PCL 惯性矩和偏心率
Posted Σίσυφος1900
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PCL 惯性矩和偏心率相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、MomentOfInertiaEstimation惯性矩估计
PCL——基于惯性矩与偏心率的描述子进行包围盒提取_emm@aaaM的博客-CSDN博客1
(1)获取基于惯性矩(moment of inertia)与偏心率(eccentricity)的描述子;
(2)提取有向包围盒OBB(Oriented Bounding Box)或者和坐标轴对齐包围盒AABB(Axis-Aligned Bounding Box);提取包围盒的作用常用来在游戏场景中做碰撞检测,或者可以做测量,本文中使用OBB的方法对物体进行长宽高的测量。
PCL源码头文件:
/** \\brief
* Implements the method for extracting features based on moment of inertia. It also
* calculates AABB, OBB and eccentricity of the projected cloud.
*/
template <typename PointT>
class PCL_EXPORTS MomentOfInertiaEstimation : public pcl::PCLBase <PointT>
public:
using PCLBase <PointT>::input_;
using PCLBase <PointT>::indices_;
using PCLBase <PointT>::fake_indices_;
using PCLBase <PointT>::use_indices_;
using PCLBase <PointT>::initCompute;
using PCLBase <PointT>::deinitCompute;
typedef typename pcl::PCLBase <PointT>::PointCloudConstPtr PointCloudConstPtr;
typedef typename pcl::PCLBase <PointT>::PointIndicesConstPtr PointIndicesConstPtr;
public:
/** \\brief Provide a pointer to the input dataset
* \\param[in] cloud the const boost shared pointer to a PointCloud message
*/
virtual void
setInputCloud (const PointCloudConstPtr& cloud);
/** \\brief Provide a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
* \\param[in] indices a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
*/
virtual void
setIndices (const IndicesPtr& indices);
/** \\brief Provide a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
* \\param[in] indices a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
*/
virtual void
setIndices (const IndicesConstPtr& indices);
/** \\brief Provide a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
* \\param[in] indices a pointer to the vector of indices that represents the input data.
*/
virtual void
setIndices (const PointIndicesConstPtr& indices);
/** \\brief Set the indices for the points laying within an interest region of
* the point cloud.
* \\note you shouldn't call this method on unorganized point clouds!
* \\param[in] row_start the offset on rows
* \\param[in] col_start the offset on columns
* \\param[in] nb_rows the number of rows to be considered row_start included
* \\param[in] nb_cols the number of columns to be considered col_start included
*/
virtual void
setIndices (size_t row_start, size_t col_start, size_t nb_rows, size_t nb_cols);
/** \\brief Constructor that sets default values for member variables. */
MomentOfInertiaEstimation ();
/** \\brief Virtual destructor which frees the memory. */
virtual
~MomentOfInertiaEstimation ();
/** \\brief This method allows to set the angle step. It is used for the rotation
* of the axis which is used for moment of inertia/eccentricity calculation.
* \\param[in] step angle step
*/
void
setAngleStep (const float step);
/** \\brief Returns the angle step. */
float
getAngleStep () const;
/** \\brief This method allows to set the normalize_ flag. If set to false, then
* point_mass_ will be used to scale the moment of inertia values. Otherwise,
* point_mass_ will be set to 1 / number_of_points. Default value is true.
* \\param[in] need_to_normalize desired value
*/
void
setNormalizePointMassFlag (bool need_to_normalize);
/** \\brief Returns the normalize_ flag. */
bool
getNormalizePointMassFlag () const;
/** \\brief This method allows to set point mass that will be used for
* moment of inertia calculation. It is needed to scale moment of inertia values.
* default value is 0.0001.
* \\param[in] point_mass point mass
*/
void
setPointMass (const float point_mass);
/** \\brief Returns the mass of point. */
float
getPointMass () const;
/** \\brief This method launches the computation of all features. After execution
* it sets is_valid_ flag to true and each feature can be accessed with the
* corresponding get method.
*/
void
compute ();
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed axis aligned bounding box. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* \\param[out] min_point min point of the AABB
* \\param[out] max_point max point of the AABB
*/
bool
getAABB (PointT& min_point, PointT& max_point) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed oriented bounding box. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* Note that in order to get the OBB, each vertex of the given AABB (specified with min_point and max_point)
* must be rotated with the given rotational matrix (rotation transform) and then positioned.
* Also pay attention to the fact that this is not the minimal possible bounding box. This is the bounding box
* which is oriented in accordance with the eigen vectors.
* \\param[out] min_point min point of the OBB
* \\param[out] max_point max point of the OBB
* \\param[out] position position of the OBB
* \\param[out] rotational_matrix this matrix represents the rotation transform
*/
bool
getOBB (PointT& min_point, PointT& max_point, PointT& position, Eigen::Matrix3f& rotational_matrix) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed eigen values. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* \\param[out] major major eigen value
* \\param[out] middle middle eigen value
* \\param[out] minor minor eigen value
*/
bool
getEigenValues (float& major, float& middle, float& minor) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed eigen vectors. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* \\param[out] major axis which corresponds to the eigen vector with the major eigen value
* \\param[out] middle axis which corresponds to the eigen vector with the middle eigen value
* \\param[out] minor axis which corresponds to the eigen vector with the minor eigen value
*/
bool
getEigenVectors (Eigen::Vector3f& major, Eigen::Vector3f& middle, Eigen::Vector3f& minor) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed moments of inertia. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* \\param[out] moment_of_inertia computed moments of inertia
*/
bool
getMomentOfInertia (std::vector <float>& moment_of_inertia) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed ecentricities. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* \\param[out] eccentricity computed eccentricities
*/
bool
getEccentricity (std::vector <float>& eccentricity) const;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed mass center. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* Note that when mass center of a cloud is computed, mass point is always considered equal 1.
* \\param[out] mass_center computed mass center
*/
bool
getMassCenter (Eigen::Vector3f& mass_center) const;
private:
/** \\brief This method rotates the given vector around the given axis.
* \\param[in] vector vector that must be rotated
* \\param[in] axis axis around which vector must be rotated
* \\param[in] angle angle in degrees
* \\param[out] rotated_vector resultant vector
*/
void
rotateVector (const Eigen::Vector3f& vector, const Eigen::Vector3f& axis, const float angle, Eigen::Vector3f& rotated_vector) const;
/** \\brief This method computes center of mass and axis aligned bounding box. */
void
computeMeanValue ();
/** \\brief This method computes the oriented bounding box. */
void
computeOBB ();
/** \\brief This method computes the covariance matrix for the input_ cloud.
* \\param[out] covariance_matrix stores the computed covariance matrix
*/
void
computeCovarianceMatrix (Eigen::Matrix <float, 3, 3>& covariance_matrix) const;
/** \\brief This method computes the covariance matrix for the given cloud.
* It uses all points in the cloud, unlike the previous method that uses indices.
* \\param[in] cloud cloud for which covariance matrix will be computed
* \\param[out] covariance_matrix stores the computed covariance matrix
*/
void
computeCovarianceMatrix (PointCloudConstPtr cloud, Eigen::Matrix <float, 3, 3>& covariance_matrix) const;
/** \\brief This method calculates the eigen values and eigen vectors
* for the given covariance matrix. Note that it returns normalized eigen
* vectors that always form the right-handed coordinate system.
* \\param[in] covariance_matrix covariance matrix
* \\param[out] major_axis eigen vector which corresponds to a major eigen value
* \\param[out] middle_axis eigen vector which corresponds to a middle eigen value
* \\param[out] minor_axis eigen vector which corresponds to a minor eigen value
* \\param[out] major_value major eigen value
* \\param[out] middle_value middle eigen value
* \\param[out] minor_value minor eigen value
*/
void
computeEigenVectors (const Eigen::Matrix <float, 3, 3>& covariance_matrix, Eigen::Vector3f& major_axis,
Eigen::Vector3f& middle_axis, Eigen::Vector3f& minor_axis, float& major_value, float& middle_value,
float& minor_value);
/** \\brief This method returns the moment of inertia of a given input_ cloud.
* Note that when moment of inertia is computed it is multiplied by the point mass.
* Point mass can be accessed with the corresponding get/set methods.
* \\param[in] current_axis axis that will be used in moment of inertia computation
* \\param[in] mean_value mean value(center of mass) of the cloud
*/
float
calculateMomentOfInertia (const Eigen::Vector3f& current_axis, const Eigen::Vector3f& mean_value) const;
/** \\brief This method simply projects the given input_ cloud on the plane specified with
* the normal vector.
* \\param[in] normal_vector nrmal vector of the plane
* \\param[in] point point belonging to the plane
* \\param[out] projected_cloud projected cloud
*/
void
getProjectedCloud (const Eigen::Vector3f& normal_vector, const Eigen::Vector3f& point, typename pcl::PointCloud <PointT>::Ptr projected_cloud) const;
/** \\brief This method returns the eccentricity of the projected cloud.
* \\param[in] covariance_matrix covariance matrix of the projected cloud
* \\param[in] normal_vector normal vector of the plane, it is used to discard the
* third eigen vector and eigen value*/
float
computeEccentricity (const Eigen::Matrix <float, 3, 3>& covariance_matrix, const Eigen::Vector3f& normal_vector);
private:
/** \\brief Indicates if the stored values (eccentricity, moment of inertia, AABB etc.)
* are valid when accessed with the get methods. */
bool is_valid_;
/** \\brief Stores the angle step */
float step_;
/** \\brief Stores the mass of point in the cloud */
float point_mass_;
/** \\brief Stores the flag for mass normalization */
bool normalize_;
/** \\brief Stores the mean value (center of mass) of the cloud */
Eigen::Vector3f mean_value_;
/** \\brief Major eigen vector */
Eigen::Vector3f major_axis_;
/** \\brief Middle eigen vector */
Eigen::Vector3f middle_axis_;
/** \\brief Minor eigen vector */
Eigen::Vector3f minor_axis_;
/** \\brief Major eigen value */
float major_value_;
/** \\brief Middle eigen value */
float middle_value_;
/** \\brief Minor eigen value */
float minor_value_;
/** \\brief Stores calculated moments of inertia */
std::vector <float> moment_of_inertia_;
/** \\brief Stores calculated eccentricities */
std::vector <float> eccentricity_;
/** \\brief Min point of the axis aligned bounding box */
PointT aabb_min_point_;
/** \\brief Max point of the axis aligned bounding box */
PointT aabb_max_point_;
/** \\brief Min point of the oriented bounding box */
PointT obb_min_point_;
/** \\brief Max point of the oriented bounding box */
PointT obb_max_point_;
/** \\brief Stores position of the oriented bounding box */
Eigen::Vector3f obb_position_;
/** \\brief Stores the rotational matrix of the oriented bounding box */
Eigen::Matrix3f obb_rotational_matrix_;
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
;
#define PCL_INSTANTIATE_MomentOfInertiaEstimation(T) template class pcl::MomentOfInertiaEstimation<T>;
#ifdef PCL_NO_PRECOMPILE
#include <pcl/features/impl/moment_of_inertia_estimation.hpp>
#endif
#endif

二、OBB和AABB
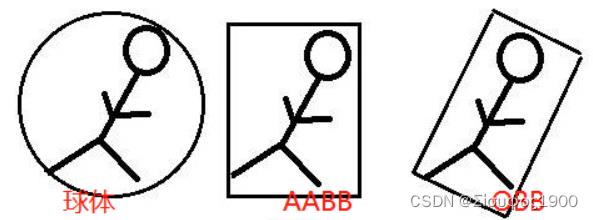
(1)OBB包围盒
根据物体表面的顶点,通过PCA(主成分分析)获得特征向量。PCA是通过正交变换将一组可能相关的变量集合变换成一组不想关的变量集合,即主成分。
(2)PCA算法具体过程
1)将原始数据进行中心化;
2)求原始数据的协方差矩阵;
3)求协方差矩阵的特征值以及对应的特征向量;
4)特征向量组成的坐标系即为OBB包围盒的坐标系
三、代码
实现流程:
加载点云—>计算惯性矩和偏心率—>计算特征值以及对应的特征向量(主方向);
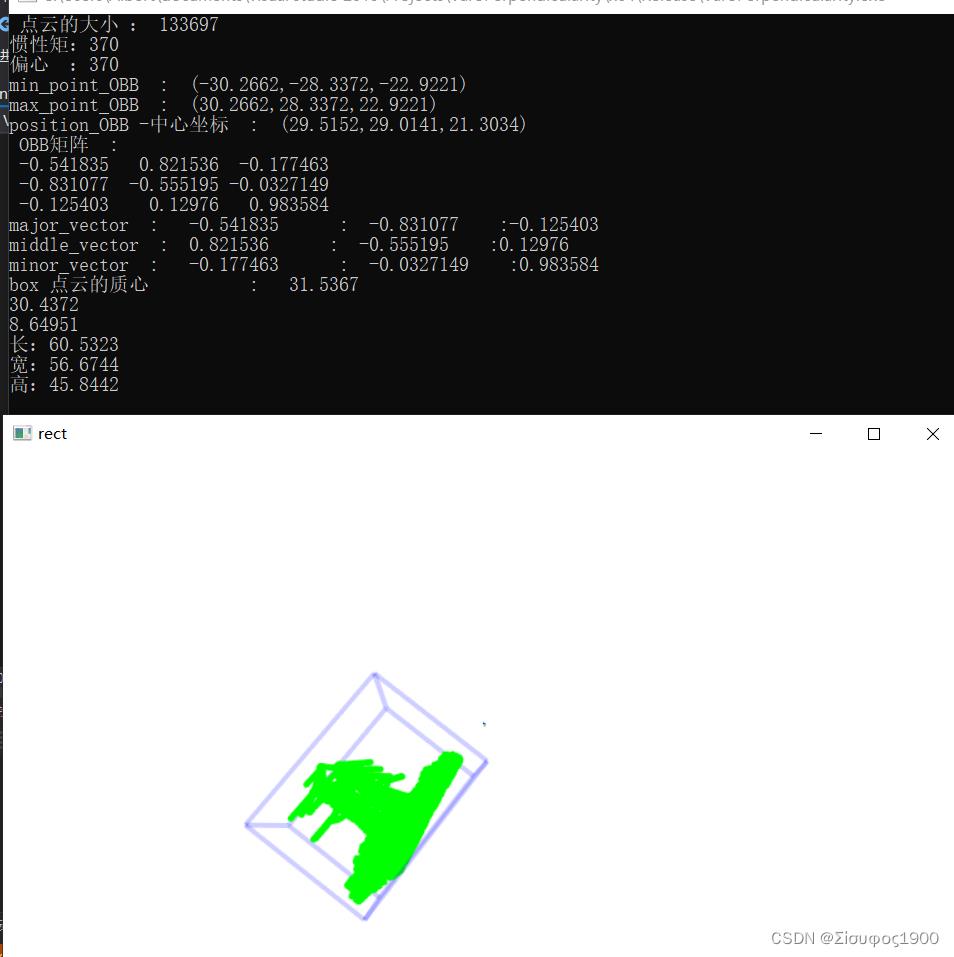
通过pcl::MomentOfInertiaEstimation 类中的成员函数getOBB()得到在质心为坐标系原点的坐标的点云的边界值(min_point_OBB,max_point_OBB),最后添加包围盒并可视化
#if 1
int main()
// Findnowd();
string path = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Albert\\\\Desktop\\\\pcd\\\\dx.pcd";
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // 创建点云(指针)
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>(path, *cloud) == -1) //* 读入PCD格式的文件,如果文件不存在,返回-1
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd \\n"); //文件不存在时,返回错误,终止程序。
return 0;
cout << " 点云的大小 : " << cloud->size() << endl;
// 开始计算惯性矩和偏心率
std::vector <float> moment_of_inertia;//存放惯性距的特征向量
std::vector <float> eccentricity;//存放偏心率的特征向量
pcl::PointXYZ min_point_OBB; // 在质心为坐标系原点的坐标的点云的最小点
pcl::PointXYZ max_point_OBB; // 在质心为坐标系原点的坐标的点云的最大点的
pcl::PointXYZ position_OBB; // 点云的中心
Eigen::Matrix3f rotational_matrix_OBB; // OBB旋转矩阵
float major_value, middle_value, minor_value; // 特征值
Eigen::Vector3f major_vector, middle_vector, minor_vector; // 特征向量
Eigen::Vector3f mass_center; // 质心
pcl::MomentOfInertiaEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ> m_e;
m_e.setInputCloud(cloud);
m_e.compute();
// 获得
m_e.getMomentOfInertia(moment_of_inertia);// 获得惯性矩
cout << "惯性矩:" << moment_of_inertia.size() << endl;
m_e.getEccentricity(eccentricity);// 获得偏心矩
cout << "偏心 :" << eccentricity.size() << endl;
/** \\brief This method gives access to the computed oriented(定向的) bounding box. It returns true
* if the current values (eccentricity, moment of inertia etc) are valid and false otherwise.
* Note that in order to get the OBB, each vertex of the given AABB (specified with min_point and max_point)
* must be rotated with the given rotational matrix (rotation transform) and then positioned.
* Also pay attention to the fact that this is not the minimal possible bounding box. This is the bounding box
* which is oriented in accordance with the eigen vectors.
* \\param[out] min_point min point of the OBB
* \\param[out] max_point max point of the OBB
* \\param[out] position position of the OBB
* \\param[out] rotational_matrix this matrix represents the rotation transform
*/
// bool getOBB(PointT& min_point, PointT& max_point, PointT& position, Eigen::Matrix3f& rotational_matrix) const;
m_e.getOBB(min_point_OBB, max_point_OBB, position_OBB, rotational_matrix_OBB);
cout << "min_point_OBB : " << min_point_OBB<< endl;
cout << "max_point_OBB : " << max_point_OBB << endl;
cout << "position_OBB -中心坐标 : " << position_OBB << endl;
cout << " OBB矩阵 :"<<endl;
cout << rotational_matrix_OBB << endl;
// 得到三个特征值
m_e.getEigenValues(major_value, middle_value, minor_value);
// 得到三个特征向量
// major_vector, middle_vector, minor_vector;
m_e.getEigenVectors(major_vector, middle_vector, minor_vector);
cout << "major_vector : " << major_vector[0] << " : " << major_vector[1] << " :" << major_vector[2] << endl;
cout << "middle_vector : " << middle_vector[0] << " : " << middle_vector[1] << " :" << middle_vector[2] << endl;
cout << "minor_vector : " << minor_vector[0] << " : " << minor_vector[1] << " :" << minor_vector[2] << endl;
// 得到质心
m_e.getMassCenter(mass_center);
std::cout << "box 点云的质心 : " << mass_center<< endl;//质心坐标 以质心为坐标原点
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("rect"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(1, 1, 1);
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0);
viewer->initCameraParameters();
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, 0, 255, 0), "sample cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 5, "sample cloud");
Eigen::Vector3f position(position_OBB.x, position_OBB.y, position_OBB.z);
Eigen::Quaternionf quat(rotational_matrix_OBB);
//cout << "四元数: " << endl;
//cout<< quat.w << endl;
//cout << quat.x << endl;
//cout << quat.y << endl;
//cout << quat.z << endl;
//cout << "s四元数--------------------- " << endl;
viewer->addCube(position, quat, max_point_OBB.x - min_point_OBB.x, max_point_OBB.y - min_point_OBB.y, max_point_OBB.z - min_point_OBB.z, "OBB");
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 0, 1, "OBB");
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.1, "OBB");
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_LINE_WIDTH, 4, "OBB");
viewer->setRepresentationToWireframeForAllActors();//将所有actor的可视化表示更改为线框表示
pcl::PointXYZ center(mass_center(0), mass_center(1), mass_center(2));
//pcl::PointXYZ x_axis(major_vector(0) + mass_center(0), major_vector(1) + mass_center(1), major_vector(2) + mass_center(2));
//pcl::PointXYZ y_axis(middle_vector(0) + mass_center(0), middle_vector(1) + mass_center(1), middle_vector(2) + mass_center(2));
//pcl::PointXYZ z_axis(minor_vector(0) + mass_center(0), minor_vector(1) + mass_center(1), minor_vector(2) + mass_center(2));
//viewer->addLine(center, x_axis, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, "major eigen vector");
//viewer->addLine(center, y_axis, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, "middle eigen vector");
//viewer->addLine(center, z_axis, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, "minor eigen vector");
float height = max_point_OBB.z - min_point_OBB.z;
float width = max_point_OBB.y - min_point_OBB.y;
float depth = max_point_OBB.x - min_point_OBB.x;
cout << "长:" << depth << endl;
cout << "宽:" << width << endl;
cout << "高:" << height << endl;
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
viewer->spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
system("pause");
return (0);
#endif Hu 矩和 SVM 不起作用
【中文标题】Hu 矩和 SVM 不起作用【英文标题】:Hu moments and SVM does not work 【发布时间】:2014-05-15 02:13:16 【问题描述】:我在尝试使用 SVM 训练数据时遇到了一个问题。 我从人脸图像中得到了一些不同的区域(一组连接的像素),而眼睛的区域非常相似,所以我想使用 Hu 矩进行形状描述和 SVM 进行训练。 但是 SVM 不能正常工作,方法 svm.predict 之后将所有内容评估为非眼睛,此外,在训练阶段标记和使用的相同区域作为眼睛,被评估为非眼睛。 特征数据仅包含 7 个 Hu 矩。稍后我会在这里发布一些源代码示例,在此先感谢:)
附加信息:
输入图像: http://i.stack.imgur.com/GyLO0.png
为 1 张图片设置基本 svm:
int image_regions = 10;
Mat training_mat(image_regions ,7,CV_32FC1); // 7 hu moments
Mat labels(image_regions ,1,CV_32FC1); // for labels 1 (eye) and -1 (non eye)
// computing hu moments
Moments moments2=moments(croppedImage,false);
double hu[7];
HuMoments(moments2,hu);
// putting them into svm traning mat
for (int k=0;k<huCounter;k++)
training_mat.at<float>(counter,k) = hu[k]; // counter is current number of region
if (isEye(...))
labels.at<float>(counter,0)=1.0;
else
labels.at<float>(counter,0)=-1.0;
//I use the following:
CvSVM svm;
CvSVMParams params;
params.svm_type = CvSVM::C_SVC;
params.kernel_type = CvSVM::LINEAR;
params.term_crit = cvTermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 1000, 1e-6);
// ... do the above mentioned phase, and then:
svm.train(training_mat, labels, Mat(), Mat(), params);
【问题讨论】:
7 个幽默可能不足以进行分类的“特征空间” 你只有 10 个特征/幽默来训练? 大家好,我只是在对训练阶段使用的相同数据进行训练后尝试运行 SVM,但我仍然得到 svmpredict() 响应 -1(非眼睛)的结果,甚至在标记为 1(眼睛)的特征上 【参考方案1】:希望下面的建议可以帮到你……..
最简单的任务是使用聚类算法并尝试将数据聚类为两类。如果像“k-means”这样的算法可以完成这项工作,为什么还要使用 SVM 和神经网络来让事情变得复杂。我建议您使用这种技术,因为您的特征向量维度非常小(7 Hu Moments)以及您的样本数量。
执行特征归一化(在第 4 点中指定)以确保值落在有限范围内。
查看“您的数据真的可分离吗?”由于您的数据很小,请从正图像中获取一些样本,从负图像中获取一些样本并绘制特征向量。如果您可以直观地看到差异,那么任何学习算法都可以为您完成这项工作。正如我之前所说,简单的技巧比复杂的数学做得更好。
只有当您决定使用 SVM 时,您才应该了解以下内容:
• 从您的代码中可以看出,您使用的是线性 SVM,可能是您的数据不能被线性内核分离。尝试使用一些多项式内核或其他内核。 openCV 有一个选项 bool CvSVM::train_auto 看看就好。
• 尝试检查你得到的特征向量值是否是正确的值(确保它们不是一些垃圾值)。
• 您还可以在将其用于训练之前执行特征归一化“ZERO MEAN and UNIT VARIENCE”。
• 最重要的是增加训练图像的数量,包括正面和负面标记。
• 最后但同样重要的是,SVM 并不神奇,归根结底,它只是在两组点之间画一条线。所以不要指望它会把你给它的任何东西分类为输入。
如果没有任何效果“只需改进您的特征提取技术”
【讨论】:
以上是关于PCL 惯性矩和偏心率的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章