Prometheus简介(基于Kubernetes)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Prometheus简介(基于Kubernetes)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
全栈工程师开发手册 (作者:栾鹏)
#Prometheus简介(基于Kubernetes)
本文中不包含Alertmanager和远程存储的内容,下次有时间在补充!!!
##1、Prometheus简介
Prometheus是一个开源的系统监控工具。根据配置的任务(job)以http/s周期性的收刮(scrape/pull)指定目标(target)上的指标(metric)。目标(target)可以以静态方式或者自动发现方式指定。Prometheus将收刮(scrape)的指标(metric)保存在本地或者远程存储上。
Prometheus以pull方式来收集指标。对比push方式,pull可以集中配置、针对不同的视角搭建不同的监控系统;
Prometheus于2016年加入CNCF,是继kubernetes之后,第二个加入CNCF的开源项目!
###1.1、体系结构
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PkD9sCDA-1650281647372)(https://prometheus.io/assets/architecture.svg)]
- Prometheus Server:核心组件,负责收刮和存储时序数据(time series data),并且提供查询接口;
- Jobs/Exporters:客户端,监控并采集指标,对外暴露HTTP服务(/metrics);目前已经有很多的软件原生就支持Prometjeus,提供/metrics,可以直接使用;对于像操作系统已经不提供/metrics的应用,可以使用现有的exporters或者开发自己的exporters来提供/metrics服务;
- Pushgateway:针对push系统设计,Short-lived jobs定时将指标push到Pushgateway,再由Prometheus Server从Pushgateway上pull;
- Alertmanager:报警组件,根据实现配置的规则(rule)进行响应,例如发送邮件;
- Web UI:Prometheus内置一个简单的Web控制台,可以查询指标,查看配置信息或者Service Discovery等,实际工作中,查看指标或者创建仪表盘通常使用Grafana,Prometheus作为Grafana的数据源;
###1.2、数据结构
Prometheus按照时间序列存储指标,每一个指标都由Notation + Samples组成:
- Notation:通常有指标名称与一组label组成:
<metric name><label name>=<label value>, ...
- Samples:样品,通常包含一个64位的浮点值和一个毫秒级的时间戳
##2、安装部署
###2.1、环境清单
- 系统环境
root@master:~# uname -a
Linux master 4.4.0-62-generic #83-Ubuntu SMP Wed Jan 18 14:10:15 UTC 2017 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
root@master:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master Ready master 11d v1.9.0+coreos.0 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS 4.4.0-62-generic docker://17.12.0-ce
node1 Ready <none> 11d v1.9.0+coreos.0 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS 4.4.0-62-generic docker://17.12.0-ce
node2 Ready <none> 11d v1.9.0+coreos.0 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS 4.4.0-62-generic docker://17.12.0-ce
node3 Ready <none> 11d v1.9.0+coreos.0 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS 4.4.0-62-generic docker://17.12.0-ce
root@master:~# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
kube-system calico-node-64btj 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.213 node3
kube-system calico-node-8wqtc 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.211 node1
kube-system calico-node-hrmql 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.210 master
kube-system calico-node-wvgtc 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.212 node2
kube-system kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.210 master
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.210 master
kube-system kube-dns-7d9c4d7876-wxss9 3/3 Running 0 11d 10.233.75.2 node2
kube-system kube-dns-7d9c4d7876-xbxbg 3/3 Running 0 11d 10.233.102.129 node1
kube-system kube-proxy-gprzq 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.211 node1
kube-system kube-proxy-k9gpk 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.213 node3
kube-system kube-proxy-kwl5c 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.212 node2
kube-system kube-proxy-plxpc 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.210 master
kube-system kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.210 master
kube-system kube-state-metrics-868cf44b5f-g8qfj 2/2 Running 0 6d 10.233.102.157 node1
kube-system kubedns-autoscaler-564b455d77-7rm9g 1/1 Running 0 11d 10.233.75.1 node2
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard-767994d8b8-wmzs7 1/1 Running 0 11d 10.233.75.3 node2
kube-system nginx-proxy-node1 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.211 node1
kube-system nginx-proxy-node2 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.212 node2
kube-system nginx-proxy-node3 1/1 Running 0 11d 192.168.115.213 node3
kube-system tiller-deploy-f9b69765d-lvw8k 1/1 Running 0 11d 10.233.71.5 node3
root@master:~# showmount -e
Export list for master:
/nfs *
- 创建namespace
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# cat namespace.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ns-monitor
labels:
name: ns-monitor
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl apply -f namespace.yml
###2.2、部署node-exporter
- node-exporter.yml文件内容
---
kind: DaemonSet
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
metadata:
labels:
app: node-exporter
name: node-exporter
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: node-exporter
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: node-exporter
spec:
containers:
- name: node-exporter
image: 192.168.101.88:5000/prom/node-exporter:v0.15.2
ports:
- containerPort: 9100
protocol: TCP
hostNetwork: true
hostPID: true
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
app: node-exporter
name: node-exporter-service
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
ports:
- port: 9100
targetPort: 9100
selector:
app: node-exporter
clusterIP: None
- 部署node-exporter
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl apply -f node-exporter.yml
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl get pods -n ns-monitor -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
node-exporter-br7wz 1/1 Running 0 3h 192.168.115.210 master
node-exporter-jzc6f 1/1 Running 0 3h 192.168.115.212 node2
node-exporter-t9s2f 1/1 Running 0 3h 192.168.115.213 node3
node-exporter-trh52 1/1 Running 0 3h 192.168.115.211 node1
Node-exporter用于采集kubernetes集群中各个节点的物理指标,比如:Memory、CPU等。可以直接在每个物理节点是直接安装,这里我们使用DaemonSet部署到每个节点上,使用
hostNetwork: true 和 hostPID: true 使其获得Node的物理指标信息;
配置tolerations使其在master节点也启动一个pod,我的集群默认情况下,master不参与负载;
- 查看node-exporter指标信息

使用浏览器访问任意节点的9100端口
###2.3、部署Prometheus
- prometheus.yml文件内容
---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: prometheus
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group resources:
- nodes - nodes/proxy - services - endpoints - pods verbs:
- get - watch - list - apiGroups: - extensions resources:
- ingresses verbs:
- get - watch - list - nonResourceURLs: ["/metrics"] verbs:
- get---apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: ns-monitor
labels:
app: prometheus
---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: prometheus
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount name: prometheus
namespace: ns-monitor
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: prometheus
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-conf
namespace: ns-monitor
labels:
app: prometheus
data:
prometheus.yml: |-
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs: - targets: # - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global evaluation_interval.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here its Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: prometheus
# metrics_path defaults to /metrics
# scheme defaults to http.
static_configs:
- targets: [localhost:9090] - job_name: grafana static_configs:
- targets: - grafana-service.ns-monitor:3000
- job_name: kubernetes-apiservers
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
# insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
# Keep only the default/kubernetes service endpoints for the https port. This
# will add targets for each API server which Kubernetes adds an endpoint to
# the default/kubernetes service.
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name] action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
# Scrape config for nodes (kubelet).
#
# Rather than connecting directly to the node, the scrape is proxied though the
# Kubernetes apiserver. This means it will work if Prometheus is running out of
# cluster, or cant connect to nodes for some other reason (e.g. because of
# firewalling).
- job_name: kubernetes-nodes
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics
# Scrape config for Kubelet cAdvisor.
#
# This is required for Kubernetes 1.7.3 and later, where cAdvisor metrics
# (those whose names begin with container_) have been removed from the
# Kubelet metrics endpoint. This job scrapes the cAdvisor endpoint to
# retrieve those metrics.
#
# In Kubernetes 1.7.0-1.7.2, these metrics are only exposed on the cAdvisor
# HTTP endpoint; use "replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1:4194/proxy/metrics"
# in that case (and ensure cAdvisors HTTP server hasnt been disabled with
# the --cadvisor-port=0 Kubelet flag).
#
# This job is not necessary and should be removed in Kubernetes 1.6 and
# earlier versions, or it will cause the metrics to be scraped twice.
- job_name: kubernetes-cadvisor
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
# Scrape config for service endpoints.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape services that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/scheme`: If the metrics endpoint is secured then you will need
# to set this to `https` & most likely set the `tls_config` of the scrape config.
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: If the metrics are exposed on a different port to the
# service then set this appropriately.
- job_name: kubernetes-service-endpoints
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\\d+)?;(\\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
# Example scrape config for probing services via the Blackbox Exporter.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/probe`: Only probe services that have a value of `true`
- job_name: kubernetes-services
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx]
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe] action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target
- target_label: __address__ replacement: blackbox-exporter.example.com:9115
- source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: kubernetes_name
# Example scrape config for probing ingresses via the Blackbox Exporter.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual ingress scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/probe`: Only probe services that have a value of `true`
- job_name: kubernetes-ingresses
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx]
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: ingress
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_annotation_prometheus_io_probe] action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_scheme,__address__,__meta_kubernetes_ingress_path] regex: (.+);(.+);(.+)
replacement: $1://$2$3
target_label: __param_target
- target_label: __address__ replacement: blackbox-exporter.example.com:9115
- source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_ingress_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_ingress_name] target_label: kubernetes_name
# Example scrape config for pods
#
# The relabeling allows the actual pod scrape endpoint to be configured via the
# following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape pods that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: Scrape the pod on the indicated port instead of the
# pods declared ports (default is a port-free target if none are declared).
- job_name: kubernetes-pods
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\\d+)?;(\\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
---apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-rules
namespace: ns-monitor
labels:
app: prometheus
data:
cpu-usage.rule: |
groups:
- name: NodeCPUUsage rules:
- alert: NodeCPUUsage expr: (100 - (avg by (instance) (irate(node_cpuname="node-exporter",mode="idle"[5m])) * 100)) > 75
for: 2m
labels:
severity: "page"
annotations:
summary: "$labels.instance: High CPU usage detected"
description: "$labels.instance: CPU usage is above 75% (current value is: $value )"
---apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: "prometheus-data-pv"
labels:
name: prometheus-data-pv
release: stable
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
nfs:
path: /nfs/prometheus/data
server: 192.168.115.210
---apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: prometheus-data-pvc
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
selector:
matchLabels:
name: prometheus-data-pv
release: stable
---kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
name: prometheus
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
spec:
serviceAccountName: prometheus
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
containers:
- name: prometheus image: 192.168.101.88:5000/prom/prometheus:v2.2.1
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /prometheus name: prometheus-data-volume
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml name: prometheus-conf-volume
subPath: prometheus.yml
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/rules name: prometheus-rules-volume
ports:
- containerPort: 9090 protocol: TCP
volumes:
- name: prometheus-data-volume persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: prometheus-data-pvc
- name: prometheus-conf-volume configMap:
name: prometheus-conf
- name: prometheus-rules-volume configMap:
name: prometheus-rules
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master effect: NoSchedule
---kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: true
labels:
app: prometheus
name: prometheus-service
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
ports:
- port: 9090 targetPort: 9090
selector:
app: prometheus
type: NodePort
说明: 1、在启用了RBAC的Kubernetes环境中,为Prometheus配置SA及其相关权限;
2、Prometheus默认使用本地存储,默认路径/prometheus,为其设置PVC;
3、使用CM配置Prometheus的prometheus.yml配置文件,挂载到默认路径/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml;关于/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml的配置参考:官方文档。
关于采集Kubernetes指标的配置参考:官方事例。
关于relabel_configs的配置参考:官方文档。4、以Deployment部署Prometheus实例并配置相应的SVC,使用NodePort暴露服务;
特别注意: 在挂载prometheus-data-volume的时候,默认情况下,挂载点属于root用户,其他用户没有写入的权限,而Prometheus默认的运行用户是nobody:nogroup,所以在在默认情况下直接挂载/prometheus将导致prometheus启动失败,解决办法:
serviceAccountName: prometheus
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
containers:
nobody:nogroup的UID和GID都是65534,可以通过容器内的/etc/passwd查看!
- 部署Prometheus
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl apply -f prometheus.yml
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl get pods -n ns-monitor -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
node-exporter-br7wz 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.210 master
node-exporter-jzc6f 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.212 node2
node-exporter-t9s2f 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.213 node3
node-exporter-trh52 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.211 node1
prometheus-985cd7c77-766sc 1/1 Running 0 20m 10.233.71.47 node3
- 查看Prometheus的Web UI

使用浏览器访问Prometheus SVC对应的NodePort
- 查看target

- 查看service-discovery

Prometheus会根据/etc/prometheus/promethues.yml中的relabel_configs配置对指标进行处理,比如:dropped、replace等
- Prometheus自己的指标

浏览器访问/metrics
###2.4、部署grafana
- grafana.yml文件内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: "grafana-data-pv"
labels:
name: grafana-data-pv
release: stable
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
nfs:
path: /nfs/grafana/data
server: 192.168.115.210---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: grafana-data-pvc
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
selector:
matchLabels:
name: grafana-data-pv
release: stable---
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
name: grafana
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: grafana
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
spec:
containers:
- name: grafana
image: 192.168.101.88:5000/grafana/grafana:5.0.4
env:
- name: GF_AUTH_BASIC_ENABLED
value: "true"
- name: GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED
value: "false"
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /login
port: 3000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/grafana
name: grafana-data-volume
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
volumes:
- name: grafana-data-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: grafana-data-pvc---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
name: grafana-service
namespace: ns-monitor
spec:
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: grafana
type: NodePort
说明:
1、使用NFS存储Grafana数据、启用基础权限认证、禁用匿名访问;
- 部署Grafana
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl apply -f grafana.yml
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl get pods -n ns-monitor -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
grafana-55494b59d6-6k4km 1/1 Running 0 2d 10.233.71.0 node3
node-exporter-br7wz 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.210 master
node-exporter-jzc6f 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.212 node2
node-exporter-t9s2f 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.213 node3
node-exporter-trh52 1/1 Running 0 6h 192.168.115.211 node1
prometheus-985cd7c77-766sc 1/1 Running 0 20m 10.233.71.47 node3
- 配置Grafana
- 登录Grafana,因为使用NodePort暴露服务,通过SVC查看端口,默认用户admin/admin
root@master:~/kubernetes/prometheus# kubectl get svc -n ns-monitor
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
grafana-service NodePort 10.233.13.130 <none> 3000:32712/TCP 2d
node-exporter-service ClusterIP None <none> 9100/TCP 6h
prometheus-service NodePort 10.233.57.158 <none> 9090:32014/TCP 26m

登录之后,跟随Grafana的引导完成设置
- 将prometheus配置为数据源、导入Prometheus和Grafana的Dashboard


- 导入Kubernetes的Dashboard模版,下文附下载链接


- 查看Dashboard

Dashboard中的每一个Panel可以自行编辑、保存和回滚!
如果instance下拉框显示有问题,点击右上方的设置(settings)~变量(Variables),修改$instance变量的Regex值,可以直接清空;
配置数据源、导入Dashboard、安装插件等这些操作可以配置到grafana.yml文件中,但是配置过程比较麻烦,这里先提供在界面上操作的说明,后期需要再处理。
##3、参考资料
- https://prometheus.io/docs/
- http://docs.grafana.org/
- https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/tree/release-2.2/documentation/examples
- https://github.com/giantswarm/kubernetes-prometheus
- https://github.com/zalando-incubator/kubernetes-on-aws/pull/861
- http://yunlzheng.github.io/2018/01/17/prometheus-sd-and-relabel/
##4、附件下载
- Kubernetes的Grafana监控模版:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1y7HDQCPXy9LCAzA01uzIBQ
Linux企业运维——Kubernetes(二十)Prometheus监控
Linux企业运维——Kubernetes(二十)Prometheus监控
文章目录
一、Prometheus简介
除了资源指标(如CPU、内存)以外,用户或管理员需要了解更多的指标数据,比如Kubernetes指标、容器指标、节点资源指标以及应用程序指标等等。自定义指标API允许请求任意的指标,其指标API的实现要指定相应的后端监视系统。
Prometheus是第一个开发了相应适配器的监控系统。

Prometheus是一个开源的服务监控系统和时序数据库,其提供了通用的数据模型和快捷数据采集、存储和查询接口。它的核心组件Prometheus服务器定期从静态配置的监控目标或者基于服务发现自动配置的目标中进行拉取数据,新拉取到的数据大于配置的内存缓存区时,数据就会持久化到存储设备当中。
如上图,每个被监控的主机都可以通过专用的exporter程序提供输出监控数据的接口,并等待Prometheus服务器周期性的进行数据抓取。如果存在告警规则,则抓取到数据之后会根据规则进行计算,满足告警条件则会生成告警,并发送到Alertmanager完成告警的汇总和分发。当被监控的目标有主动推送数据的需求时,可以以Pushgateway组件进行接收并临时存储数据,然后等待Prometheus服务器完成数据的采集。
二、k8s部署Prometheus
server2添加apphub仓库源
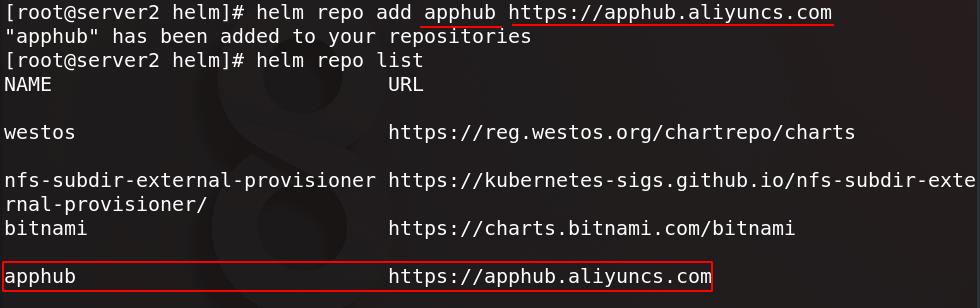
查找prometheus-operator并拉取
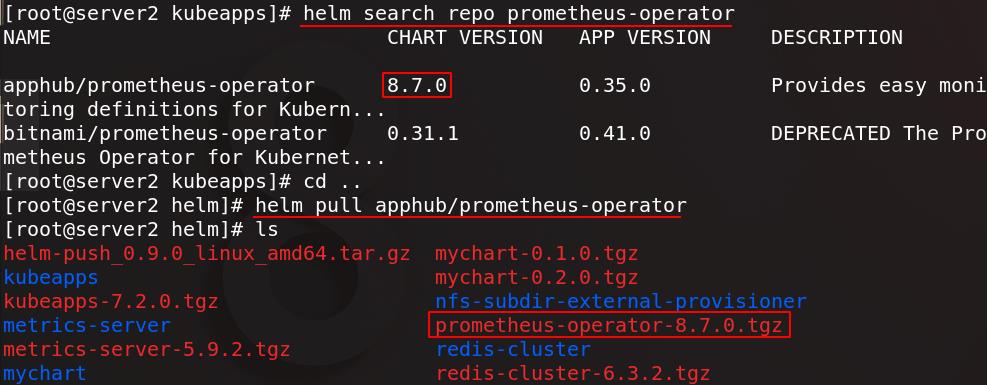
在harbor仓库新建一个项目名为kubeapps

真实主机将prometheus-operator包发送给server1

server1加载prometheus-operator镜像
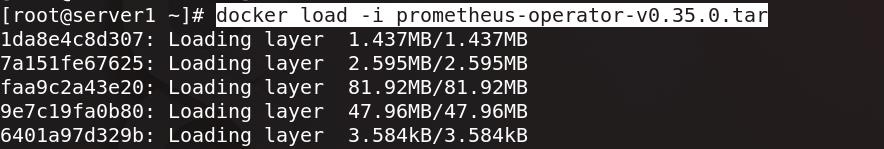
将prometheus-operator镜像上传至仓库

server2解压prometheus-operator包并进入目录,编辑values.yaml

把报警、Grafana、Prometheus三个组件的Ingress打开,将所有镜像(8个)都指向私有仓库



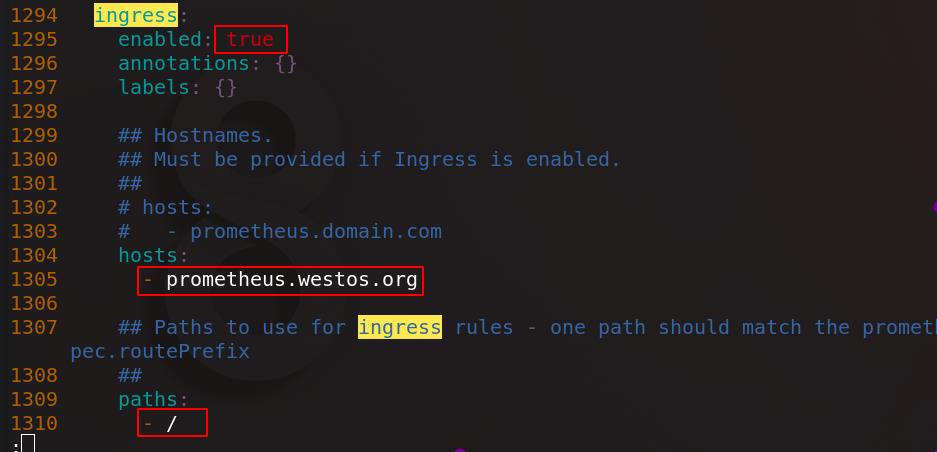
248 repository: kubeapps/quay-alertmanager
991 repository: kubeapps/ghostunnel
1008 repository: kubeapps/kube-webhook-certgen
1177 repository: kubeapps/quay-prometheus-operator
1184 repository: kubeapps/quay-configmap-reload
1190 repository: kubeapps/quay-prometheus-config-reloader
1204 repository: kubeapps/k8s-gcr-hyperkube
1417 repository: kubeapps/quay-prometheus
编辑完成后去依赖性子目录charts/中,可以看到三个组件:
- kube-state-metrics:
Prometheus提供的多项指标数据格式与k8s数据格式不兼容,还需要一个中间组件,kube-state-metrics负责从prometheus的数据格式转换为k8s集群可以识别的格式。 - prometheus-node-exporter:
安装在被监控端,负责采集多种数据。Prometheus通常去不同client端拉取数据,但有些应用数据无法拉取,这时候这些应用将数据push到Pushgateway网关,由Pushgateway网关将数据发送给server端。 - grafana:
是用来展示指标的图形化管理工具
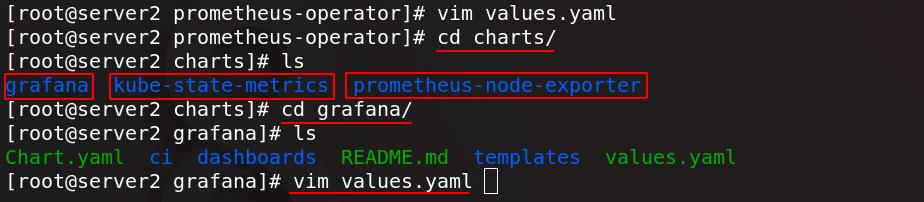
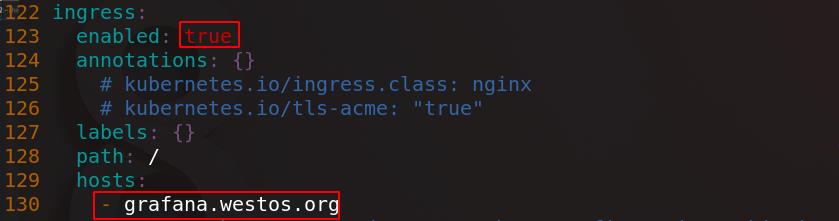
进入grafana/目录下,编辑values.yaml配置文件,打开Ingress,配置hosts,将镜像指向私有仓库
52 repository: kubeapps/grafana
65 image: "kubeapps/bats"
91 repository: kubeapps/curl
209 repository: kubeapps/busybox
432 image: kubeapps/k8s-sidecar:0.1.20
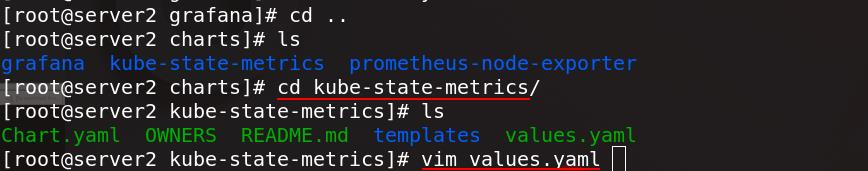
进入kube-state-metrics/目录下,编辑values.yaml配置文件
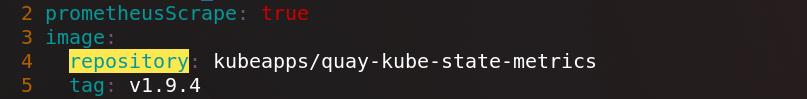
将镜像指向私有仓库
进入prometheus-node-exporter/目录下,编辑values.yaml配置文件

将镜像指向私有仓库
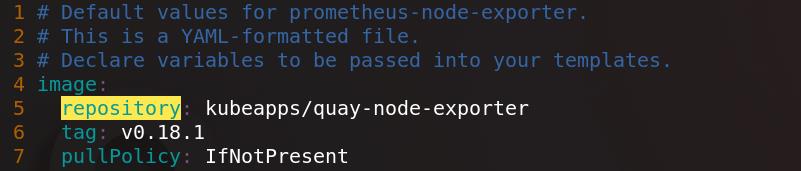
创建prometheus-operator命名空间,将prometheus-operator安装在prometheus-operator命名空间下
(注意宿主机和集群虚拟机时间要同步,因为Prometheus是以时间序列方式采集数据)
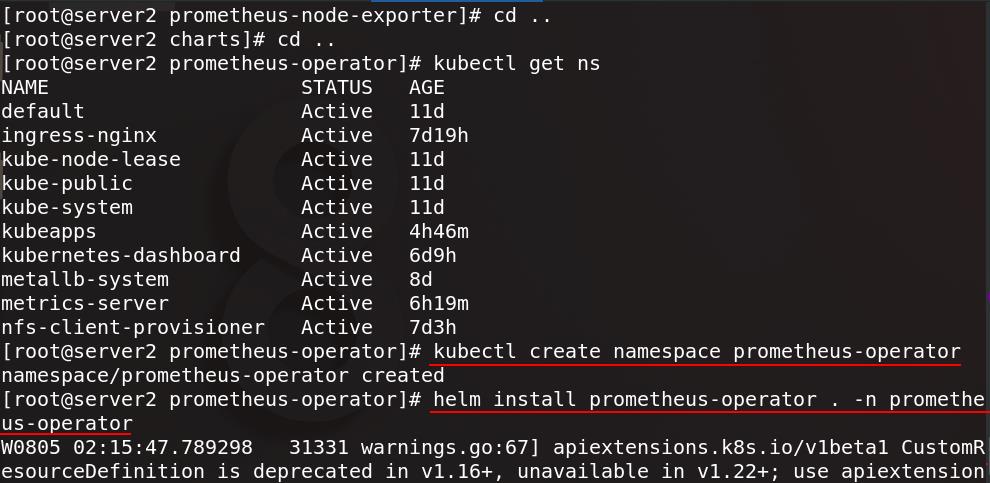
查看所有pod
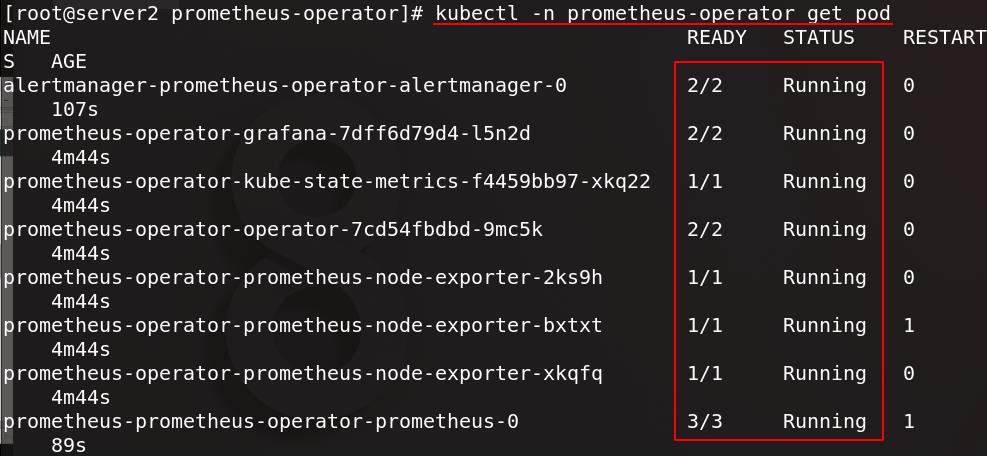
控制器也就绪
prometheus-operator-kube-state-metrics:兼容数据
查看prometheus-operator命名空间内的ingress也正常运行
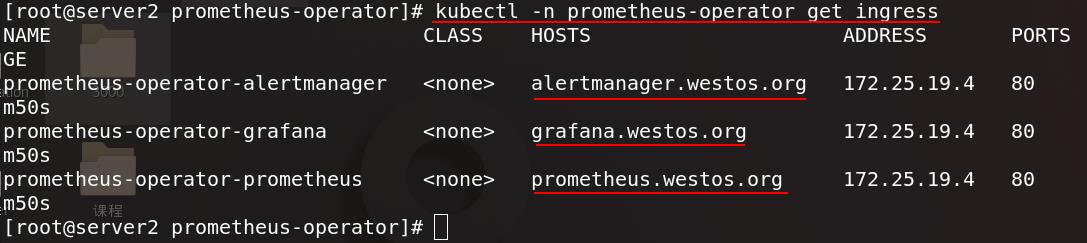
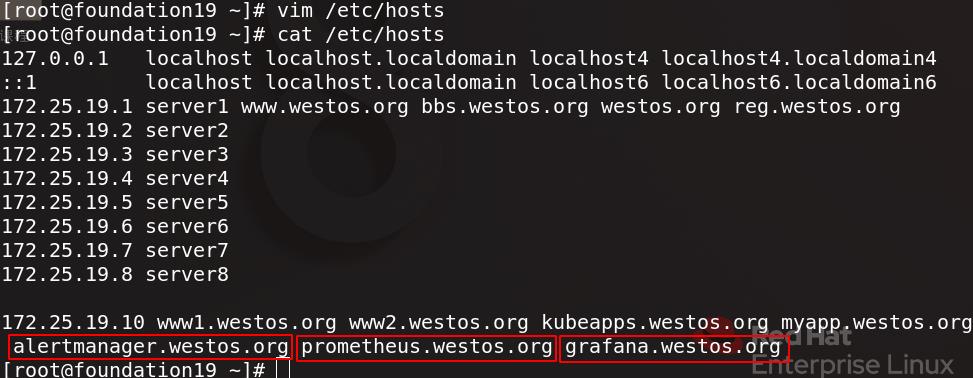
为测试访问,为真实主机添加域名解析
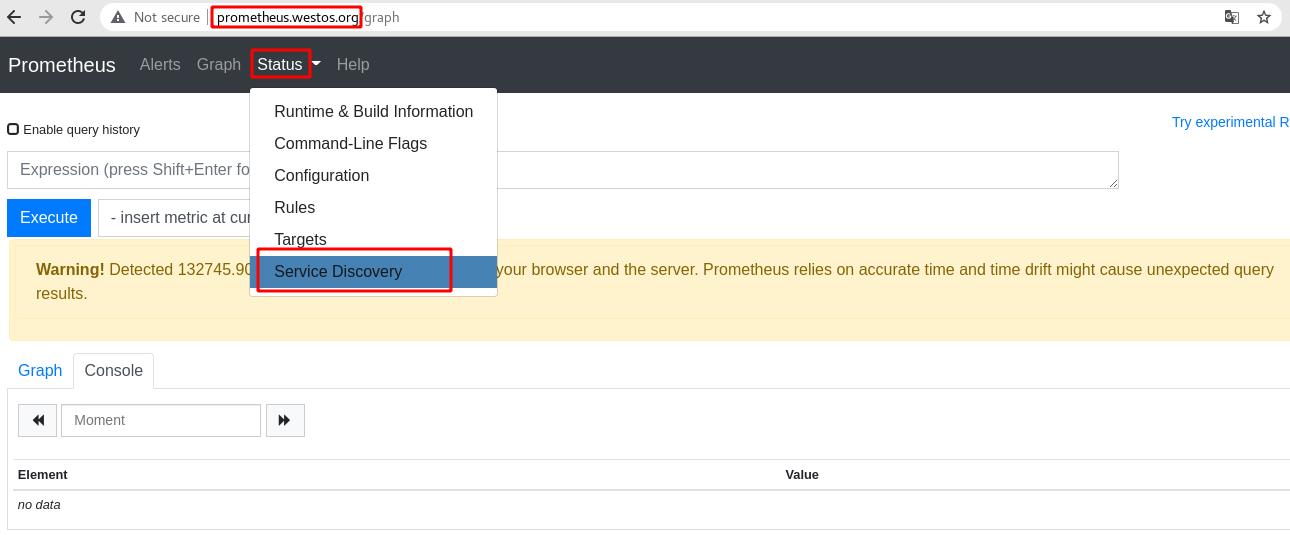
通过浏览器访问prometheus.westos.org,进入status菜单栏内的service discovery
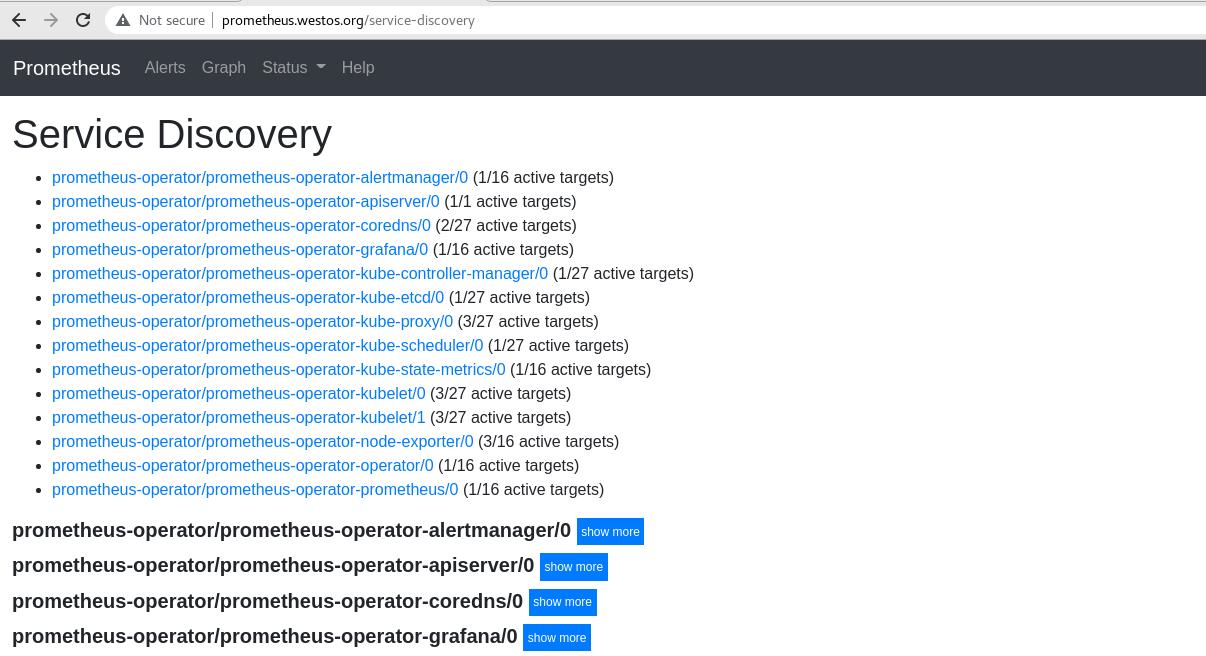
服务正常显示
访问grafana.westos.org,输入配置文件中设定好的用户名和密码
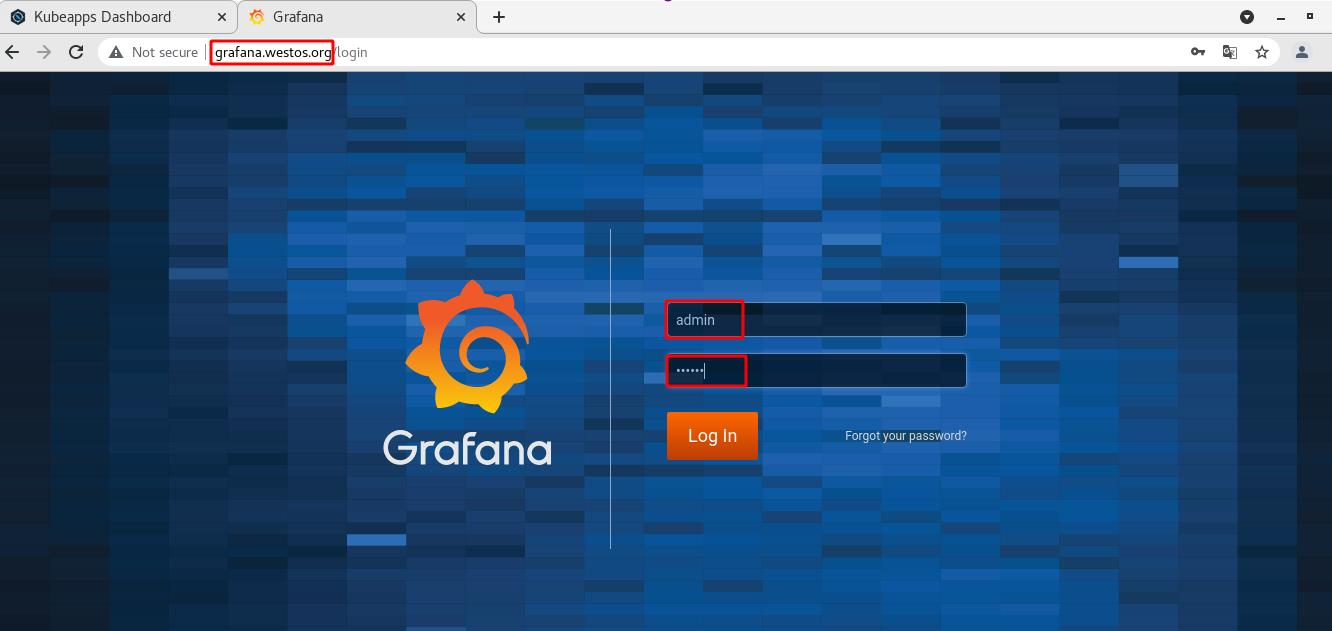
在设置中,数据源默认为prometheus
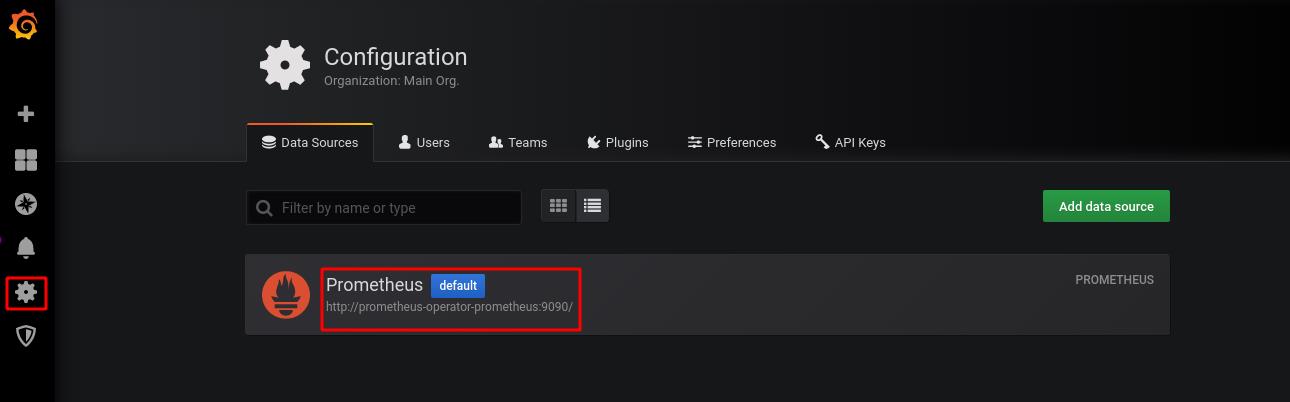
显示数据源正常工作,点击测试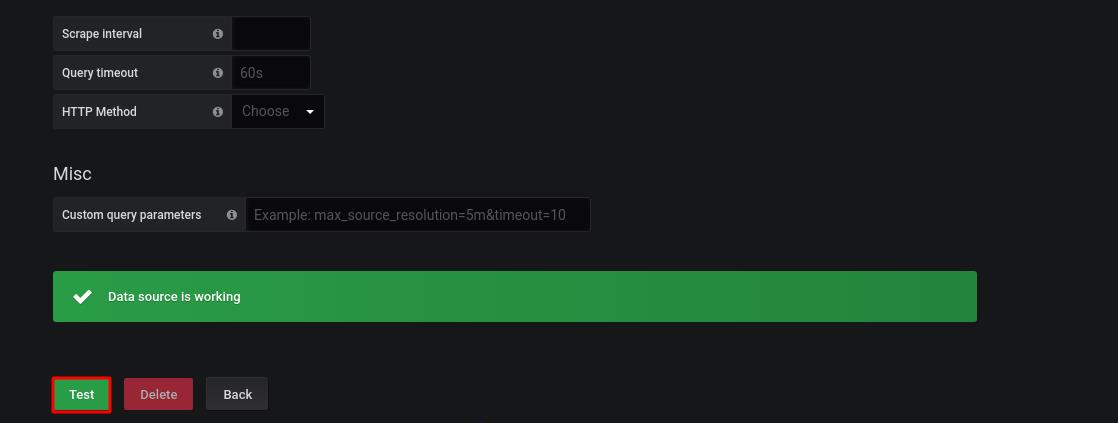
找到prometheus将其添加到监控面板
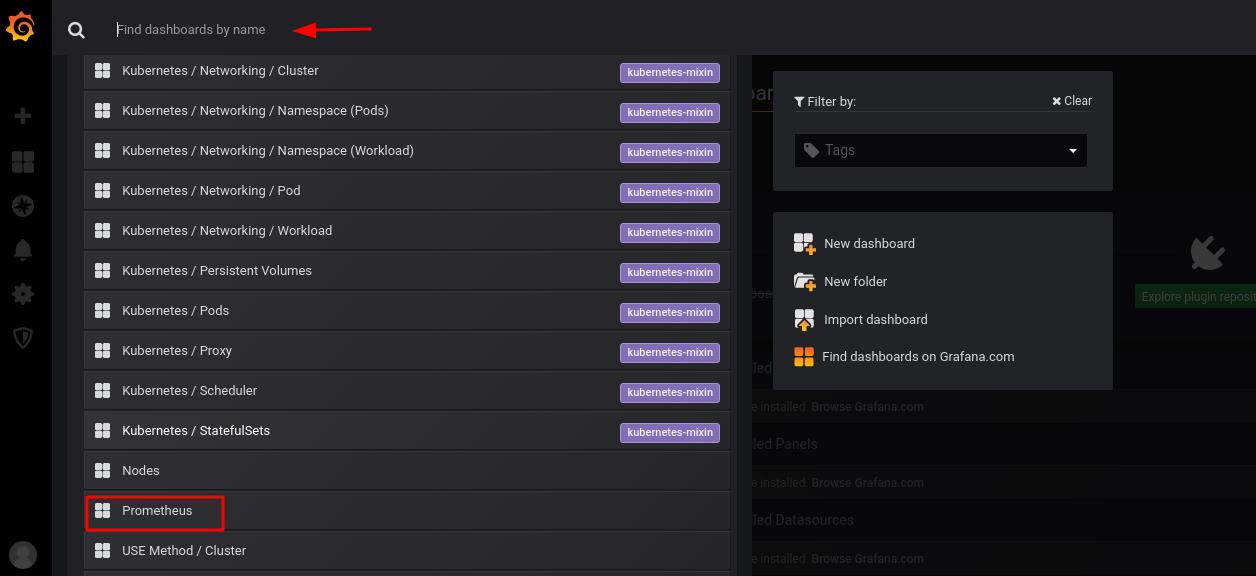
可以看到监控页面正常运行
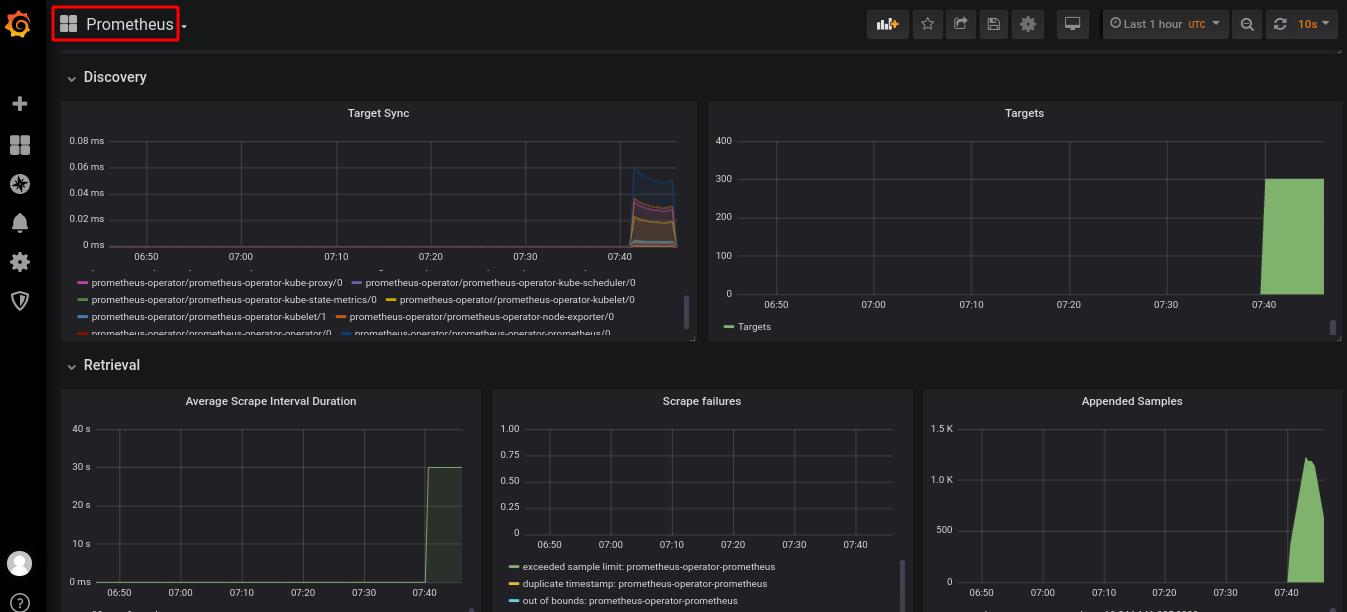
三、Prometheus监控nginx访问量
通过图形化界面直接安装nginx
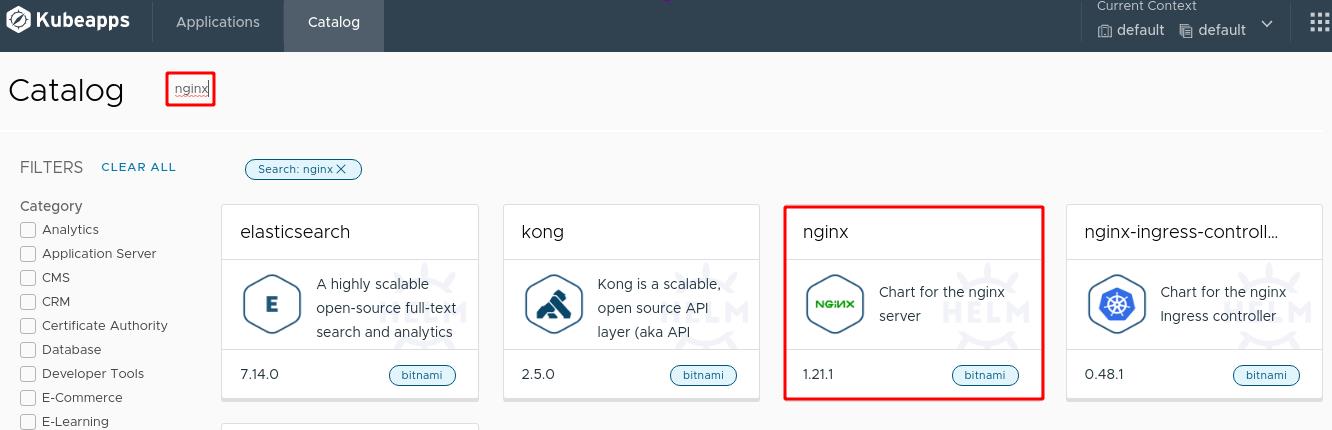
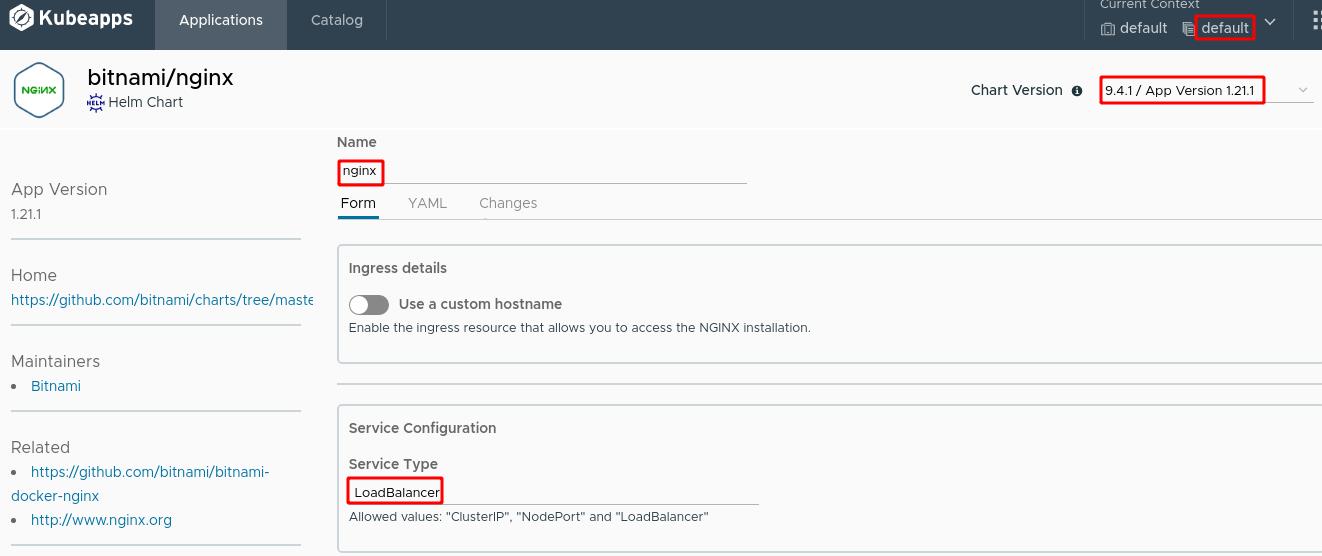
应用名称设置为nginx,使用9.4.1版本,服务类型为LoadBalancer
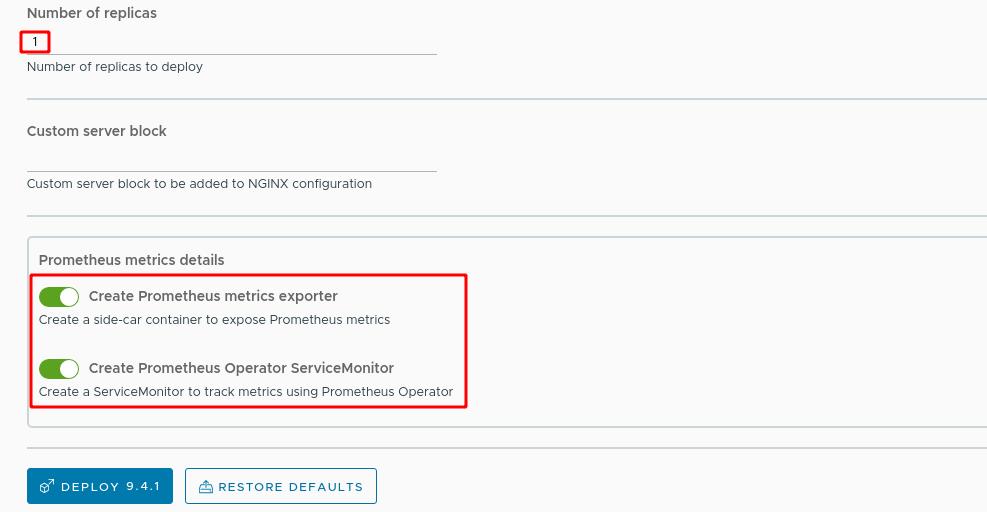
副本数量选择1个,打开Prometheus监控选项,Prometheus专门监控nginx的agent插件:nginx-exporter
修改yaml配置文件,更改镜像仓库地址
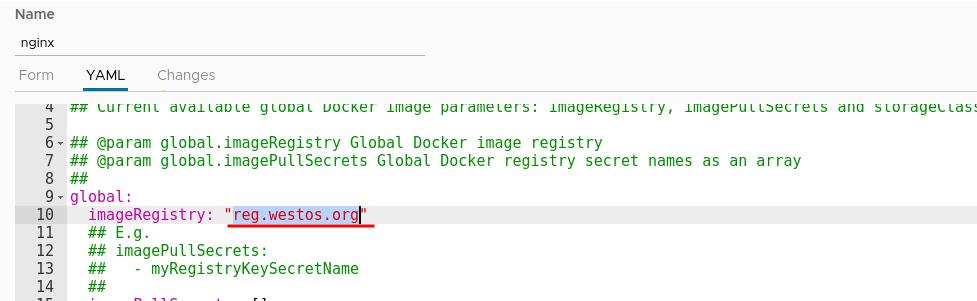
设置镜像仓库和标签
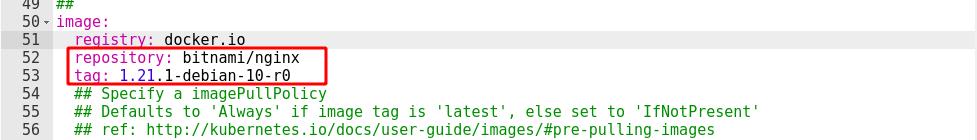
下图是我们刚指定的镜像
指定服务部署在prometheus-operator命名空间内
整体配置如下图所示
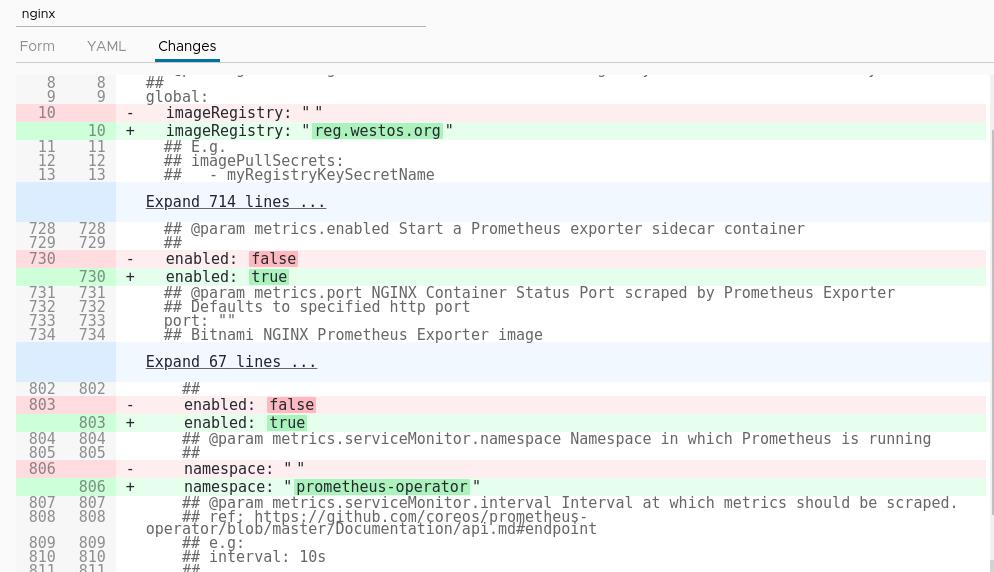
配置完成后等待镜像部署完成

通过浏览器访问上图nginx应用的URL,可以看到正常访问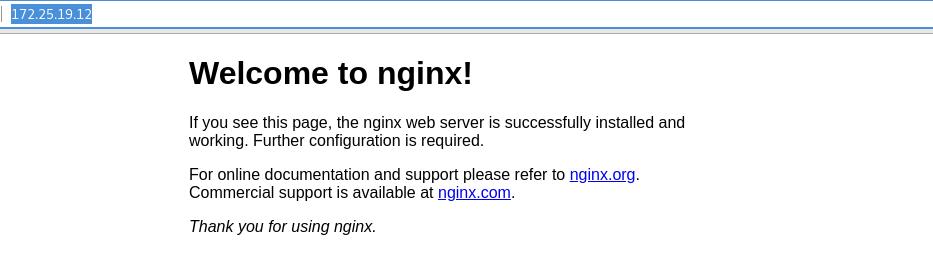
在命令行界面查看pod信息,可以看到刚创建的nginx及其服务和外部访问地址
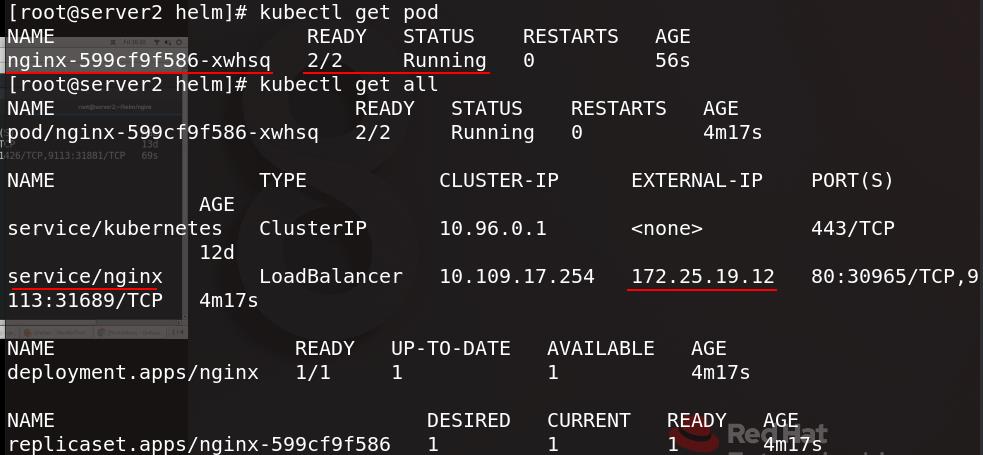
为nginx添加release=prometheus-operator这个标签
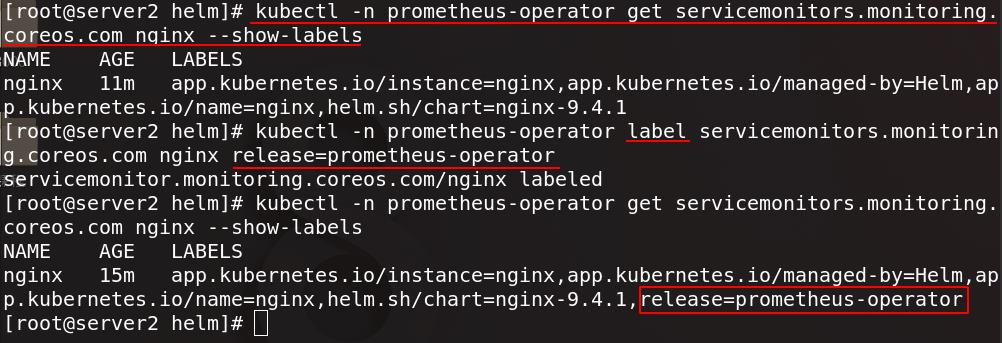
现在在图形管理界面可以看到nginx服务
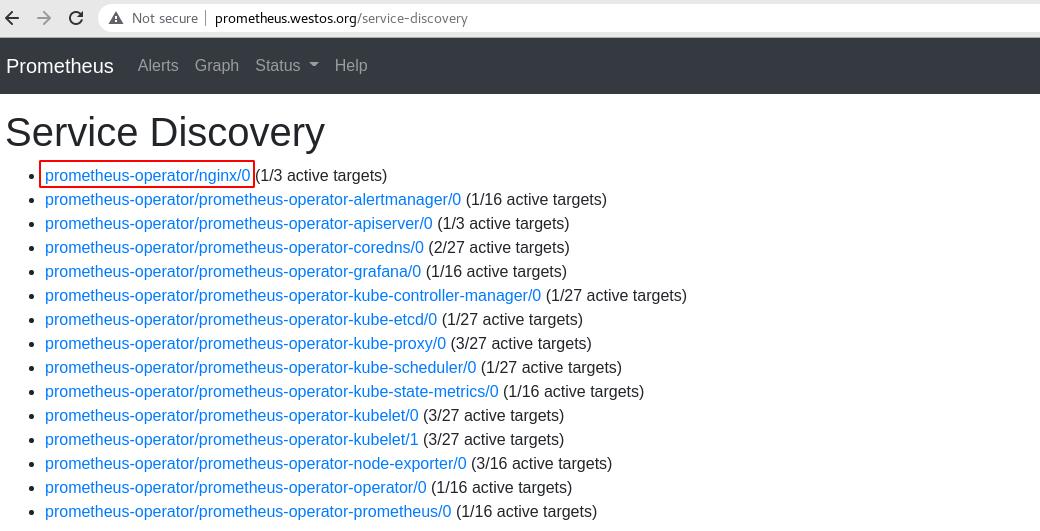
点击Graph,将访问流量统计图添加进统计页
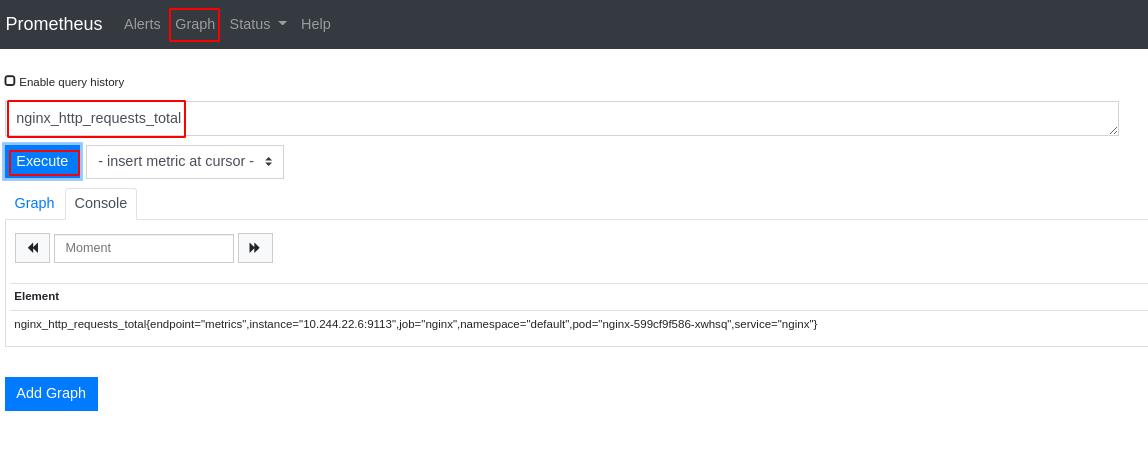
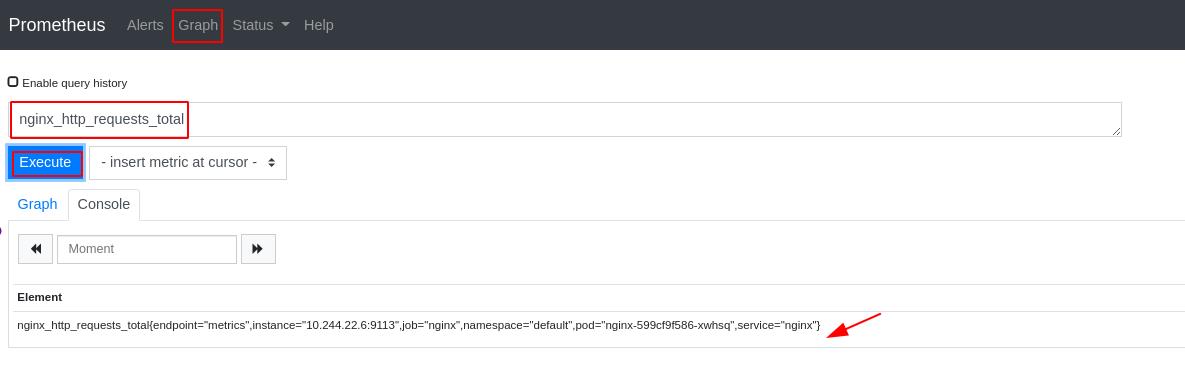
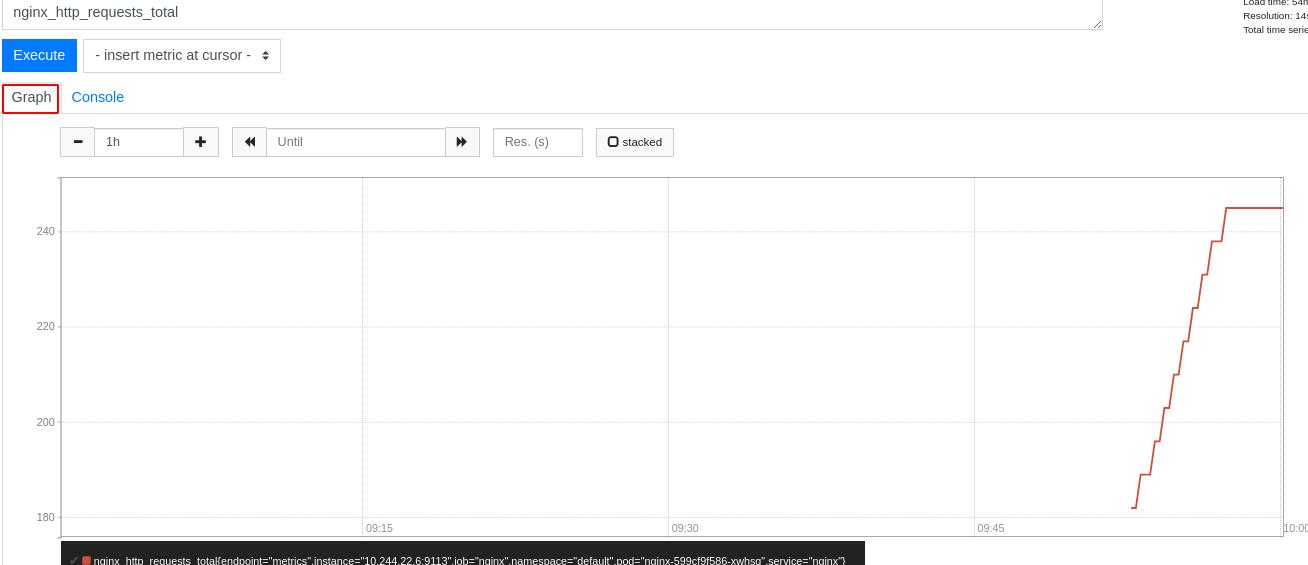
可以看到nginx访问流量效果图
四、Prometheus实现hpa动态伸缩
server2查看pod信息可以看到prometheus-operator-kube-state-metrics
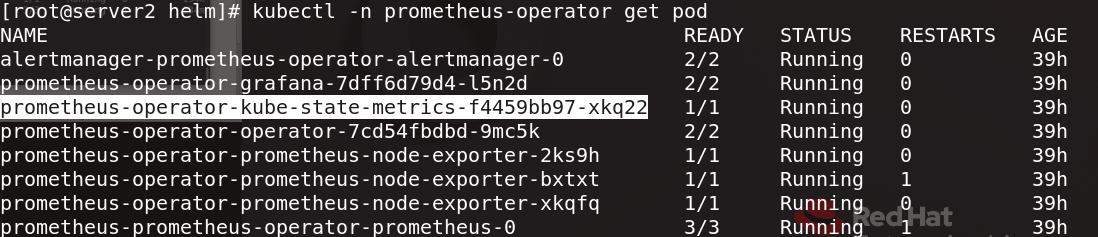
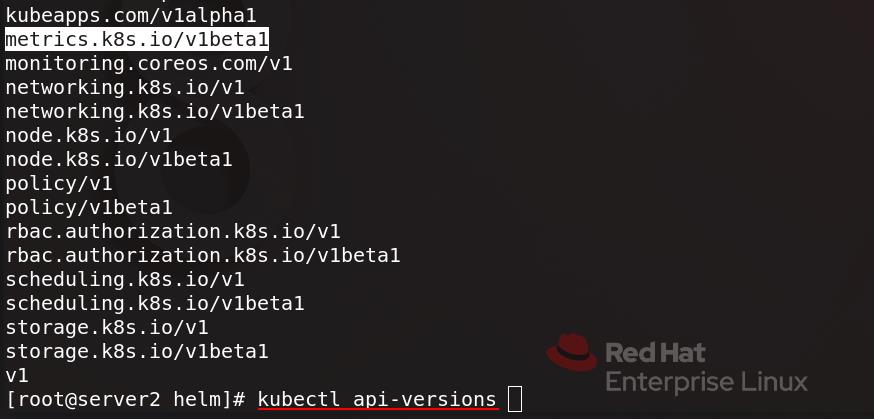
执行 kubectl api-versions 查看api group ,metrics为v1beta1版本
查找prometheus-adapter插件,拉取到本地并解压,编辑values.yaml配置文件

配置镜像地址和prometheus的服务地址
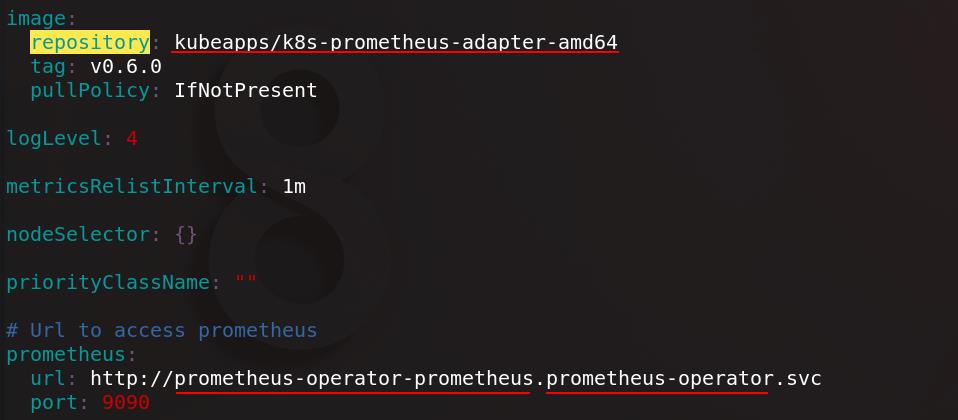
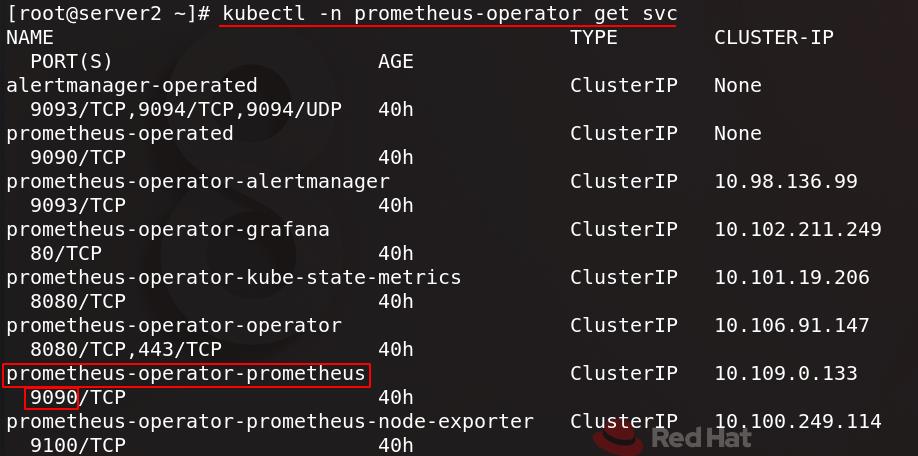
配置文件中的prometheus的服务地址可以通过下图命令查看
可以拉起一个新的容器并进入,测试是否能访问到上面prometheus的服务地址
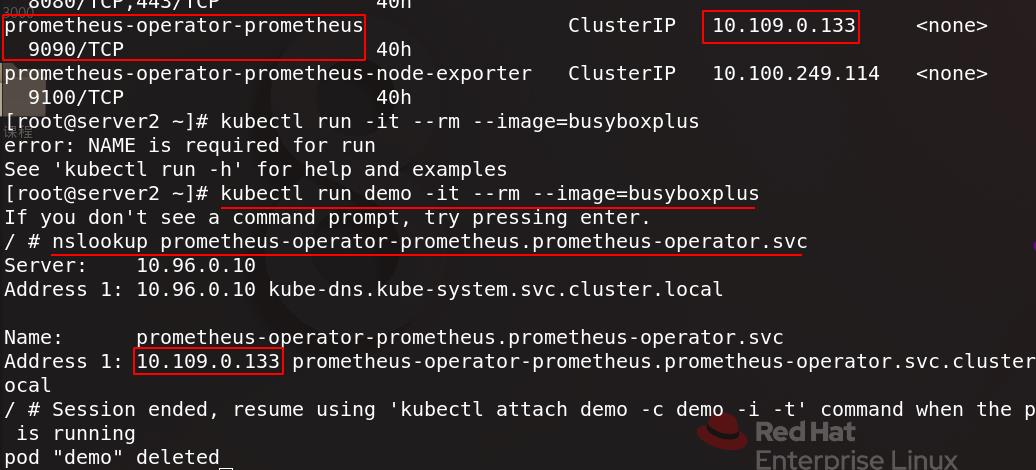
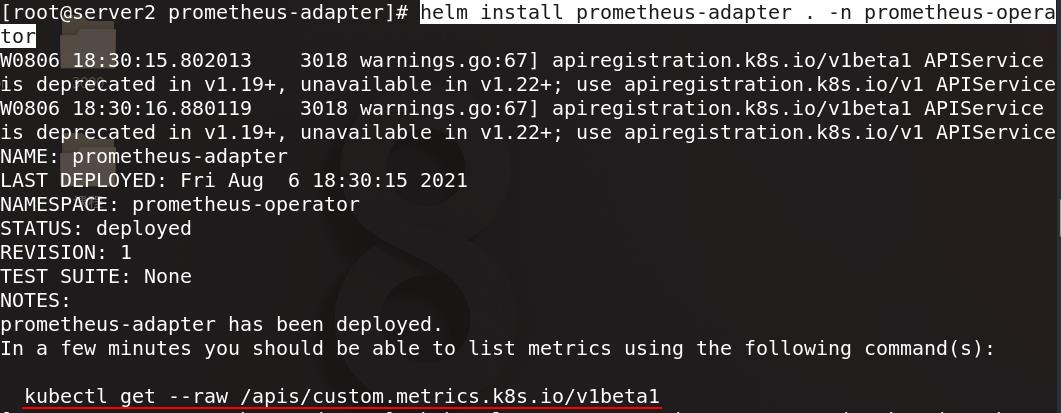
在prometheus-operator命名空间下安装prometheus-adapter,复制下图指令
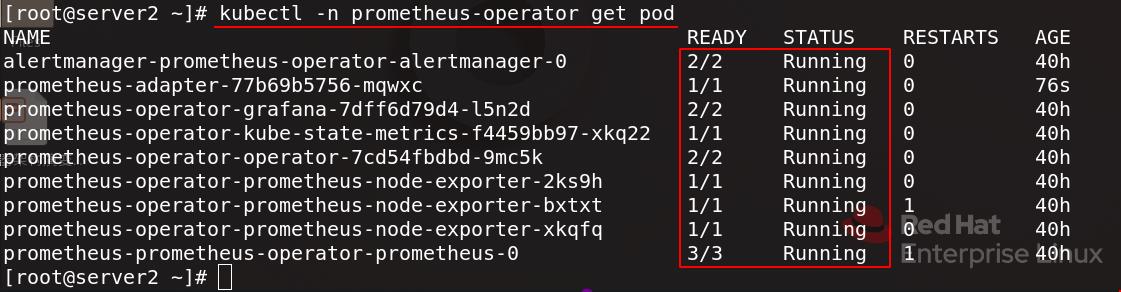
查看prometheus-operator命名空间下的pod信息,都正常运行
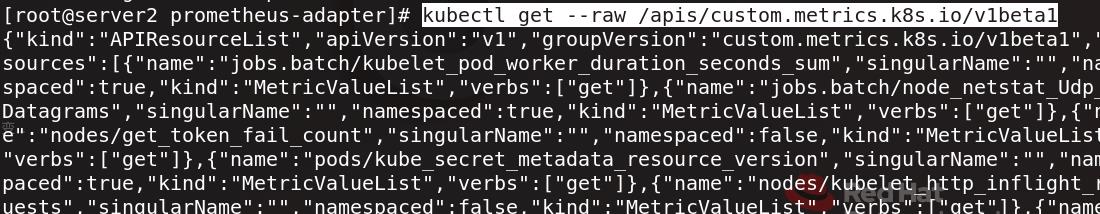
可以查看到刚才复制的指令中的api

执行刚才复制的指令
再次执行刚才复制的指令,这次指定命名空间、pod和监控指标

指定的监控指标名字就是下图红框部分
也可以编写python脚本运行指令进行参数配置
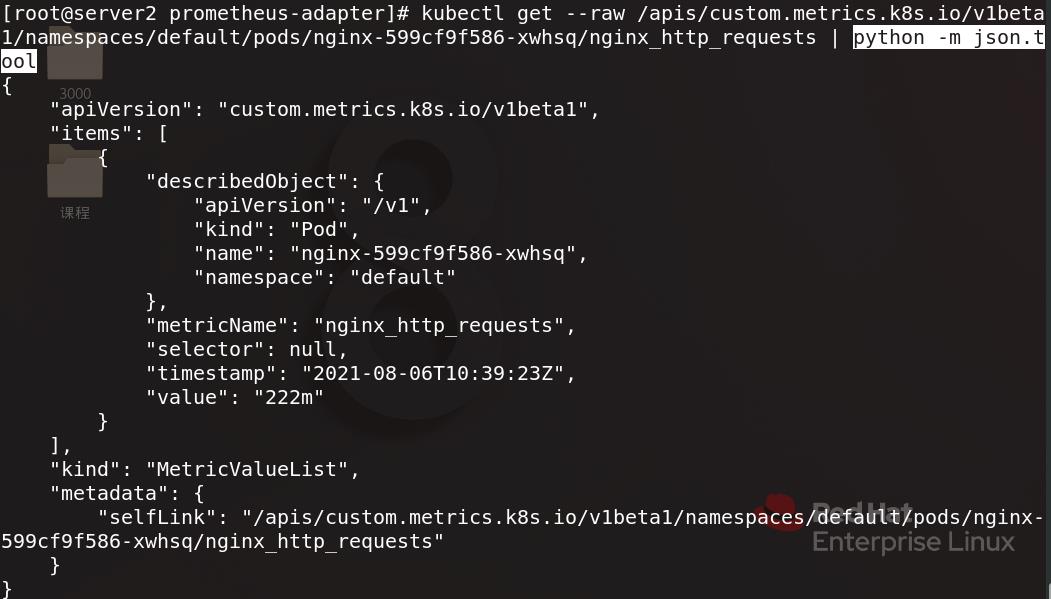
编辑hpa-nginx.yaml配置文件并应用
[root@server2 helm]# cat hpa-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: hpa-example
spec:
maxReplicas: 10 #最多伸缩到10个副本
minReplicas: 1 #最少伸缩为1个副本
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx
metrics:
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: nginx_http_requests #指定监控nginx访问流量
target:
type: AverageValue #伸缩依据是均值是否在10
averageValue: 10

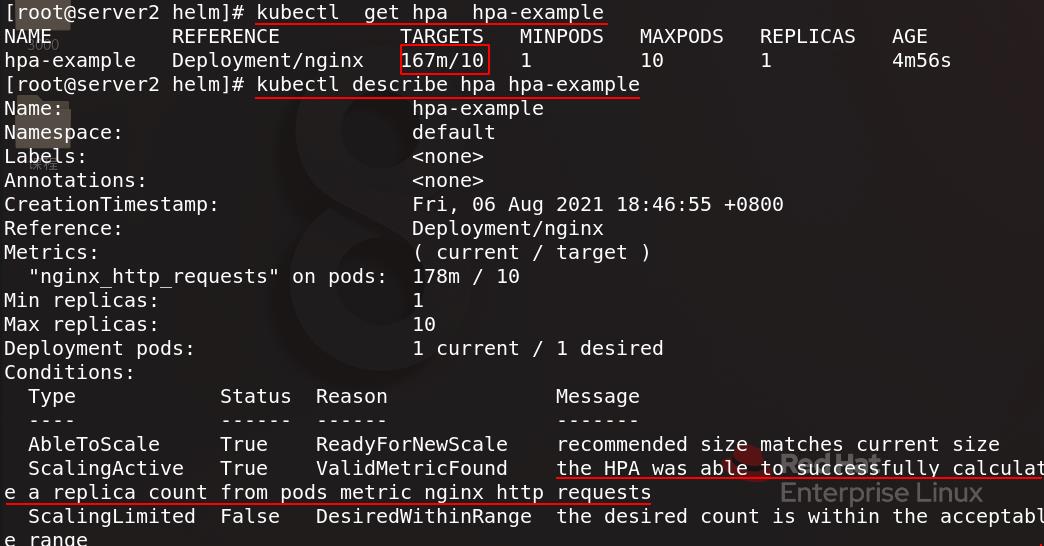
查看hpa详细信息,HPA可以根据pods的nginx访问流量度量成功计算副本计数
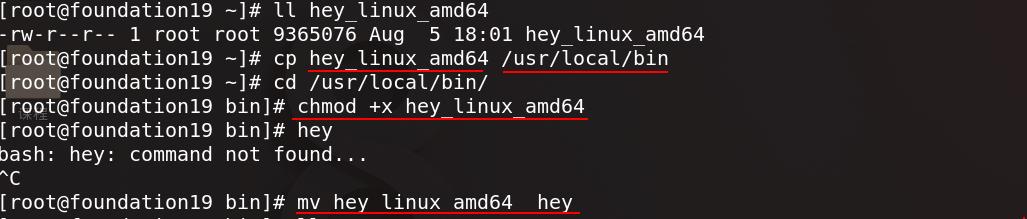
hey用来进行压力测试,真实主机把hey复制到/usr/local/bin,赋予可执行权限
命令行输入hey可以看到参数用法
真实主机运行hey进行访问测试,参数设置总共访问一万次,每秒访问五次,5个线程并发

kubectl get hpa hpa-example -w查看hpa的动态状态变化,可以随着访问压力的增大hpa开始生效并增加副本数量,逐渐扩容到3个

可以看到图形化展示
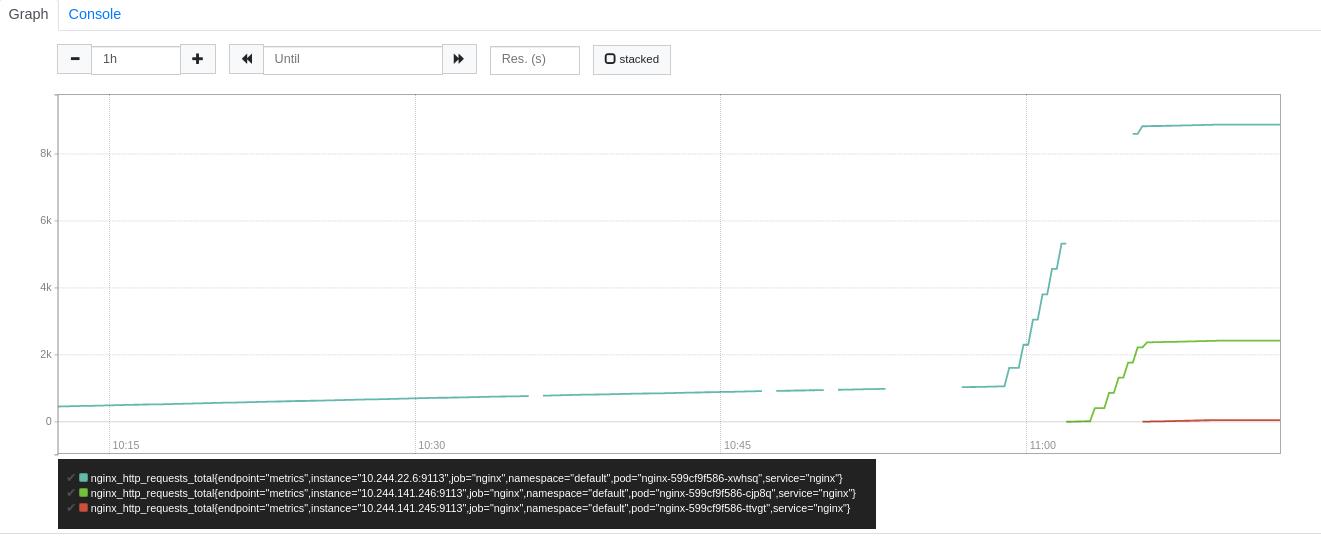
以上是关于Prometheus简介(基于Kubernetes)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章