面试专栏Guava - ListenableFuture,避免Future获取阻塞问题,增加回调
Posted C3Stones
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了面试专栏Guava - ListenableFuture,避免Future获取阻塞问题,增加回调相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 简介
相比Future(【面试专栏】Java5 - Future,基本使用),Guava提供的ListenableFuture支持不阻塞主线程进行任务执行完成后的业务处理。
使用Future的实现类FutureTask想要实现一旦获取到结果立即执行后续的业务,就需要阻塞主线程等待结果或者使用其他线程循环的判断任务是否结束,这样导致性能较低,且代码负责。ListenableFuture在Future的基础上增加了任务执行后自动调用后续业务处理的逻辑,方便我们使用。
2. ListenableFuture回调函数
- 调用ListenableFuture接口的addListener(Runnable listener, Executor executor)方法,其中第一个参数为回调函数的处理逻辑,第二个运行监听器的线程池,一般使用执行任务的线程池
public interface ListenableFuture<V extends @Nullable Object> extends Future<V>
/**
* Registers a listener to be @linkplain Executor#execute(Runnable) run on the given executor.
* The listener will run when the @code Future's computation is @linkplain Future#isDone()
* complete or, if the computation is already complete, immediately.
*
* <p>There is no guaranteed ordering of execution of listeners, but any listener added through
* this method is guaranteed to be called once the computation is complete.
*
* <p>Exceptions thrown by a listener will be propagated up to the executor. Any exception thrown
* during @code Executor.execute (e.g., a @code RejectedExecutionException or an exception
* thrown by @linkplain MoreExecutors#directExecutor direct execution) will be caught and
* logged.
*
* <p>Note: If your listener is lightweight -- and will not cause stack overflow by completing
* more futures or adding more @code directExecutor() listeners inline -- consider @link
* MoreExecutors#directExecutor. Otherwise, avoid it: See the warnings on the docs for @code
* directExecutor.
*
* <p>This is the most general listener interface. For common operations performed using
* listeners, see @link Futures. For a simplified but general listener interface, see @link
* Futures#addCallback addCallback().
*
* <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions in a thread prior to adding a listener <a
* href="https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se7/html/jls-17.html#jls-17.4.5">
* <i>happen-before</i></a> its execution begins, perhaps in another thread.
*
* <p>Guava implementations of @code ListenableFuture promptly release references to listeners
* after executing them.
*
* @param listener the listener to run when the computation is complete
* @param executor the executor to run the listener in
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if we tried to execute the listener immediately but the
* executor rejected it.
*/
void addListener(Runnable listener, Executor executor);
- 调用Futures类的静态方法addCallback(final ListenableFuture future, final FutureCallback<? super V> callback, Executor executor)方法,其中第一个参数为任务执行后的Future,第二个为回调函数,第三个为运行回调函数的线程池,一般使用执行任务的线程池
public final class Futures extends GwtFuturesCatchingSpecialization
// ......
/**
* Registers separate success and failure callbacks to be run when the @code Future's
* computation is @linkplain java.util.concurrent.Future#isDone() complete or, if the
* computation is already complete, immediately.
*
* <p>The callback is run on @code executor. There is no guaranteed ordering of execution of
* callbacks, but any callback added through this method is guaranteed to be called once the
* computation is complete.
*
* <p>Exceptions thrown by a @code callback will be propagated up to the executor. Any exception
* thrown during @code Executor.execute (e.g., a @code RejectedExecutionException or an
* exception thrown by @linkplain MoreExecutors#directExecutor direct execution) will be caught
* and logged.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>@code
* ListenableFuture<QueryResult> future = ...;
* Executor e = ...
* addCallback(future,
* new FutureCallback<QueryResult>()
* public void onSuccess(QueryResult result)
* storeInCache(result);
*
* public void onFailure(Throwable t)
* reportError(t);
*
* , e);
* </pre>
*
* <p>When selecting an executor, note that @code directExecutor is dangerous in some cases. See
* the warnings the @link MoreExecutors#directExecutor documentation.
*
* <p>For a more general interface to attach a completion listener to a @code Future, see @link
* ListenableFuture#addListener addListener.
*
* @param future The future attach the callback to.
* @param callback The callback to invoke when @code future is completed.
* @param executor The executor to run @code callback when the future completes.
* @since 10.0
*/
public static <V extends @Nullable Object> void addCallback(
final ListenableFuture<V> future,
final FutureCallback<? super V> callback,
Executor executor)
Preconditions.checkNotNull(callback);
future.addListener(new CallbackListener<V>(future, callback), executor);
3. ListenableFuture应用
- 前期准备:实现Callable创建线程,支持指定执行时间,并增加执行时间校验逻辑
/**
* 创建线程
*/
@RequiredArgsConstructor
class MyCallable implements Callable<Long>
/**
* 任务执行时间
*/
private final long execTime;
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception
if (execTime <= 0)
throw new RuntimeException("执行时间必须大于0");
log.info("任务执行,耗时:" + execTime + " ms");
Thread.sleep(execTime);
return execTime;
- 引入Guava依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>31.1-jre</version>
</dependency>- 增加监听器
/**
* 增加监听器
*/
@Test
public void testAddListener() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ListenableFuture<Long> future = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
// 增加监听器
future.addListener(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
log.info("任务执行结束,结果为:" + future.get());
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(3000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
19:18:29.256 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
19:18:30.263 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行结束,结果为:1000- 测试任务执行成功回调
/**
* 测试任务执行成功回调
*/
@Test
public void addCallbackOfSuccess() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ListenableFuture<Long> future = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<Long> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<Long>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(Long result)
try
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + future.get());
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(future, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(3000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
19:19:34.162 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
19:19:35.173 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行成功,结果为:1000- 测试任务执行失败回调
/**
* 测试任务执行失败回调
*/
@Test
public void addCallbackOfFailure() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ListenableFuture<Long> future = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(-1));
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<Long> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<Long>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(Long result)
try
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + future.get());
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(future, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(3000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
19:21:29.158 [pool-1-thread-1] ERROR com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行失败,异常原因:执行时间必须大于0- 测试所有任务执行成功并获取结果集
/**
* 测试所有任务执行成功并获取结果集
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void testAsListSuccess() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
// 创建3个任务,3个都成功
ListenableFuture<Long> future1 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
ListenableFuture<Long> future2 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(2000));
ListenableFuture<Long> future3 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(3000));
ListenableFuture<List<Long>> future = Futures.allAsList(future1, future2, future3);
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<List<Long>> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<List<Long>>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<Long> result)
try
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + future.get().stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(future, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(5000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
20:11:13.057 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:2000 ms
20:11:13.051 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
20:11:13.059 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:3000 ms
20:11:16.063 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行成功,结果为:1000,2000,3000- 测试包含失败任务执行并获取结果集
/**
* 测试包含失败任务执行并获取结果集
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void testAsListFailure() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
// 创建3个任务,2个都成功,1个失败
ListenableFuture<Long> future1 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
ListenableFuture<Long> future2 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(-2));
ListenableFuture<Long> future3 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(3000));
ListenableFuture<List<Long>> future = Futures.allAsList(future1, future2, future3);
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<List<Long>> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<List<Long>>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<Long> result)
try
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + future.get().stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(future, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(5000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
20:12:51.029 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:3000 ms
20:12:51.030 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
20:12:51.091 [pool-1-thread-2] ERROR com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行失败,异常原因:执行时间必须大于0通过结果可以看出,只要有任务失败,则不会执行回调方法中成功的处理逻辑,而是仅执行回调方法中失败的处理逻辑。适用于任务不会失败,或者专门获取任意失败任务时的场景。
- 测试所有任务执行成功或失败获取结果,失败结果替换为null
/**
* 测试所有任务执行成功或失败获取结果,失败结果替换为null
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void testSuccessfulAsList() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
// 创建3个任务,2个都成功,1个失败
ListenableFuture<Long> future1 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
ListenableFuture<Long> future2 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(-2));
ListenableFuture<Long> future3 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(3000));
ListenableFuture<List<Long>> future = Futures.successfulAsList(future1, future2, future3);
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<List<Long>> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<List<Long>>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<Long> result)
try
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + future.get().stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(future, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(5000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
20:16:10.092 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
20:16:10.092 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:3000 ms
20:16:13.104 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行成功,结果为:1000,null,3000- 测试返回结果同步转换
/**
* 测试返回结果同步转换
*/
@Test
public void testTransform() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ListenableFuture<Long> future1 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
// 将返回结果转换为字符串
ListenableFuture<String> transform = Futures.transform(future1, new Function<Long, String>()
@Override
public String apply(Long input)
String result = String.valueOf(input);
log.info("将Long[" + input + "] 转换为 String[" + result + "]");
return "String -> " + result;
, listeningExecutorService);
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<String> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<String>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result)
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + result);
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(transform, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(3000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
20:40:11.661 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
20:40:12.830 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 将Long[1000] 转换为 String[1000]
20:40:12.832 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行成功,结果为:String -> 1000- 测试返回结果异步转换
/**
* 测试返回结果异步转换
*/
@Test
public void testTransformAsync() throws InterruptedException
ListeningExecutorService listeningExecutorService = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ListenableFuture<Long> future1 = listeningExecutorService.submit(new MyCallable(1000));
// 将返回结果转换为字符串
ListenableFuture<String> transform = Futures.transformAsync(future1, new AsyncFunction<Long, String>()
@Override
public ListenableFuture<String> apply(Long input) throws Exception
String result = String.valueOf(input);
log.info("将Long[" + input + "] 转换为 String[" + result + "]");
return Futures.immediateFuture("String -> " + result);
, listeningExecutorService);
// 增加回调
FutureCallback<String> futureCallback = new FutureCallback<String>()
/**
* 成功时调用
* @param result
*/
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result)
log.info("任务执行成功,结果为:" + result);
/**
* 失败时调用
* @param t
*/
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
log.error("任务执行失败,异常原因:" + t.getMessage());
;
Futures.addCallback(transform, futureCallback, listeningExecutorService);
// 为了验证测试结果,阻塞主线程,等待监听器任务异步执行
// 真实使用不需要阻塞主线程
Thread.sleep(3000);
listeningExecutorService.shutdown();
控制台打印:
20:42:02.687 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行,耗时:1000 ms
20:42:03.697 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 将Long[1000] 转换为 String[1000]
20:42:03.699 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.c3stones.test.ListenableFutureTest - 任务执行成功,结果为:String -> 10004. 项目地址
缓存之王Caffeine Cache,性能比Guava更强,命中率更高!
在项目开发中,为提升系统性能,减少 IO 开销,本地缓存是必不可少的。最常见的本地缓存是 Guava 和 Caffeine,本篇文章将为大家介绍 Caffeine。
Caffeine 是基于 Google Guava Cache 设计经验改进的结果,相较于 Guava 在性能和命中率上更具有效率,你可以认为其是 Guava Plus。
毋庸置疑的,你应该尽快将你的本地缓存从 Guava 迁移至 Caffeine,本文将重点和 Guava 对比二者性能占据,给出本地缓存的最佳实践,以及迁移策略。
二、PK Guava
2.1 功能
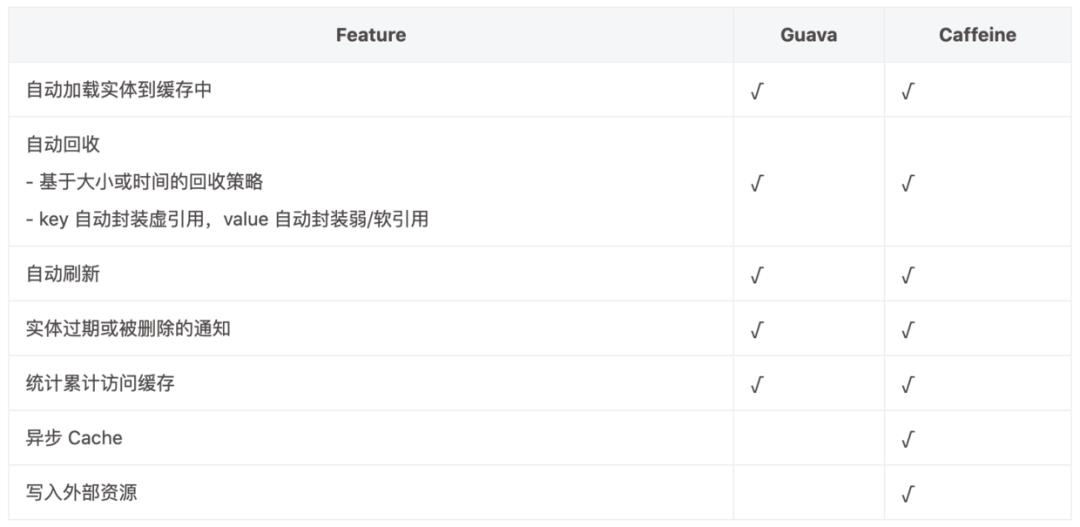
从功能上看,Guava 已经比较完善了,满足了绝大部分本地缓存的需求。Caffine 除了提供 Guava 已有的功能外,同时还加入了一些扩展功能。
2.2 性能
Guava 中其读写操作夹杂着过期时间的处理,也就是你在一次 put 操作中有可能会做淘汰操作,所以其读写性能会受到一定影响。
Caffeine 在读写操作方面完爆 Guava,主要是因为 Caffeine 对这些事件的操作是异步的,将事件提交至队列(使用 Disruptor RingBuffer),然后会通过默认的 ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),或自己配置的线程池,进行取队列操作,然后再进行后续的淘汰、过期操作。
以下性能对比来自 Caffeine 官方提供数据:
(1)在此基准测试中,从配置了最大大小的缓存中,8 个线程并发读: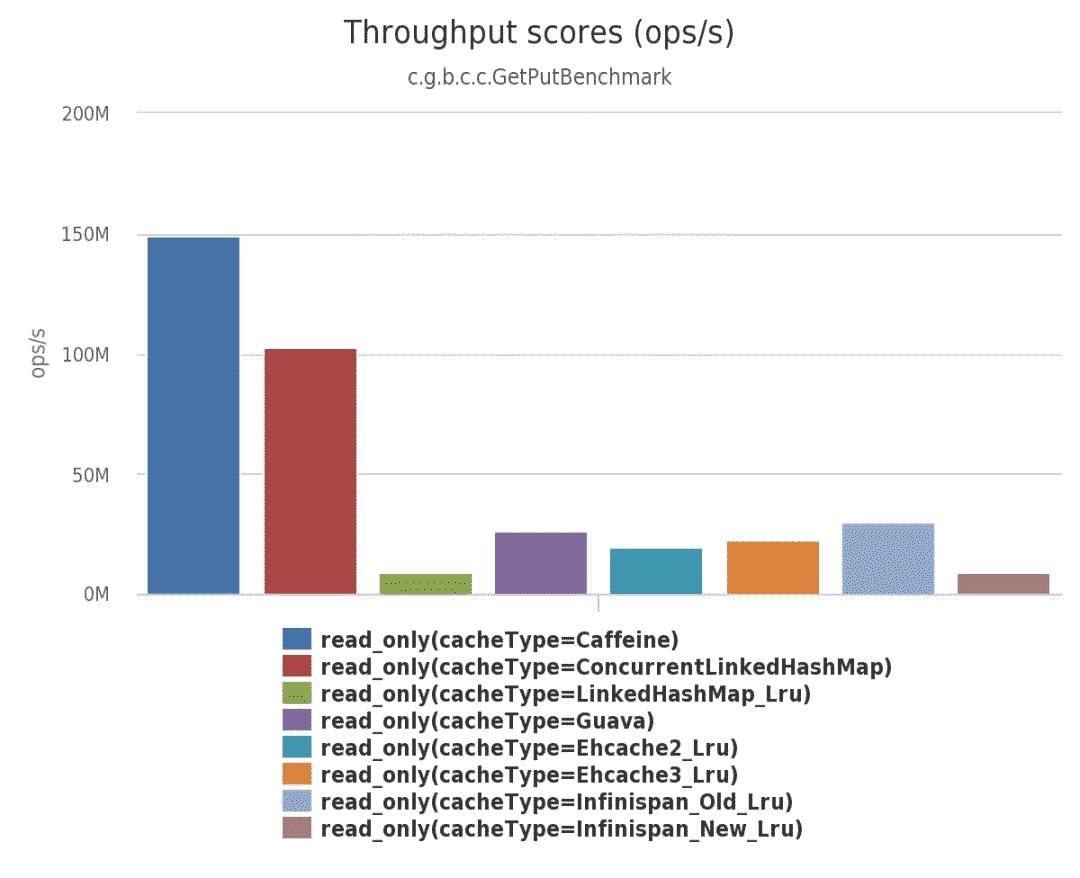
(2)在此基准测试中,从配置了最大大小的缓存中,6个线程并发读、2个线程并发写:
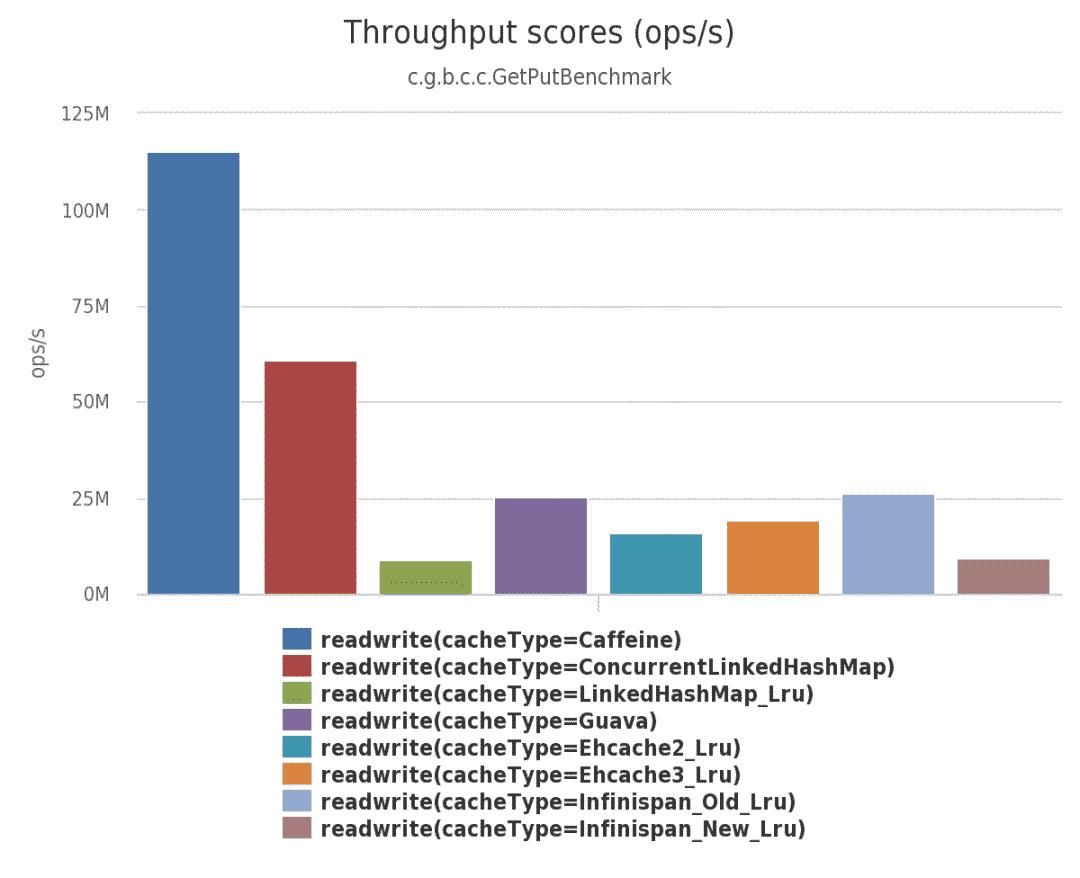
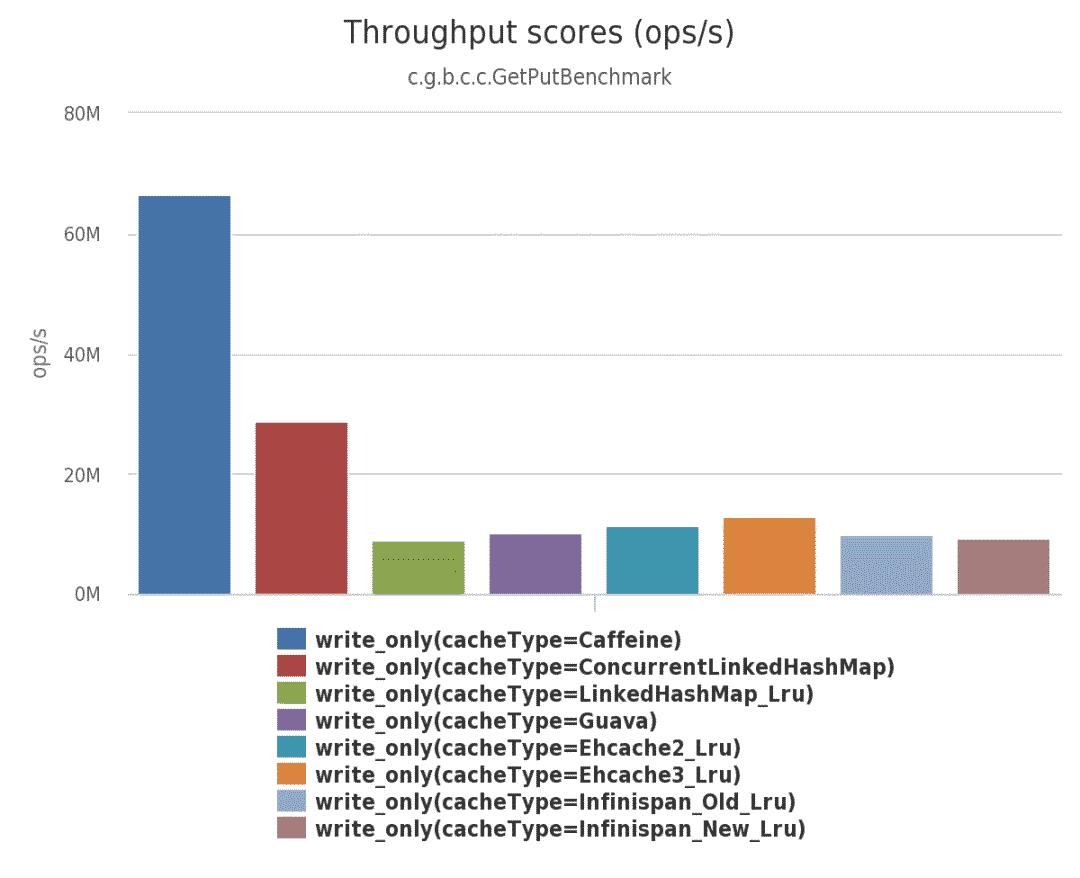
(3)在此基准测试中,从配置了最大大小的缓存中,8 个线程并发写:
2.3 命中率
缓存的淘汰策略是为了预测哪些数据在短期内最可能被再次用到,从而提升缓存的命中率。Guava 使用 S-LRU 分段的最近最少未使用算法,Caffeine 采用了一种结合 LRU、LFU 优点的算法:W-TinyLFU,其特点是:高命中率、低内存占用。
2.3.1 LRU
Least Recently Used:如果数据最近被访问过,将来被访问的概率也更高。每次访问就把这个元素放到队列的头部,队列满了就淘汰队列尾部的数据,即淘汰最长时间没有被访问的。
需要维护每个数据项的访问频率信息,每次访问都需要更新,这个开销是非常大的。
其缺点是,如果某一时刻大量数据到来,很容易将热点数据挤出缓存,留下来的很可能是只访问一次,今后不会再访问的或频率极低的数据。比如外卖中午时候访问量突增、微博爆出某明星糗事就是一个突发性热点事件。当事件结束后,可能没有啥访问量了,但是由于其极高的访问频率,导致其在未来很长一段时间内都不会被淘汰掉。
2.3.2 LFU
Least Frequently Used:如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的概率也更高。也就是淘汰一定时间内被访问次数最少的数据(时间局部性原理)。
需要用 Queue 来保存访问记录,可以用 LinkedHashMap 来简单实现一个基于 LRU 算法的缓存。
其优点是,避免了 LRU 的缺点,因为根据频率淘汰,不会出现大量进来的挤压掉老的,如果在数据的访问的模式不随时间变化时候,LFU 能够提供绝佳的命中率。
其缺点是,偶发性的、周期性的批量操作会导致LRU命中率急剧下降,缓存污染情况比较严重。
2.3.3 TinyLFU
TinyLFU 顾名思义,轻量级LFU,相比于 LFU 算法用更小的内存空间来记录访问频率。
TinyLFU 维护了近期访问记录的频率信息,不同于传统的 LFU 维护整个生命周期的访问记录,所以他可以很好地应对突发性的热点事件(超过一定时间,这些记录不再被维护)。这些访问记录会作为一个过滤器,当新加入的记录(New Item)访问频率高于将被淘汰的缓存记录(Cache Victim)时才会被替换。流程如下:
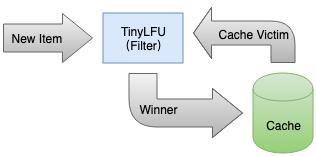
尽管维护的是近期的访问记录,但仍然是非常昂贵的,TinyLFU 通过 Count-Min Sketch 算法来记录频率信息,它占用空间小且误报率低,关于 Count-Min Sketch 算法可以参考论文:pproximating Data with the Count-Min Data Structure
2.3.4 W-TinyLFU
W-TinyLFU 是 Caffeine 提出的一种全新算法,它可以解决频率统计不准确以及访问频率衰减的问题。这个方法让我们从空间、效率、以及适配举证的长宽引起的哈希碰撞的错误率上做均衡。
下图是一个运行了 ERP 应用的数据库服务中各种算法的命中率,实验数据来源于 ARC 算法作者,更多场景的性能测试参见官网:
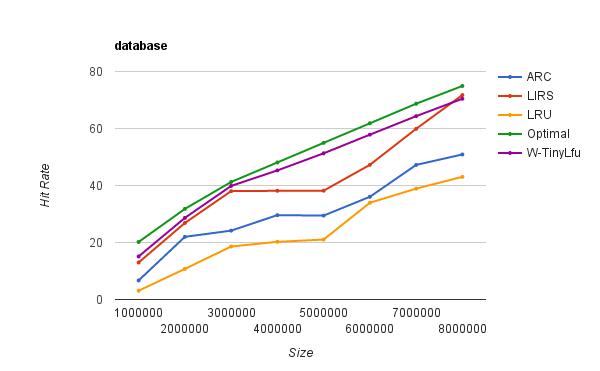
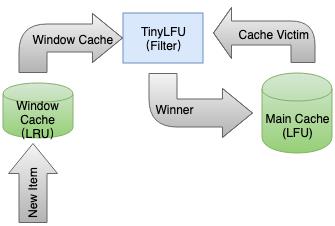
W-TinyLFU 算法是对 TinyLFU算法的优化,能够很好地解决一些稀疏的突发访问元素。在一些数目很少但突发访问量很大的场景下,TinyLFU将无法保存这类元素,因为它们无法在短时间内积累到足够高的频率,从而被过滤器过滤掉。W-TinyLFU 将新记录暂时放入 Window Cache 里面,只有通过 TinLFU 考察才能进入 Main Cache。大致流程如下图:
三、最佳实践
3.1 实践1
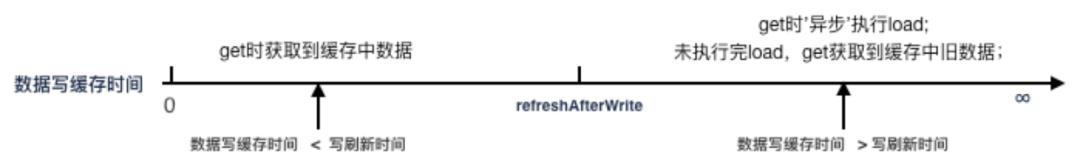
配置方式:设置 maxSize、refreshAfterWrite,不设置 expireAfterWrite
存在问题:get 缓存间隔超过 refreshAfterWrite 后,触发缓存异步刷新,此时会获取缓存中的旧值
适用场景:
-
缓存数据量大,限制缓存占用的内存容量 -
缓存值会变,需要刷新缓存 -
可以接受任何时间缓存中存在旧数据
设置 maxSize、refreshAfterWrite,不设置 expireAfterWrite
3.2 实践2
配置方式:设置 maxSize、expireAfterWrite,不设置 refreshAfterWrite
存在问题:get 缓存间隔超过 expireAfterWrite 后,针对该 key,获取到锁的线程会同步执行 load,其他未获得锁的线程会阻塞等待,获取锁线程执行延时过长会导致其他线程阻塞时间过长
适用场景:
-
缓存数据量大,限制缓存占用的内存容量 -
缓存值会变,需要刷新缓存 -
不可以接受缓存中存在旧数据 -
同步加载数据延迟小(使用 redis 等)
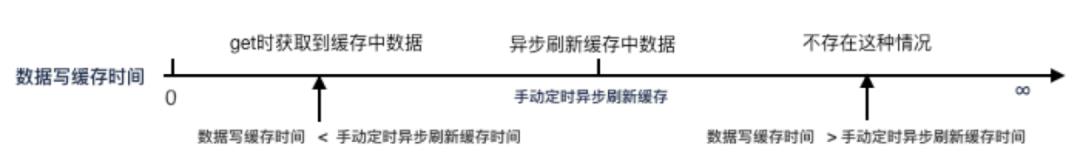
设置 maxSize、expireAfterWrite,不设置refreshAfterWrite
3.3 实践3
配置方式:设置 maxSize,不设置 refreshAfterWrite、expireAfterWrite,定时任务异步刷新数据
存在问题:需要手动定时任务异步刷新缓存
适用场景:
-
缓存数据量大,限制缓存占用的内存容量 -
缓存值会变,需要刷新缓存 -
不可以接受缓存中存在旧数据 -
同步加载数据延迟可能会很大

设置 maxSize,不设置 refreshAfterWrite、expireAfterWrite,定时任务异步刷新数据
3.4 实践4
配置方式:设置 maxSize、refreshAfterWrite、expireAfterWrite,refreshAfterWrite < expireAfterWrite
存在问题:
-
get 缓存间隔在 refreshAfterWrite和expireAfterWrite之间,触发缓存异步刷新,此时会获取缓存中的旧值 -
get 缓存间隔大于 expireAfterWrite,针对该 key,获取到锁的线程会同步执行 load,其他未获得锁的线程会阻塞等待,获取锁线程执行延时过长会导致其他线程阻塞时间过长
适用场景:
-
缓存数据量大,限制缓存占用的内存容量 -
缓存值会变,需要刷新缓存 -
可以接受有限时间缓存中存在旧数据 -
同步加载数据延迟小(使用 redis 等)
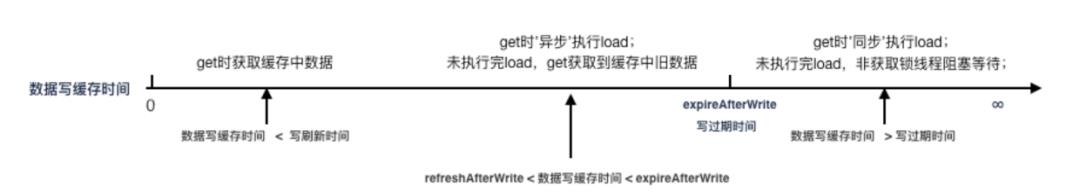
设置 maxSize、refreshAfterWrite、expireAfterWrite
四、迁移指南
4.1 切换至 Caffeine
在 pom 文件中引入 Caffeine 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>
Caffeine 兼容 Guava API,从 Guava 切换到 Caffeine,仅需要把 CacheBuilder.newBuilder()改成 Caffeine.newBuilder() 即可。
4.2 Get Exception
需要注意的是,在使用 Guava 的 get()方法时,当缓存的 load()方法返回 null 时,会抛出 ExecutionException。切换到 Caffeine 后,get()方法不会抛出异常,但允许返回为 null。
Guava 还提供了一个getUnchecked()方法,它不需要我们显示的去捕捉异常,但是一旦 load()方法返回 null时,就会抛出 UncheckedExecutionException。切换到 Caffeine 后,不再提供 getUnchecked()方法,因此需要做好判空处理。
最近面试BAT,整理一份面试资料
《Java面试BAT通关手册》
,覆盖了Java核心技术、JVM、Java并发、SSM、微服务、数据库、数据结构等等。
以上是关于面试专栏Guava - ListenableFuture,避免Future获取阻塞问题,增加回调的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章