Android热修复学习之旅——HotFix完全解析
Posted 伯努力不努力
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android热修复学习之旅——HotFix完全解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在上一篇博客 Android热修复学习之旅开篇——热修复概述中,简单介绍了各个热修复框架的原理,本篇博客我将详细分析QQ空间热修复方案。
Android dex分包原理介绍
QQ空间热修复方案基于android dex分包基础之上,简单概述android dex分包的原理就是:就是把多个dex文件塞入到app的classloader之中,但是android dex拆包方案中的类是没有重复的,如果classes.dex和classes1.dex中有重复的类,当classes.dex和classes1.dex中都具有同一个类的时候,那么classloader会选择加载哪个类呢?这要从classloader的源码入手,加载类是通过classloader的loadClass方法实现的,所以我们看一下loadClass的源码:
/**
* Loads the class with the specified name. Invoking this method is
* equivalent to calling {@code loadClass(className, false)}.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> In the Android reference implementation, the
* second parameter of {@link #loadClass(String, boolean)} is ignored
* anyway.
* </p>
*
* @return the {@code Class} object.
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class can not be found.
*/
public Class<?> loadClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(className, false);
}protected Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = findLoadedClass(className);
if (clazz == null) {
ClassNotFoundException suppressed = null;
try {
clazz = parent.loadClass(className, false);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
suppressed = e;
}
if (clazz == null) {
try {
clazz = findClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.addSuppressed(suppressed);
throw e;
}
}
}
return clazz;
}classloader是基于 双亲代理模型的,具体关于classloader的详细解析,可以查看我的这篇文章:Android插件化学习之路(二)之ClassLoader完全解析
简单来说就是ClassLoader用loadClass方法调用了findClass方法,点进去发现findClass是抽象方法,而这个方法的实现是在它的子类BaseDexClassLoader中,而BaseDexClassLoader重载了这个方法,得到BaseDexClassLoader,进入到BaseDexClassLoader类的findClass方法中
#BaseDexClassLoader
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = pathList.findClass(name);
if (clazz == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
return clazz;
}
#DexPathList
public Class findClass(String name) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
if (dex != null) {
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
return null;
}
#DexFile
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie);
}
private native static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, int cookie);一个ClassLoader可以包含多个dex文件,每个dex文件是一个Element,多个dex文件排列成一个有序的数组dexElements,当找类的时候,会按顺序遍历dex文件,然后从当前遍历的dex文件中找类,如果找类则返回,如果找不到从下一个dex文件继续查找。
理论上,如果在不同的dex中有相同的类存在,那么会优先选择排在前面的dex文件的类
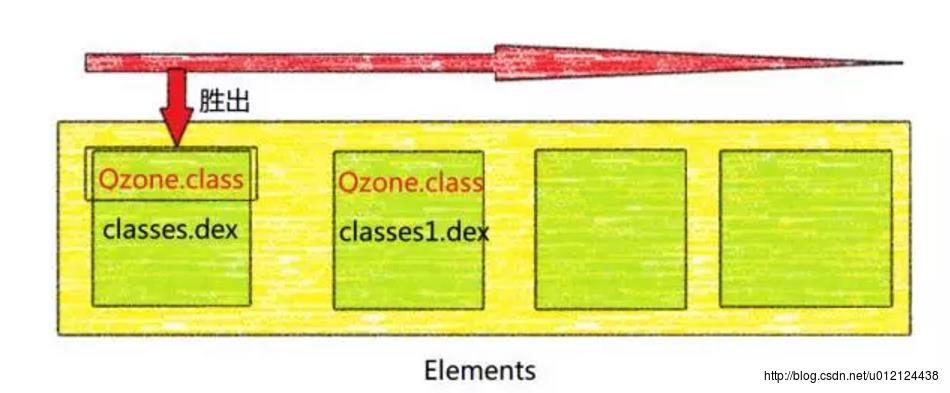
所以,QQ空间正是基于ClassLoader的这个原理,把有问题的类打包到一个dex(patch.dex)中去,然后把这个dex插入到Elements的最前面
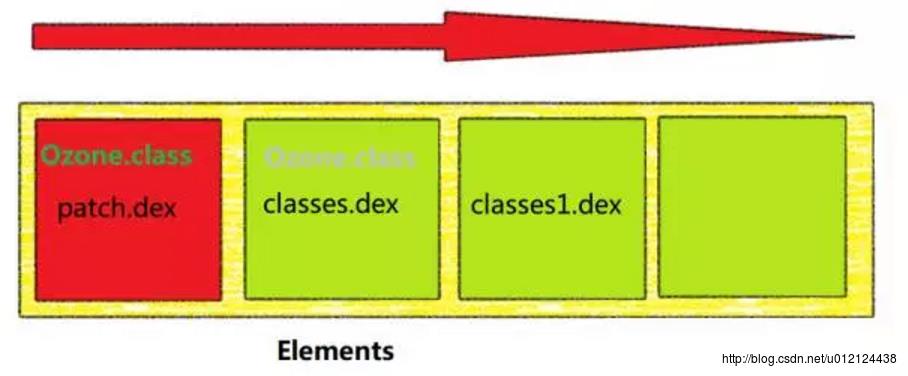
关于如何进行dex分包后面再单独开一篇博客进行分析。
CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED的问题
采用dex分包方案会遇到的问题,也就是CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED的问题,简单来概括就是:
在虚拟机启动的时候,当verify选项被打开的时候,如果static方法、private方法、构造函数等,其中的直接引用(第一层关系)到的类都在同一个dex文件中,那么该类就会被打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED标志。
那么,我们要做的就是,阻止该类打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED的标志。
注意下,是阻止引用者的类,也就是说,假设你的app里面有个类叫做AClass,再其内部引用了BClass。发布过程中发现BClass有编写错误,那么想要发布一个新的BClass类,那么你就要阻止AClass这个类打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED的标志。
也就是说,你在生成apk之前,就需要阻止相关类打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED的标志了。如何阻止,简单来说,让AClass在构造方法中,去引用别的dex文件,比如:C.dex中的某个类即可。
所以总结下来,防止这个错误,只需要:
1、动态改变BaseDexClassLoader对象间接引用的dexElements;2、在app打包的时候,阻止相关类去打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED标志。
热修复框架HotFix解析
采用QQ空间的热修复方案而实现的开源热修复框架就是HotFix,说到了使用dex分包方案会遇到CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED问题,而解决方案就是在dx工具执行之前,将所有的class文件,进行修改,再其构造中添加System.out.println(dodola.hackdex.AntilazyLoad.class),然后继续打包的流程。注意:AntilazyLoad.class这个类是独立在hack.dex中。
dex分包方案实现需要关注以下问题:
1.如何解决CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED问题
2.如何将修复的.dex文件插入到dexElements的最前面
那么如何达到这个目的呢?在HotFix中采用的javassist来达到这个目的,以下是HotFix中的PatchClass.groovy代码
public class PatchClass {
/**
* 植入代码
* @param buildDir 是项目的build class目录,就是我们需要注入的class所在地
* @param lib 这个是hackdex的目录,就是AntilazyLoad类的class文件所在地
*/
public static void process(String buildDir, String lib) {
println(lib)
ClassPool classes = ClassPool.getDefault()
classes.appendClassPath(buildDir)
classes.appendClassPath(lib)
//下面的操作比较容易理解,在将需要关联的类的构造方法中插入引用代码
CtClass c = classes.getCtClass("dodola.hotfix.BugClass")
if (c.isFrozen()) {
c.defrost()
}
println("====添加构造方法====")
def constructor = c.getConstructors()[0];
constructor.insertBefore("System.out.println(dodola.hackdex.AntilazyLoad.class);")
c.writeFile(buildDir)
CtClass c1 = classes.getCtClass("dodola.hotfix.LoadBugClass")
if (c1.isFrozen()) {
c1.defrost()
}
println("====添加构造方法====")
def constructor1 = c1.getConstructors()[0];
constructor1.insertBefore("System.out.println(dodola.hackdex.AntilazyLoad.class);")
c1.writeFile(buildDir)
}
static void growl(String title, String message) {
def proc = ["osascript", "-e", "display notification \\"${message}\\" with title \\"${title}\\""].execute()
if (proc.waitFor() != 0) {
println "[WARNING] ${proc.err.text.trim()}"
}
}
}其实内部做的逻辑就是:通过ClassPool对象,然后添加classpath。然后从classpath中找到LoadBugClass,拿到其构造方法,在其中插入一行代码。
到这里插入代码的操作已经完成,但是还存在另外一个问题,那就是如何在dx之前去进行上述脚本的操作?
答案就在HotFix的app/build.gradle中
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
task('processWithJavassist') << {
String classPath = file('build/intermediates/classes/debug')//项目编译class所在目录
dodola.patch.PatchClass.process(classPath, project(':hackdex').buildDir
.absolutePath + '/intermediates/classes/debug')//第二个参数是hackdex的class所在目录
}
buildTypes {
debug {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.dex.dependsOn << processWithJavassist //在执行dx命令之前将代码打入到class中
}
可以看到在build.gradle中,在执行dx之前,会先执行processWithJavassist这个任务。这样会执行PatchClass.groovy的脚本,在构造方法中进行注入
将修复的.dex文件插入dexElements
寻找class是遍历dexElements;然后我们的AntilazyLoad.class实际上并不包含在apk的classes.dex中,并且根据上面描述的需要,我们需要将AntilazyLoad.class这个类打成独立的hack_dex.jar,注意不是普通的jar,必须经过dx工具进行转化。
具体做法:
jar cvf hack.jar dodola/hackdex/*
dx --dex --output hack_dex.jar hack.jar 还记得之前我们将所有的类的构造方法中都引用了AntilazyLoad.class,所以我们需要把hack_dex.jar插入到dexElements,而在hotfix中,就是在Application中完成这个操作的
ublic class HotfixApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
File dexPath = new File(getDir("dex", Context.MODE_PRIVATE), "hackdex_dex.jar");
Utils.prepareDex(this.getApplicationContext(), dexPath, "hackdex_dex.jar");
HotFix.patch(this, dexPath.getAbsolutePath(), "dodola.hackdex.AntilazyLoad");
try {
this.getClassLoader().loadClass("dodola.hackdex.AntilazyLoad");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}在app的私有目录创建一个文件,然后调用Utils.prepareDex将assets中的hackdex_dex.jar写入该文件。 Utils.prepareDex中其实就是文件的读写操作,注意:前提是你把hackdex_dex.jar放入到assets中
public class Utils {
private static final int BUF_SIZE = 2048;
public static boolean prepareDex(Context context, File dexInternalStoragePath, String dex_file) {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
OutputStream dexWriter = null;
try {
bis = new BufferedInputStream(context.getAssets().open(dex_file));
dexWriter = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dexInternalStoragePath));
byte[] buf = new byte[BUF_SIZE];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buf, 0, BUF_SIZE)) > 0) {
dexWriter.write(buf, 0, len);
}
dexWriter.close();
bis.close();
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
if (dexWriter != null) {
try {
dexWriter.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
}
}接下来HotFix.patch就是去反射去修改dexElements了
public static void patch(Context context, String patchDexFile, String patchClassName) {
if (patchDexFile != null && new File(patchDexFile).exists()) {
try {
if (hasLexClassLoader()) {
injectInAliyunOs(context, patchDexFile, patchClassName);
} else if (hasDexClassLoader()) {
injectAboveEqualApiLevel14(context, patchDexFile, patchClassName);
} else {
injectBelowApiLevel14(context, patchDexFile, patchClassName);
}
} catch (Throwable th) {
}
}
}可以看到patch方法中有几个分支,说白了是根据不同的系统中ClassLoader的类型来做相应的处理
private static void injectInAliyunOs(Context context, String patchDexFile, String patchClassName)
throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException,
InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
PathClassLoader obj = (PathClassLoader) context.getClassLoader();
String replaceAll = new File(patchDexFile).getName().replaceAll("\\\\.[a-zA-Z0-9]+", ".lex");
Class cls = Class.forName("dalvik.system.LexClassLoader");
Object newInstance =
cls.getConstructor(new Class[] {String.class, String.class, String.class, ClassLoader.class}).newInstance(
new Object[] {context.getDir("dex", 0).getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + replaceAll,
context.getDir("dex", 0).getAbsolutePath(), patchDexFile, obj});
cls.getMethod("loadClass", new Class[] {String.class}).invoke(newInstance, new Object[] {patchClassName});
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths",
appendArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths"), getField(newInstance, cls, "mRawDexPath")));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles"), getField(newInstance, cls, "mFiles")));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips"), getField(newInstance, cls, "mZips")));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mLexs",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mLexs"), getField(newInstance, cls, "mDexs")));
}上述方法中的LexClassLoader应该是阿里自己的ClassLoader,可以看到上面将修复的文件的结尾都换成了.lex的结尾,这些文件就是专门需要通过LexClassLoader进行加载的
我们分 API 14以上和以下进行分析
API 14以下
private static void injectBelowApiLevel14(Context context, String str, String str2)
throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
PathClassLoader obj = (PathClassLoader) context.getClassLoader();
DexClassLoader dexClassLoader =
new DexClassLoader(str, context.getDir("dex", 0).getAbsolutePath(), str, context.getClassLoader());
dexClassLoader.loadClass(str2);
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths",
appendArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mRawDexPath")
));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mFiles")
));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mZips")));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mDexs",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mDexs"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mDexs")));
obj.loadClass(str2);
}通过setField方法将mPaths属性,修改为通过appendArray方法创造的新元素
private static Object getField(Object obj, Class cls, String str)
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field declaredField = cls.getDeclaredField(str);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
return declaredField.get(obj);
}private static Object appendArray(Object obj, Object obj2) {
Class componentType = obj.getClass().getComponentType();
int length = Array.getLength(obj);
Object newInstance = Array.newInstance(componentType, length + 1);
Array.set(newInstance, 0, obj2);
for (int i = 1; i < length + 1; i++) {
Array.set(newInstance, i, Array.get(obj, i - 1));
}
return newInstance;
}而appendArray中就是创建一个新的Array,把obj2插入到obj的前面,注意这里的obj2长度只有1
所以,在injectBelowApiLevel14的以下方法中,就是把mRawDexPath的元素插入到mPaths中所有元素之前,而重新组合而成的新mPaths替换掉旧的mPaths
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths",
appendArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mPaths"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mRawDexPath")
));接下来的替换,是通过combineArray生成的新元素替换掉旧元素,这里分别是mFiles,mZips,mDexs
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mFiles"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mFiles")
));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mZips"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mZips")));
setField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mDexs",
combineArray(getField(obj, PathClassLoader.class, "mDexs"), getField(dexClassLoader, DexClassLoader.class,
"mDexs")));于是我们需要看一下combineArray方法里面做了什么
private static Object combineArray(Object obj, Object obj2) {
Class componentType = obj2.getClass().getComponentType();
int length = Array.getLength(obj2);
int length2 = Array.getLength(obj) + length;
Object newInstance = Array.newInstance(componentType, length2);
for (int i = 0; i < length2; i++) {
if (i < length) {
Array.set(newInstance, i, Array.get(obj2, i));
} else {
Array.set(newInstance, i, Array.get(obj, i - length));
}
}
return newInstance;
}逻辑也很简单,也就是两个数组的合并而已
API14以上
private static void injectAboveEqualApiLevel14(Context context, String str, String str2)
throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
PathClassLoader pathClassLoader = (PathClassLoader) context.getClassLoader();
Object a = combineArray(getDexElements(getPathList(pathClassLoader)),
getDexElements(getPathList(
new DexClassLoader(str, context.getDir("dex", 0).getAbsolutePath(), str, context.getClassLoader()))));
Object a2 = getPathList(pathClassLoader);
setField(a2, a2.getClass(), "dexElements", a);
pathClassLoader.loadClass(str2);
}根据context拿到PathClassLoader,然后通过getPathList(pathClassLoader),拿到PathClassLoader中的pathList对象,在调用getDexElements通过pathList取到dexElements对象。
private static Object getDexElements(Object obj) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
return getField(obj, obj.getClass(), "dexElements");
}private static Object getPathList(Object obj) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException,
IllegalAccessException {
return getField(obj, Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader"), "pathList");
}同样是通过combineArray方法,对数组进行合并,合并完成后,将新的数组通过反射的方式设置给pathList.
通过上面的一系列流程,那么hack_dex.jar已经插入到dexElements最前面了,补丁插入的过程也和hack_dex.jar的插入流程是一致的
到这里,dex分包方案实现热修复的HotFix的分析就已经完毕了。
以上是关于Android热修复学习之旅——HotFix完全解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章