python代码运行助手怎么打开
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python代码运行助手怎么打开相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
python代码运行助手是能在网页上运行python语言的工具。因为python的运行环境在很多教程里都是用dos的,黑乎乎的界面看的有点简陋,所以出了这python代码运行助手,作为ide。
实际上,python代码运行助手界面只能算及格分,如果要找ide,推荐使用jupyter。jupyter被集成到ANACONDA里,只要安装了anacoda就能使用了。
回到这个问题:
1、要打开这运行助手首先要下载一个learning.py,如果找不到可以复制如下代码另存为“learning.py”,编辑器用sublime、或者notepad++。
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
r'''
learning.py
A Python 3 tutorial from http://www.liaoxuefeng.com
Usage:
python3 learning.py
'''
import sys
def check_version():
v = sys.version_info
if v.major == 3 and v.minor >= 4:
return True
print('Your current python is %d.%d. Please use Python 3.4.' % (v.major, v.minor))
return False
if not check_version():
exit(1)
import os, io, json, subprocess, tempfile
from urllib import parse
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
EXEC = sys.executable
PORT = 39093
HOST = 'local.liaoxuefeng.com:%d' % PORT
TEMP = tempfile.mkdtemp(suffix='_py', prefix='learn_python_')
INDEX = 0
def main():
httpd = make_server('127.0.0.1', PORT, application)
print('Ready for Python code on port %d...' % PORT)
httpd.serve_forever()
def get_name():
global INDEX
INDEX = INDEX + 1
return 'test_%d' % INDEX
def write_py(name, code):
fpath = os.path.join(TEMP, '%s.py' % name)
with open(fpath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(code)
print('Code wrote to: %s' % fpath)
return fpath
def decode(s):
try:
return s.decode('utf-8')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
return s.decode('gbk')
def application(environ, start_response):
host = environ.get('HTTP_HOST')
method = environ.get('REQUEST_METHOD')
path = environ.get('PATH_INFO')
if method == 'GET' and path == '/':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return [b'<html><head><title>Learning Python</title></head><body><form method="post" action="/run"><textarea name="code" style="width:90%;height: 600px"></textarea><p><button type="submit">Run</button></p></form></body></html>']
if method == 'GET' and path == '/env':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
L = [b'<html><head><title>ENV</title></head><body>']
for k, v in environ.items():
p = '<p>%s = %s' % (k, str(v))
L.append(p.encode('utf-8'))
L.append(b'</html>')
return L
if host != HOST or method != 'POST' or path != '/run' or not environ.get('CONTENT_TYPE', '').lower().startswith('application/x-www-form-urlencoded'):
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"bad_request"']
s = environ['wsgi.input'].read(int(environ['CONTENT_LENGTH']))
qs = parse.parse_qs(s.decode('utf-8'))
if not 'code' in qs:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"invalid_params"']
name = qs['name'][0] if 'name' in qs else get_name()
code = qs['code'][0]
headers = [('Content-Type', 'application/json')]
origin = environ.get('HTTP_ORIGIN', '')
if origin.find('.liaoxuefeng.com') == -1:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"invalid_origin"']
headers.append(('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', origin))
start_response('200 OK', headers)
r = dict()
try:
fpath = write_py(name, code)
print('Execute: %s %s' % (EXEC, fpath))
r['output'] = decode(subprocess.check_output([EXEC, fpath], stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, timeout=5))
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Exception', output=decode(e.output))
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired as e:
r = dict(error='Timeout', output='执行超时')
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Error', output='执行错误')
print('Execute done.')
return [json.dumps(r).encode('utf-8')]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2,再用一个记事本写如下的代码:
@echo offpython learning.py
pause
另存为‘运行.bat’
3、把“运行.bat”和“learning.py”放到同一目录下,
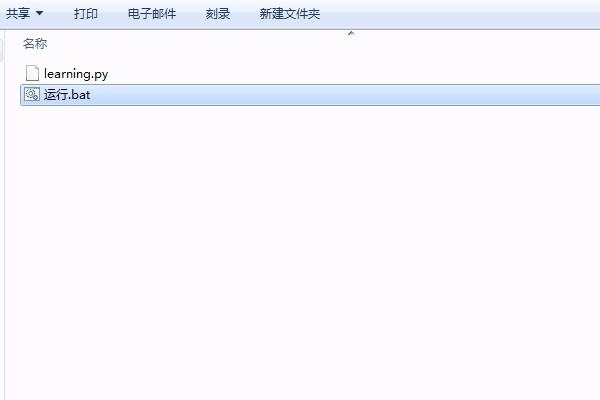
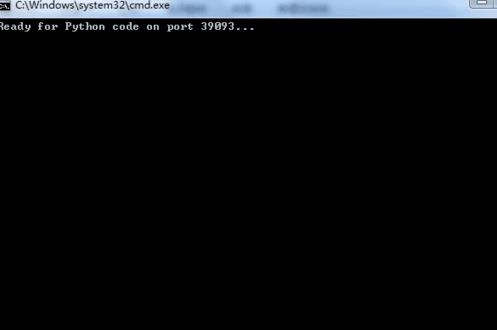
4、双击运行“运行.bat",之后会弹出黑色的dos窗口,这个窗口不要关闭。

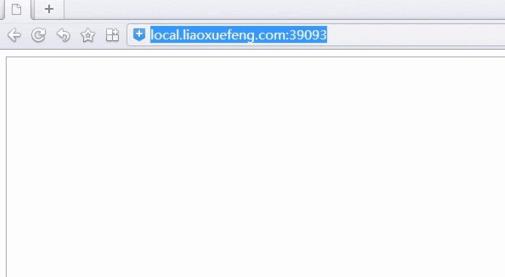
5、输入网址对应的网址和端口,整个过程就完成了。
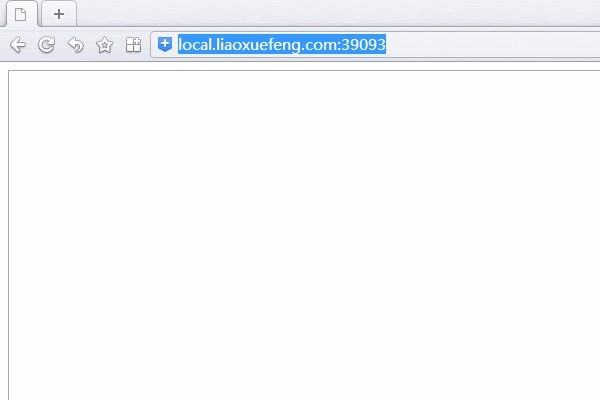
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
r'''
learning.py
A Python 3 tutorial from http://www.liaoxuefeng.com
Usage:
python3 learning.py
'''
import sys
def check_version():
v = sys.version_info
if v.major == 3 and v.minor >= 4:
return True
print('Your current python is %d.%d. Please use Python 3.4.' % (v.major, v.minor))
return False
if not check_version():
exit(1)
import os, io, json, subprocess, tempfile
from urllib import parse
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
EXEC = sys.executable
PORT = 39093
HOST = 'local.liaoxuefeng.com:%d' % PORT
TEMP = tempfile.mkdtemp(suffix='_py', prefix='learn_python_')
INDEX = 0
def main():
httpd = make_server('127.0.0.1', PORT, application)
print('Ready for Python code on port %d...' % PORT)
httpd.serve_forever()
def get_name():
global INDEX
INDEX = INDEX + 1
return 'test_%d' % INDEX
def write_py(name, code):
fpath = os.path.join(TEMP, '%s.py' % name)
with open(fpath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(code)
print('Code wrote to: %s' % fpath)
return fpath
def decode(s):
try:
return s.decode('utf-8')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
return s.decode('gbk')
def application(environ, start_response):
host = environ.get('HTTP_HOST')
method = environ.get('REQUEST_METHOD')
path = environ.get('PATH_INFO')
if method == 'GET' and path == '/':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return [b'<html><head><title>Learning Python</title></head><body><form method="post" action="/run"><textarea name="code" style="width:90%;height: 600px"></textarea><p><button type="submit">Run</button></p></form></body></html>']
if method == 'GET' and path == '/env':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
L = [b'<html><head><title>ENV</title></head><body>']
for k, v in environ.items():
p = '<p>%s = %s' % (k, str(v))
L.append(p.encode('utf-8'))
L.append(b'</html>')
return L
if host != HOST or method != 'POST' or path != '/run' or not environ.get('CONTENT_TYPE', '').lower().startswith('application/x-www-form-urlencoded'):
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"bad_request"']
s = environ['wsgi.input'].read(int(environ['CONTENT_LENGTH']))
qs = parse.parse_qs(s.decode('utf-8'))
if not 'code' in qs:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"invalid_params"']
name = qs['name'][0] if 'name' in qs else get_name()
code = qs['code'][0]
headers = [('Content-Type', 'application/json')]
origin = environ.get('HTTP_ORIGIN', '')
if origin.find('.liaoxuefeng.com') == -1:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'"error":"invalid_origin"']
headers.append(('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', origin))
start_response('200 OK', headers)
r = dict()
try:
fpath = write_py(name, code)
print('Execute: %s %s' % (EXEC, fpath))
r['output'] = decode(subprocess.check_output([EXEC, fpath], stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, timeout=5))
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Exception', output=decode(e.output))
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired as e:
r = dict(error='Timeout', output='执行超时')
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Error', output='执行错误')
print('Execute done.')
return [json.dumps(r).encode('utf-8')]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Python代码运行助手 参考技术C
python代码运行助手怎么打开:
Python代码运行助手可以在线输入Python代码,通过本机运行的一个Python脚本来执行代码。

在网页输入代码。
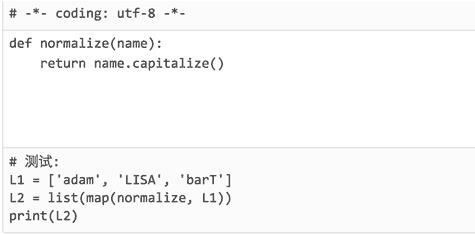
点击Run按钮,代码被发送到本机正在运行的Python代码运行助手。Python代码运行助手将代码保存为临时文件,然后调用Python解释器执行代码。网页显示代码执行结果。
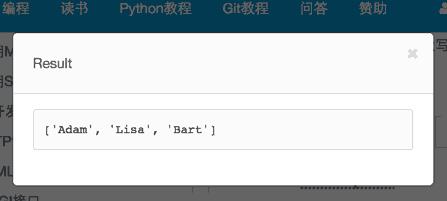
运行在存放learning.py的目录下运行命令。(需要支持HTML5的浏览器)
python代码运行助手怎么打开的延伸:
python代码运行助手的使用方法:
要打开这运行助手首先要下载一个learning.py。(找不到可以复制如下代码另存为learning.py)
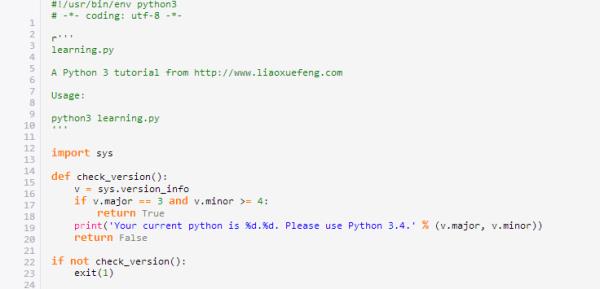
用一个记事本写如下的代码:
 另存为运行.bat
另存为运行.bat
把运行.bat和learning.py放到同一目录下。

双击运行运行.bat,之后会弹出黑色的dos窗口,这个窗口不要关闭。
输入网址对应的网址和端口,整个过程完成。
以上是关于python代码运行助手怎么打开的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章