PostgreSQL服务器启动及关闭方法
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PostgreSQL服务器启动及关闭方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术APostgreSQL服务器启动及关闭方法
PostgreSQL采用C/S(客户机/服务器)模式结构。应用层通过INET或者Unix Socket利用既定的协议与数据库服务器进行通信。下面我为大家搜集相关的PostgreSQL服务器启动及关闭方法!

1. 启动数据库服务器(posgres用户):
[postgres@localhost bin]$ postgres -D /opt/postgresql/data/ > /opt/postgresql/log/pg_server.log 2>&1 &
[1] 4508
当然如果设置了环境变量
PGDATA=/opt/postgresql/data
export PGDATA
后,可使用pg_ctl工具进行启动:
[postgres@localhost log]$ pg_ctl start -l /opt/postgresql/log/pg_server.log
pg_ctl: another server might be running; trying to start server anyway
pg_ctl: could not start server
Examine the log output.
[postgres@localhost log]$
因为之前已经启动,所以打印“another server might be running”。此时,查看日志,有如下信息:
[postgres@localhost log]$ cat pg_server.log
FATAL: lock file "postmaster.pid" already exists
HINT: Is another postmaster (PID 4491) running in data directory "/opt/postgresql/data"?
[postgres@localhost log]$
当然,最简的.启动方式是:
[postgres@localhost ~]$ pg_ctl start
server starting
[postgres@localhost ~]$ LOG: database system was shut down at 2011-07-09 13:58:00 CST
LOG: autovacuum launcher started
LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
如果要在操作系统启动时就启动PG,可以在/etc/rc.d/rc.local 文件中加以下语句:
/opt/postgresql/bin/pg_ctl start -l /opt/postgresql/log/pg_server.log -D /opt/postgresql/data
2.关闭服务器
最简单方法:
[postgres@localhost ~]$ pg_ctl stop
waiting for server to shut down.... done
server stopped
与Oracle相同,在关闭时也可采用不同的模式,简介如下:
SIGTERM
不再允许新的连接,但是允许所有活跃的会话正常完成他们的工作,只有在所有会话都结束任务后才关闭。这是智能关闭。
SIGINT
不再允许新的连接,向所有活跃服务器发送 SIGTERM(让它们立刻退出),然后等待所有子进程退出并关闭数据库。这是快速关闭。
SIGQUIT
令 postgres 向所有子进程发送 SIGQUIT 并且立即退出(所有子进程也会立即退出),而不会妥善地关闭数据库系统。这是立即关闭。这样做会导致下次启动时的恢复(通过重放 WAL 日志)。我们推荐只在紧急的时候使用这个方法。
SIGKILL
此选项尽量不要使用,这样会阻止服务器清理共享内存和信号灯资源,那样的话你只能在启动服务器之前自己手工做这件事。另外,SIGKILL 直接把 postgres 杀掉,而不会等它把信号中继给它的子进程,因此我们还需要手工杀掉每个独立子进程。
使用方法举例:
[postgres@localhost ~]$ pg_ctl stop -o SIGTERM
LOG: received smart shutdown request
LOG: autovacuum launcher shutting down
waiting for server to shut down....LOG: shutting down
LOG: database system is shut down
done
server stopped
[postgres@localhost ~]$
最快速关闭方法:kill postgres 进程
[postgres@localhost ~]$ kill -INT `head -1 /opt/postgresql/data/postmaster.pid`
[postgres@localhost ~]$ LOG: received fast shutdown request
LOG: aborting any active transactions
LOG: autovacuum launcher shutting down
LOG: shutting down
LOG: database system is shut down
附:postgre启动后的进程,如下:
[postgres@localhost ~]$ ps -ef|grep post
root 4609 4543 0 13:57 pts/2 00:00:00 su - postgres
postgres 4610 4609 0 13:57 pts/2 00:00:00 -bash
postgres 4724 1 0 14:08 pts/2 00:00:00 /opt/postgresql/bin/postgres
postgres 4726 4724 0 14:08 ? 00:00:00 postgres: writer process
postgres 4727 4724 0 14:08 ? 00:00:00 postgres: wal writer process
postgres 4728 4724 0 14:08 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher process
postgres 4729 4724 0 14:08 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector process
postgres 4752 4610 0 14:11 pts/2 00:00:00 ps -ef
postgres 4753 4610 0 14:11 pts/2 00:00:00 grep post
[postgres@localhost ~]$
;
PostgreSQL进程及体系结构
本文主要讲述了PG的几个主要进程,以及PG的核心架构。进程和体系结构详见下图:
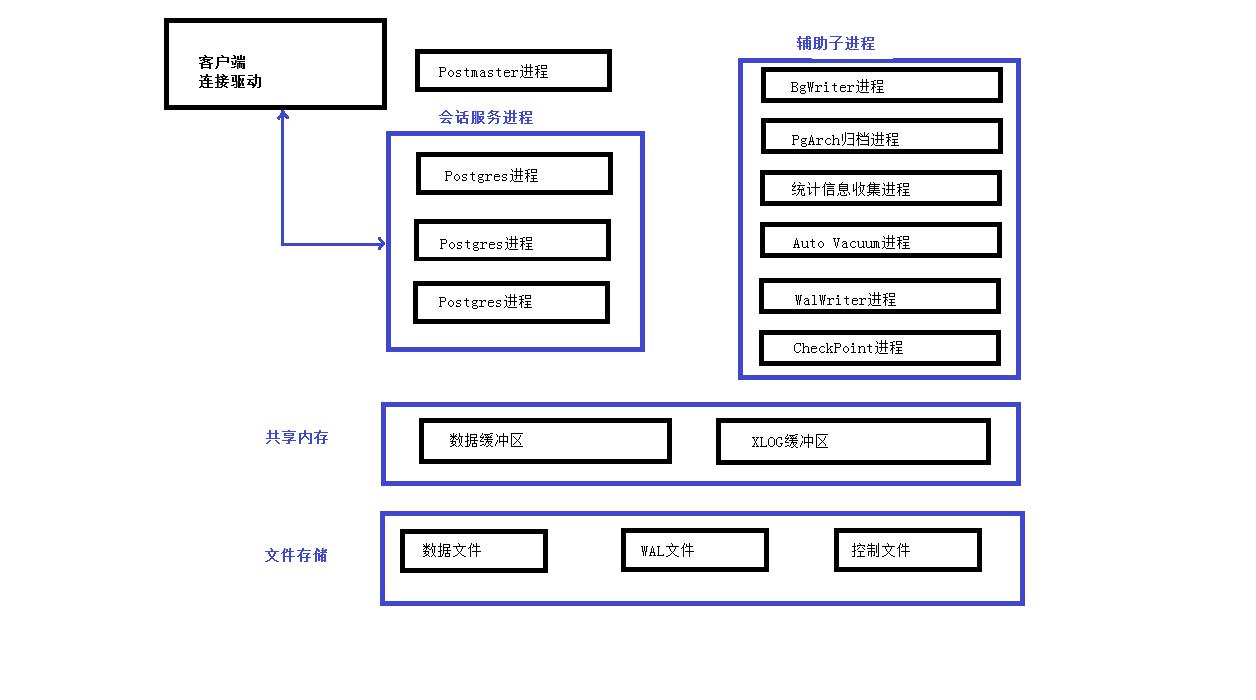
从上面的体系结构图可以看出来,PG使用经典的C/S架构,进程架构。在服务器端有主进程、服务进程、子进程、共享内存以及文件存储几大部分,下面着重讲述服务器端的进程部分:
1. Postmaster主进程和服务进程
当PG数据库启动时,首先会启动Postmaster主进程。这个进程是PG数据库的总控制进程,负责启动和关闭数据库实例。实际上Postmaster进程是一个指向postgres命令的链接,如下:
[postgres@drz ~]$ ll /opt/postgresql/bin/postmaster
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 postgres dba 8 Aug 7 23:33 /opt/postgresql/bin/postmaster -> postgres
当用户和PG数据库建立连接时,要先与Postmaster进程建立连接,此时客户端进程会发送身份验证消息给Postmaster主进程,Postmaster主进程根据消息进行身份验证,验证通过后,Postmaster主进程会fork出一个会话服务进程为这个用户连接服务。可以通过pg_stat_activity表来查看服务进程的pid,如下:
test=# select pid,usename,client_addr,client_port from pg_stat_activity;
pid | usename | client_addr | client_port
-------+----------+-------------+-------------
26402 | postgres | | -1
(1 row)
2. BgWriter(后台写)进程
BgWriter进程是把共享内存中的脏页写到磁盘上的进程。它的作用有两个:一是定期把脏数据从内存缓冲区刷出到磁盘中,减少查询时的阻塞;二是PG在定期作检查点时需要把所有脏页写出到磁盘,通过BgWriter预先写出一些脏页,可以减少设置检查点(CheckPoint,数据库恢复技术的一种)时要进行的IO操作,使系统的IO负载趋向平稳。BgWriter是PostgreSQL 8.0以后新加的特性,它的机制可以通过postgresql.conf文件中以"bgwriter_"开头配置参数来控制:
# - Background Writer -
#bgwriter_delay = 200ms # 10-10000ms between rounds
#bgwriter_lru_maxpages = 100 # 0-1000 max buffers written/round
#bgwriter_lru_multiplier = 2.0 # 0-10.0 multiplier on buffers scanned/round
#bgwriter_flush_after = 512kB # measured in pages, 0 disables
bgwriter_delay:
backgroud writer进程连续两次flush数据之间的时间的间隔。默认值是200,单位是毫秒。
bgwriter_lru_maxpages:
backgroud writer进程每次写的最多数据量,默认值是100,单位buffers。如果脏数据量小于该数值时,写操作全部由backgroud writer进程完成;反之,大于该值时,大于的部分将有server process进程完成。设置该值为0时表示禁用backgroud writer写进程,完全有server process来完成;配置为-1时表示所有脏数据都由backgroud writer来完成。(这里不包括checkpoint操作)
bgwriter_lru_multiplier:
这个参数表示每次往磁盘写数据块的数量,当然该值必须小于bgwriter_lru_maxpages。设置太小时需要写入的脏数据量大于每次写入的数据量,这样剩余需要写入磁盘的工作需要server process进程来完成,将会降低性能;值配置太大说明写入的脏数据量多于当时所需buffer的数量,方便了后面再次申请buffer工作,同时可能出现IO的浪费。该参数的默认值是2.0。
bgwriter的最大数据量计算方式:
1000/bgwriter_delay*bgwriter_lru_maxpages*8K=最大数据量
bgwriter_flush_after:
数据页大小达到bgwriter_flush_after时触发BgWriter,默认是512KB。
3. PgArch(归档)进程
类似于Oracle数据库的ARCH归档进程,不同的是ARCH是吧redo log进行归档,PgArch是把WAL日志进行归档。再深入点,WAL日志会被循环使用,也就是说,过去的WAL日志会被新产生的日志覆盖,PgArch进程就是为了在覆盖前把WAL日志备份出来。归档日志的作用是为了数据库能够使用全量备份和备份后产生的归档日志,从而让数据库回到过去的任一时间点。PG从8.X版本开始提供的PITR(Point-In-Time-Recovery)技术,就是运用的归档日志。
PgArch进程通过postgresql.conf文件中的如下参数进行配置:
# - Archiving -
#archive_mode = off # enables archiving; off, on, or always
# (change requires restart)
#archive_command = \'\' # command to use to archive a logfile segment
# placeholders: %p = path of file to archive
# %f = file name only
# e.g. \'test ! -f /mnt/server/archivedir/%f && cp %p /mnt/server/archivedir/%f\'
#archive_timeout = 0 # force a logfile segment switch after this
# number of seconds; 0 disables
archive_mode:
表示是否进行归档操作,可选择为off(关闭)、on(启动)和always(总是开启),默认值为off(关闭)。
archive_command:
由管理员设置的用于归档WAL日志的命令。在用于归档的命令中,预定义变量“%p”用来指代需要归档的WAL全路径文件名,“%f”表示不带路径的文件名(这里的路径都是相对于当前工作目录的路径)。每个WAL段文件归档时将调用archive_command所指定的命令。当归档命令返回0时,PostgreSQL就会认为文件被成功归档,然后就会删除或循环使用该WAL段文件。否则,如果返回一个非零值,PostgreSQL会认为文件没有被成功归档,便会周期性地重试直到成功。
archive_timeout:
表示归档周期,在超过该参数设定的时间时强制切换WAL段,默认值为0(表示禁用该功能)。
4. PgStat(统计数据收集)进程
PgStat进程是PostgreSQL数据库的统计信息收集器,用来收集数据库运行期间的统计信息,如表的增删改次数,数据块的个数,索引的变化等等。收集统计信息主要是为了让优化器做出正确的判断,选择最佳的执行计划。postgresql.conf文件中与PgStat进程相关的参数,如下:
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# RUNTIME STATISTICS
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# - Query/Index Statistics Collector -
#track_activities = on
#track_counts = on
#track_io_timing = off
#track_functions = none # none, pl, all
#track_activity_query_size = 1024 # (change requires restart)
#stats_temp_directory = \'pg_stat_tmp\'
track_activities:表示是否对会话中当前执行的命令开启统计信息收集功能,该参数只对超级用户和会话所有者可见,默认值为on(开启)。
track_counts:表示是否对数据库活动开启统计信息收集功能,由于在AutoVacuum自动清理进程中选择清理的数据库时,需要数据库的统计信息,因此该参数默认值为on。
track_io_timing:定时调用数据块I/O,默认是off,因为设置为开启状态会反复的调用数据库时间,这给数据库增加了很多开销。只有超级用户可以设置
track_functions:表示是否开启函数的调用次数和调用耗时统计。
track_activity_query_size:设置用于跟踪每一个活动会话的当前执行命令的字节数,默认值为1024,只能在数据库启动后设置。
stats_temp_directory:统计信息的临时存储路径。路径可以是相对路径或者绝对路径,参数默认为pg_stat_tmp,设置此参数可以减少数据库的物理I/O,提高性能。此参数只能在postgresql.conf文件或者服务器命令行中修改。
5. AutoVacuum(自动清理)进程
在PG数据库中,对数据进行UPDATE或者DELETE操作后,数据库不会立即删除旧版本的数据,而是标记为删除状态。这是因为PG数据库具有多版本的机制,如果这些旧版本的数据正在被另外的事务打开,那么暂时保留他们是很有必要的。当事务提交后,旧版本的数据已经没有价值了,数据库需要清理垃圾数据腾出空间,而清理工作就是AutoVacuum进程进行的。postgresql.conf文件中与AutoVacuum进程相关的参数有:
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# AUTOVACUUM PARAMETERS
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#autovacuum = on # Enable autovacuum subprocess? \'on\'
# requires track_counts to also be on.
#log_autovacuum_min_duration = -1 # -1 disables, 0 logs all actions and
# their durations, > 0 logs only
# actions running at least this number
# of milliseconds.
#autovacuum_max_workers = 3 # max number of autovacuum subprocesses
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_naptime = 1min # time between autovacuum runs
#autovacuum_vacuum_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before
# vacuum
#autovacuum_analyze_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before
# analyze
#autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of table size before vacuum
#autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of table size before analyze
#autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age = 400000000 # maximum multixact age
# before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 20ms # default vacuum cost delay for
# autovacuum, in milliseconds;
# -1 means use vacuum_cost_delay
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for
# autovacuum, -1 means use
# vacuum_cost_limit
autovacuum:是否启动系统自动清理功能,默认值为on。
log_autovacuum_min_duration:这个参数用来记录 autovacuum 的执行时间,当 autovaccum 的执行时间超过 log_autovacuum_min_duration参数设置时,则autovacuum信息记录到日志里,默认为 "-1", 表示不记录。
autovacuum_max_workers:设置系统自动清理工作进程的最大数量。
autovacuum_naptime:设置两次系统自动清理操作之间的间隔时间。
autovacuum_vacuum_threshold和autovacuum_analyze_threshold:设置当表上被更新的元组数的阈值超过这些阈值时分别需要执行vacuum和analyze。
autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor和autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor:设置表大小的缩放系数。
autovacuum_freeze_max_age:设置需要强制对数据库进行清理的XID上限值。
autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay:当autovacuum进程即将执行时,对 vacuum 执行 cost 进行评估,如果超过 autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit设置值时,则延迟,这个延迟的时间即为 autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay。如果值为 -1, 表示使用 vacuum_cost_delay 值,默认值为 20 ms。
autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit:这个值为 autovacuum 进程的评估阀值, 默认为 -1, 表示使用 "vacuum_cost_limit " 值,如果在执行 autovacuum 进程期间评估的cost 超过 autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit, 则 autovacuum 进程则会休眠。
6. WalWriter(预写式日志写)进程
预写式日志WAL(Write Ahead Log,也称为Xlog)的中心思想是对数据文件的修改必须是只能发生在这些修改已经记录到日志之后,也就是先写日志后写数据(日志先行)。使用这种机制可以避免数据频繁的写入磁盘,可以减少磁盘I/O。数据库在宕机重启后可以运用这些WAL日志来恢复数据库。postgresql.conf文件中与WalWriter进程相关的参数如下:
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# WRITE AHEAD LOG
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# - Settings -
#wal_level = minimal # minimal, replica, or logical
# (change requires restart)
#fsync = on # flush data to disk for crash safety
# (turning this off can cause
# unrecoverable data corruption)
#synchronous_commit = on # synchronization level;
# off, local, remote_write, remote_apply, or on
#wal_sync_method = fsync # the default is the first option
# supported by the operating system:
# open_datasync
# fdatasync (default on Linux)
# fsync
# fsync_writethrough
# open_sync
#full_page_writes = on # recover from partial page writes
#wal_compression = off # enable compression of full-page writes
#wal_log_hints = off # also do full page writes of non-critical updates
# (change requires restart)
#wal_buffers = -1 # min 32kB, -1 sets based on shared_buffers
# (change requires restart)
#wal_writer_delay = 200ms # 1-10000 milliseconds
#wal_writer_flush_after = 1MB # measured in pages, 0 disables
#commit_delay = 0 # range 0-100000, in microseconds
#commit_siblings = 5 # range 1-1000
wal_level:控制wal存储的级别。wal_level决定有多少信息被写入到WAL中。 默认值是最小的(minimal),其中只写入从崩溃或立即关机中恢复的所需信息。replica 增加 wal 归档信息 同时包括 只读服务器需要的信息。(9.6 中新增,将之前版本的 archive 和 hot_standby 合并)
logical 主要用于logical decoding 场景
fsync:该参数直接控制日志是否先写入磁盘。默认值是ON(先写入),表示更新数据写入磁盘时系统必须等待WAL的写入完成。可以配置该参数为OFF,表示更新数据写入磁盘完全不用等待WAL的写入完成。
synchronous_commit:参数配置是否等待WAL完成后才返回给用户事务的状态信息。默认值是ON,表明必须等待WAL完成后才返回事务状态信息;配置成OFF能够更快地反馈回事务状态。
wal_sync_method:WAL写入磁盘的控制方式,默认值是fsync,可选用值包括open_datasync、fdatasync、fsync_writethrough、fsync、open_sync。open_datasync和open_sync分别表示在打开WAL文件时使用O_DSYNC和O_SYNC标志;fdatasync和fsync分别表示在每次提交时调用fdatasync和fsync函数进行数据写入,两个函数都是把操作系统的磁盘缓存写回磁盘,但前者只写入文件的数据部分,而后者还会同步更新文件的属性;fsync_writethrough表示在每次提交并写回磁盘会保证操作系统磁盘缓存和内存中的内容一致。
full_page_writes:表明是否将整个page写入WAL。
wal_buffers:用于存放WAL数据的内存空间大小,系统默认值是64K,该参数还受wal_writer_delay、commit_delay两个参数的影响。
wal_writer_delay:WalWriter进程的写间隔时间,默认值是200毫秒,如果时间过长可能造成WAL缓冲区的内存不足;时间过短将会引起WAL的不断写入,增加磁盘I/O负担。
wal_writer_flush_after:
commit_delay:表示一个已经提交的数据在WAL缓冲区中存放的时间,默认值是0毫秒,表示不用延迟;设置为非0值时事务执行commit后不会立即写入WAL中,而仍存放在WAL缓冲区中,等待WalWriter进程周期性地写入磁盘。
commit_siblings:表示当一个事务发出提交请求时,如果数据库中正在执行的事务数量大于commit_siblings值,则该事务将等待一段时间(commit_delay的值);否则该事务则直接写入WAL。系统默认值是5,该参数还决定了commit_delay的有效性。
wal_writer_flush_after:当脏数据超过阈值时,会被刷出到磁盘。
7. CheckPoint(检查点)进程
检查点是系统设置的事务序列点,设置检查点保证检查点前的日志信息刷到磁盘中。postgresql.conf文件中与之相关的参数有:
# - Checkpoints -
#checkpoint_timeout = 5min # range 30s-1d
#max_wal_size = 1GB
#min_wal_size = 80MB
#checkpoint_completion_target = 0.5 # checkpoint target duration, 0.0 - 1.0
#checkpoint_flush_after = 256kB # measured in pages, 0 disables
#checkpoint_warning = 30s # 0 disables
The End!
2017-08-31
以上是关于PostgreSQL服务器启动及关闭方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章