如你不使用${…}占位符的话,可以不使用这个bean。 9 @Bean 10 public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigure() { 11 return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(); 12 } 13 14 public void outputSource() { 15 System.out.println(bookName); 16 } 17 }
以上是关于SpringBoot 常用读取配置文件的 3 种方法!的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章