Open Cluster Management 部署应用实践
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Open Cluster Management 部署应用实践相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

文章目录
- 简介
- 1. 搭建两个 kubernetes 集群
- 2. 配置托管集群
- 3. 部署 OCM 组件
- 4. 将托管集群加入 hub 集群
- 5. 部署测试应用
- 6. 添加应用生命周期管理插件
- 7. 注销已管理集群
简介
1. 搭建两个 kubernetes 集群
- Ubuntu 18.04 通过 Minikube 安装 Kubernetes v1.20
- Minikube v1.25.2 在 Centos 7.9 部署 Kubernetes v1.23.8
2. 配置托管集群
配置/root/.kube/config 的 context,如何配置 context 管理多集群请参考。
实现可以切换集群,这里 两个集群的context 名称分别为kubernetes-admin@cluster.local与default
$ kubectl get node --context kubernetes-admin@cluster.local
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
dbscale-control-plan01 Ready <none> 20h v1.25.6
kube-control-plan01 Ready control-plane 20h v1.25.6
kube-node01 Ready <none> 20h v1.25.6
kube-node02 Ready <none> 20h v1.25.6
kube-node03 Ready <none> 20h v1.25.6
$ kubectl get node --context default
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k3smaster Ready control-plane,master 131d v1.25.3+k3s1
3. 部署 OCM 组件
安装 clusteradm
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/open-cluster-management-io/clusteradm/main/install.sh | bash
安装 OCM,先配置环境变量,确认托管集群
export CTX_HUB_CLUSTER=kubernetes-admin@cluster.local
$ clusteradm init --wait --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
CRD successfully registered.
Registration operator is now available.
ClusterManager registration is now available.
The multicluster hub control plane has been initialized successfully!
You can now register cluster(s) to the hub control plane. Log onto those cluster(s) and run the following command:
clusteradm join --hub-token eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ik5VcVp4YXkyanFyZTllMWt2Z21UWXZwbmRvNkdkSHhnM005X3lmVTRMRjAifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiXSwiZXhwIjoxNjc4OTUwNTYzLCJpYXQiOjE2Nzg5NDY5NjMsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJvcGVuLWNsdXN0ZXItbWFuYWdlbWVudCIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJjbHVzdGVyLWJvb3RzdHJhcCIsInVpZCI6ImE5OGE4ZWE1LWVlMzYtNDUzNS05OWY5LTA0OTFmZjFhZTc1ZCJ9fSwibmJmIjoxNjc4OTQ2OTYzLCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6b3Blbi1jbHVzdGVyLW1hbmFnZW1lbnQ6Y2x1c3Rlci1ib290c3RyYXAifQ.VU_I_67dlIJ9WlMnFaJL-930OHAkm0tvYmWqzGRURYa31wOnPQMTzq-mUddNU_pvEuFBbqX__b9QGz5WEisHlGnPUcBjpyPGQihDFKaz-UciK_A03D9Rpy6VA1cE4vcDM0lr2uZv7edf09F_9LI9Oo7MajHWK0bdAF6UMkOmWHIlHVVIC9DMqSrzsyZrZf-4mv4ciyVQp3PgpZEgXfogi--_-qWWuTGZM-el5z29c3uJfPdFnxDopL3YFedWJ9dkepnasO4l1RWhwxYGTUFN5lIkKSMx-RFH8BkNfJfz8Vb4AO8HvUb9niWCRt1dn61UmLClsrjipvBCN8gtItUGjg --hub-apiserver https://10.168.110.21:6443 --wait --cluster-name <cluster_name>
Replace <cluster_name> with a cluster name of your choice. For example, cluster1.
查看托管集群部署了哪些内容
$ kubectl get ns --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME STATUS AGE
clusternet-system Active 3h37m
default Active 20h
kube-node-lease Active 20h
kube-public Active 20h
kube-system Active 20h
open-cluster-management Active 34m
open-cluster-management-agent Active 17m
open-cluster-management-agent-addon Active 17m
open-cluster-management-hub Active 31m
$ kubectl get clustermanager --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME AGE
cluster-manager 32m
$ kubectl -n open-cluster-management get pod --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-manager-79dcdf496f-c2lgx 1/1 Running 0 35m
klusterlet-6555776c99-2s84c 1/1 Running 0 19m
klusterlet-6555776c99-ksmxl 1/1 Running 0 19m
klusterlet-6555776c99-pxpgr 1/1 Running 0 19m
$ kubectl -n open-cluster-management-hub get pod --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-manager-placement-controller-6597644b5b-znhv2 1/1 Running 0 33m
cluster-manager-registration-controller-7d774d4866-mlhfm 1/1 Running 0 33m
cluster-manager-registration-webhook-f549cb5bd-j45pv 2/2 Running 0 33m
cluster-manager-work-webhook-64f95b566d-wmvhk 2/2 Running 0 33m
查看 cluster-manager 信息
kubectl get clustermanager cluster-manager -o yaml --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ClusterManager
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2023-03-16T05:57:14Z"
finalizers:
- operator.open-cluster-management.io/cluster-manager-cleanup
generation: 4
managedFields:
- apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:spec:
.:
f:deployOption:
.:
f:mode:
f:placementImagePullSpec:
f:registrationConfiguration:
.:
f:featureGates:
f:registrationImagePullSpec:
f:workImagePullSpec:
manager: clusteradm
operation: Update
time: "2023-03-16T05:57:14Z"
- apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:finalizers:
.:
v:"operator.open-cluster-management.io/cluster-manager-cleanup":
f:spec:
f:nodePlacement:
manager: Go-http-client
operation: Update
time: "2023-03-16T06:09:23Z"
- apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:status:
.:
f:conditions:
f:generations:
f:observedGeneration:
f:relatedResources:
manager: Go-http-client
operation: Update
subresource: status
time: "2023-03-16T06:09:24Z"
name: cluster-manager
resourceVersion: "68256"
uid: 0249a3ff-bc76-488d-8a8d-1960367ac8be
spec:
deployOption:
mode: Default
nodePlacement:
placementImagePullSpec: quay.io/open-cluster-management/placement:v0.10.0
registrationConfiguration:
featureGates:
- feature: DefaultClusterSet
mode: Enable
registrationImagePullSpec: quay.io/open-cluster-management/registration:v0.10.0
workImagePullSpec: quay.io/open-cluster-management/work:v0.10.0
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-03-16T06:03:32Z"
message: Registration is managing credentials
observedGeneration: 4
reason: RegistrationFunctional
status: "False"
type: HubRegistrationDegraded
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-03-16T06:00:57Z"
message: Placement is scheduling placement decisions
observedGeneration: 4
reason: PlacementFunctional
status: "False"
type: HubPlacementDegraded
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-03-16T05:57:18Z"
message: Feature gates are all valid
reason: FeatureGatesAllValid
status: "True"
type: ValidFeatureGates
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-03-16T06:06:07Z"
message: Components of cluster manager are up to date
reason: ClusterManagerUpToDate
status: "False"
type: Progressing
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-03-16T05:57:18Z"
message: Components of cluster manager are applied
reason: ClusterManagerApplied
status: "True"
type: Applied
generations:
- group: apps
lastGeneration: 1
name: cluster-manager-registration-controller
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
lastGeneration: 1
name: cluster-manager-registration-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
lastGeneration: 1
name: cluster-manager-work-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
lastGeneration: 1
name: cluster-manager-placement-controller
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
observedGeneration: 4
relatedResources:
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: clustermanagementaddons.addon.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: managedclusters.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: managedclustersets.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: manifestworks.work.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: managedclusteraddons.addon.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: managedclustersetbindings.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: placements.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: addondeploymentconfigs.addon.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: placementdecisions.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: apiextensions.k8s.io
name: addonplacementscores.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: customresourcedefinitions
version: v1
- group: ""
name: open-cluster-management-hub
namespace: ""
resource: namespaces
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-registration:controller
namespace: ""
resource: clusterroles
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-registration:controller
namespace: ""
resource: clusterrolebindings
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-registration-controller-sa
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: serviceaccounts
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-registration:webhook
namespace: ""
resource: clusterroles
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-registration:webhook
namespace: ""
resource: clusterrolebindings
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-registration-webhook-sa
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: serviceaccounts
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-work:webhook
namespace: ""
resource: clusterroles
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-work:webhook
namespace: ""
resource: clusterrolebindings
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-work-webhook-sa
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: serviceaccounts
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-placement:controller
namespace: ""
resource: clusterroles
version: v1
- group: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
name: open-cluster-management:cluster-manager-placement:controller
namespace: ""
resource: clusterrolebindings
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-placement-controller-sa
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: serviceaccounts
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-registration-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: services
version: v1
- group: ""
name: cluster-manager-work-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: services
version: v1
- group: apps
name: cluster-manager-registration-controller
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
name: cluster-manager-registration-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
name: cluster-manager-work-webhook
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: apps
name: cluster-manager-placement-controller
namespace: open-cluster-management-hub
resource: deployments
version: v1
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
name: managedclustervalidators.admission.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: validatingwebhookconfigurations
version: v1
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
name: managedclustermutators.admission.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: mutatingwebhookconfigurations
version: v1
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
name: managedclustersetbindingvalidators.admission.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: validatingwebhookconfigurations
version: v1
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
name: managedclustersetbindingv1beta1validators.admission.cluster.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: validatingwebhookconfigurations
version: v1
- group: admissionregistration.k8s.io
name: manifestworkvalidators.admission.work.open-cluster-management.io
namespace: ""
resource: validatingwebhookconfigurations
version: v1
4. 将托管集群加入 hub 集群
每次注册这个命令执行一次
$ clusteradm get token --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER | grep clusteradm
clusteradm join --hub-token eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ik5VcVp4YXkyanFyZTllMWt2Z21UWXZwbmRvNkdkSHhnM005X3lmVTRMRjAifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiXSwiZXhwIjoxNjc5MDUxODM4LCJpYXQiOjE2NzkwNDgyMzgsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJvcGVuLWNsdXN0ZXItbWFuYWdlbWVudCIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJjbHVzdGVyLWJvb3RzdHJhcCIsInVpZCI6ImE5OGE4ZWE1LWVlMzYtNDUzNS05OWY5LTA0OTFmZjFhZTc1ZCJ9fSwibmJmIjoxNjc5MDQ4MjM4LCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6b3Blbi1jbHVzdGVyLW1hbmFnZW1lbnQ6Y2x1c3Rlci1ib290c3RyYXAifQ.UPAoJoxwtorHXhwK9gFelmPGFncFij5S3lQ31sm4ABJWNZhSJcbm0fujHmlbtfFIwgcgONOmEfyYbWyTisw1SHGDZx3whiz2S9AID1LMF_eJfO9mp-8nbZ0flYwsGePO7JYoiYVs3vde3VqGLl7b1ZZ4fbPDqJIaC0uGoBPFU8DjraB0lMbzY2pX6W4QbG0mvXQPMBBvGldKAUGZNnkNHhhznPJrbEyJ33Dz-N08-8mXnNEdzWnRVhHssEN1-XmBop1pS_b65QnjrbSua7q9e2quPD3gPYfuubK4Y1AkKNHdYJAIJEbAHe7nTg3Ef7ruXAN4oQsLU1BivPAadq73tg --hub-apiserver https://10.168.110.21:6443 --cluster-name <cluster_name>
不同的k8s 集群 加入方式略微不同。
k3s & openshift
clusteradm join \\
--hub-token <your token data> \\
--hub-apiserver <your hub cluster endpoint> \\
--wait \\
--cluster-name "cluster1" \\ # Or other arbitrary unique name
--context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
kind 集群
# NOTE: For KinD clusters use the parameter: --force-internal-endpoint-lookup
clusteradm join \\
--hub-token <your token data> \\
--hub-apiserver <your hub cluster endpoint> \\
--wait \\
--cluster-name "cluster1" \\ # Or other arbitrary unique name
--force-internal-endpoint-lookup \\
--context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
我的 k8s 集群其实是k3s创建的, 将 另一个集群加入托管集群。将<cluster_name>换成 default
$ clusteradm join --hub-token eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ik5VcVp4YXkyanFyZTllMWt2Z21UWXZwbmRvNkdkSHhnM005X3lmVTRMRjAifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiXSwiZXhwIjoxNjc5MDUxODM4LCJpYXQiOjE2NzkwNDgyMzgsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJvcGVuLWNsdXN0ZXItbWFuYWdlbWVudCIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJjbHVzdGVyLWJvb3RzdHJhcCIsInVpZCI6ImE5OGE4ZWE1LWVlMzYtNDUzNS05OWY5LTA0OTFmZjFhZTc1ZCJ9fSwibmJmIjoxNjc5MDQ4MjM4LCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6b3Blbi1jbHVzdGVyLW1hbmFnZW1lbnQ6Y2x1c3Rlci1ib290c3RyYXAifQ.UPAoJoxwtorHXhwK9gFelmPGFncFij5S3lQ31sm4ABJWNZhSJcbm0fujHmlbtfFIwgcgONOmEfyYbWyTisw1SHGDZx3whiz2S9AID1LMF_eJfO9mp-8nbZ0flYwsGePO7JYoiYVs3vde3VqGLl7b1ZZ4fbPDqJIaC0uGoBPFU8DjraB0lMbzY2pX6W4QbG0mvXQPMBBvGldKAUGZNnkNHhhznPJrbEyJ33Dz-N08-8mXnNEdzWnRVhHssEN1-XmBop1pS_b65QnjrbSua7q9e2quPD3gPYfuubK4Y1AkKNHdYJAIJEbAHe7nTg3Ef7ruXAN4oQsLU1BivPAadq73tg --hub-apiserver https://10.168.110.21:6443 --wait --cluster-name cluster1 --force-internal-endpoint-lookup --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
CRD successfully registered.
Registration operator is now available.
Klusterlet is now available.
Please log onto the hub cluster and run the following command:
clusteradm accept --clusters default
-
--cluster-name 并不是 context的名字,而是可以根据自己应用需求自定义的名称。 -
--context 确定哪个集群加入hub集群
OCM 代理在您的托管集群上运行后,它将向您的 hub 集群发送“握手”并等待 hub 集群管理员的批准。在本节中,我们将从 OCM 中心管理员的角度逐步接受注册请求。
等待 CSR 对象的创建,该对象将由您的托管集群的 OCM 代理在 hub 集群上创建:
# or the previously chosen cluster name
kubectl get csr -w --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER | grep cluster1
待处理 CSR 请求的示例如下所示:
cluster1-tqcjj 33s kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:serviceaccount:open-cluster-management:cluster-bootstrap Pending
使用工具接受加入请求clusteradm:
$ clusteradm accept --clusters cluster1 --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
Starting approve csrs for the cluster cluster1
CSR cluster1-5t2zz approved
set hubAcceptsClient to true for managed cluster cluster1
Your managed cluster cluster1 has joined the Hub successfully. Visit https://open-cluster-management.io/scenarios or https://github.com/open-cluster-management-io/OCM/tree/main/solutions for next steps.
运行该accept命令后,来自名为“cluster1”的托管集群的 CSR 将获得批准。此外,它将指示 OCM hub 控制平面自动设置相关对象(例如 hub 集群中名为“cluster1”的命名空间)和 RBAC 权限。
CSR请求成功效果:
$ kubectl get csr -w --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER | grep cluster1
cluster1-5t2zz 16m kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:serviceaccount:open-cluster-management:cluster-bootstrap <none> Approved,Issued
通过运行以下命令验证托管集群上 OCM 代理的安装:
$ kubectl -n open-cluster-management-agent get pod --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
klusterlet-registration-agent-598fd79988-jxx7n 1/1 Running 0 19d
klusterlet-work-agent-7d47f4b5c5-dnkqw 1/1 Running 0 19d
查看已成功创建cluster1 ManagedCluster对象
$ kubectl get managedcluster --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME HUB ACCEPTED MANAGED CLUSTER URLS JOINED AVAILABLE AGE
cluster1 true https://10.168.110.21:6443 True True 28m
5. 部署测试应用
注册托管群集后,测试是否可以从中心群集将Pod部署到托管群集。创建一个manifest-work.yaml,如下例所示:
apiVersion: work.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ManifestWork
metadata:
name: mw-01
namespace: $MANAGED_CLUSTER_NAME
spec:
workload:
manifests:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hello
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", echo "Hello, Kubernetes!" && sleep 3600]
restartPolicy: OnFailure
将yaml文件应用到集线器集群。
kubectl apply -f manifest-work.yaml --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
验证manifestwork资源是否已应用于中心。
kubectl -n $MANAGED_CLUSTER_NAME get manifestwork/mw-01 --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER -o yaml
检查托管集群,查看hello Pod是否已从集线器集群部署。
$ kubectl -n default get pod --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello 1/1 Running 0 108s
6. 添加应用生命周期管理插件

Deploy the subscription operators to the hub cluster.
$ kubectl config use-context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
$ clusteradm install hub-addon --names application-manager
Installing built-in application-manager add-on to the Hub cluster...
$ kubectl -n open-cluster-management get deploy multicluster-operators-subscription --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
multicluster-operators-subscription 1/1 1 1 25s
Create the open-cluster-management-agent-addon namespace on the managed cluster.
7. 注销已管理集群
注销 集群 default
$ clusteradm unjoin --cluster-name cluster1 --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
Remove applied resources in the managed cluster default ...
Applied resources have been deleted during the default joined stage. The status of mcl default will be unknown in the hub cluster.
查看已注销资源对象
$ kubectl -n open-cluster-management-agent get pod --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
No resources found in open-cluster-management-agent namespace.
检查已注销的集群对应的 klusterlet 是否被删除
$ kubectl get klusterlet --context $CTX_MANAGED_CLUSTER
error: the server doesnt have a resource type "klusterlet"
$ kubectl get managedcluster --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME HUB ACCEPTED MANAGED CLUSTER URLS JOINED AVAILABLE AGE
cluster1 true https://10.168.110.21:6443 True Unknown 148m
$ kubectl delete managedcluster cluster1 --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
managedcluster.cluster.open-cluster-management.io "cluster1" deleted
删除 CSR
$ kubectl get csr --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
NAME AGE SIGNERNAME REQUESTOR
REQUESTEDDURATION CONDITION
cluster1-njdvh 13m kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:serviceaccount:open-cluster-management:cluster-bootstrap <none> Approved,Issued
$ kubectl delete csr cluster1-njdvh --context $CTX_HUB_CLUSTER
certificatesigningrequest.certificates.k8s.io "cluster1-njdvh" deleted
参考:
Quasar:Resource-Efficient and Qos-Aware Cluster Management
我的论文笔记框架(Markdown格式)
Quasar:Resource-Efficient and Qos-Aware Cluster Management
2014, Christina, ASPLOS
Summary
写完笔记之后最后填,概述文章的内容,以后查阅笔记的时候先看这一段。注:写文章summary切记需要通过自己的思考,用自己的语言描述。忌讳直接Ctrl + c原文。
Research Objective(s)
Background / Problem Statement:
Method(s)
作者解决问题的方法/算法是什么?是否基于前人的方法?基于了哪些?
In Paragon, collaborative filtering was used to quickly classfiy worklaods with respect to interference and heterogeneity. A few applications are profiled exhaustively offline to derive their performance on different servers and with varying amounts of interference. An incoming application is profiled for one mintue on two of the many server configurations, with and without interferences in two shared resources. SVD and PQ-reconstruction are used to accurately estimate the performance of the workload on the remaining server configurations and with the interference on the remaining types of resources. Paragon showed that collaborative filtering can quickly and accurately classify unknown applications with respect to tens of server configurations and tens of sources of interfernces.
The classfication engine in Quasar extends the one in Paragon in two ways. First, it uses collaborative filtering to estimate the impact of resource scale-out(more servers) and scale-up (more resources per server) on application performance. These additional classfications are necessary for resource allocation. Second, it tailors classifications to differnt workload types. This is necessary because differnt types for workloads have different constraints and allocation knobs.
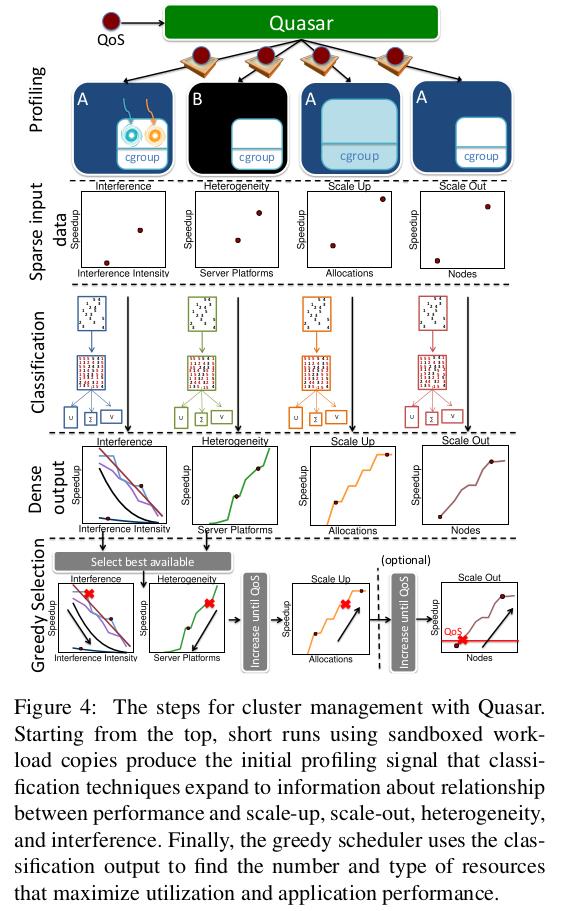
scale-up classfication
Profiling collects performance measurements in the format of each application’s performance goal(e.g. expected completion time or QPS) and inserts them into a matrix A with workloads as rows and scale-up configurations as columns. A configuration include compute, memory, and storage allocations or the values of the framework parameters for a workload like Hadoop. To constrain the number of columns, we quantize the vectors to integer multiples of cores and blocks of memory and storage. This may result into somewhat suboptimal decicsions, but the deviations are small in practice. Classfication using SVD and PQ-reconstruction then derive the workload’s performance across all scale-up allocations.
Heterogeneity classfication
This classfication requires one more profiling run on a different and randomly-chosen server type using the same workload parameters and for the same duration as a scale-up run. Collaborative filtering estimates workload performance across all other server types.
Interference classfication
This classification quantifies the sensitivity of the workload to interference caused and tolerated in various shared resources, including the CPU, cache hierarchy, memory capacity and bandwidth, and storage and network bandwidth. This classfication does not require an extra profiling run. Instead, it leverages the first copy of the scale-up classification to inject, one at a time, two microbenchmarks that create contention in a specific shared resource[19]. Once the microbenchmark is injected, Quasar tunes up its intensity until the workload performance drops below an acceptable level of QoS(typically 5%). This point is recorded as the workload’s sensitivity to this type of interference in a new row in the corresponding matrix A. The columns of the matrix are the different sources of interferences. Classification is then applied to derive the sensitivities to the remaining sources of interferences.
3.3 Greedy Allocation Assignment
The classification output is given to a greedy scheduler that jointly determines the amount, type, and exact set of allocated resources. The scheduler’s objective is to allocate the least amount of resources needed to satisfy a workloads’s performance target. This greatly reduces the space the scheduler traverse, allowing it to examine higher quality resources first, as smaller quantities of them will meet the performance constraint. This approach also scales well to many servers.
The scheduler uses the classfication output, to first rank the available severs by decreasing resource quality, i.e., high performing platforms with minimal interference first. Next, it sizes the allocation based on available resources until the performance constraint is met. Fir example, is a webserver must meet a throughput of 100K QPS with 10msec 9 9 t h 99_th 99th percentile latency and the highest-ranked servers can achieve at most 20K QPS, the workload would need five servers to meet the constraints. If the number of highest-ranked servers available is not sufficient, the scheduler will also allocate lower-randked servers and increase their number. The feedback between allocation and assignment ensures that the amount and quality of resources are accounted for jointly. When sizing the allocation, the algorithm first increases the per-node resource(scale-up) to better pack work in few servers, and then distributes the load across machines(scale-out). Nevertheless, alternative heuristics can be used based on workload’s locality properties or to address fault tolerance concerns.
The greedy algorithm has O ( M ∗ l o g M + S ) O(M*logM + S) O(M∗logM+S) complexity**, where the first** component accounts for the sorting overhead and the second for the examination of the top S S S servers, and in practice takes a few msec to determine an allocation/assignment even for systems with thousands of servers. Despite tis greedy nature, we show in Section 6 that the decision quality is quite high, leading to both high workload performance and high resource utilization.
4.1 Dynamic Adaptation
Some workloads change behavior during their runtime, either due to phase changes or due to variation in user traffic. Quasar detects such changes and adjusts resource allocation and/or assignement to perserve the performance contraints.
Phase detection
Quasar continuously monitors the performance of all active workloads in the cluster. If a workload runs below its performance constraint, it either went through a phase change or was incorrectly classified or assigned. In any case, Quasar reclassifies the application at current state and adjusts its resources ad needed.
Evaluation
作者如何评估自己的方法?实验的setup是什么样的?感兴趣实验数据和结果有哪些?有没有问题或者可以借鉴的地方?
Conclusion
作者给出了哪些结论?哪些是strong conclusions, 哪些又是weak的conclusions(即作者并没有通过实验提供evidence,只在discussion中提到;或实验的数据并没有给出充分的evidence)?
以上是关于Open Cluster Management 部署应用实践的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章