Spring Cloud @RefreshScope 原理分析:代理类调用流程
Posted 毕小宝
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Cloud @RefreshScope 原理分析:代理类调用流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
本文类分析 SpringCloud 的 @RefreshScope 注解的 refresh 类型下,获取实例的过程。关键技术点:
- 扫描过程中对
@RefreshScope注解做了特殊处理,会额外注册两个BeanDefinition。 GenericScope实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,并对 refresh 的BeanDefinition添加了构造函数参数为自己,同时设置 beanClass 属性为GenericScope.LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean.class,合成属性为true。GenericScope.LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean类实现了FactoryBean、BeanFactoryAware、MethodInterceptor接口。
代理类调用流程
我们前面分析了被 @RefreshScope 标注的类,在获取 Bean 实例时,得到的是一个代理类 JdkDynamicAopProxy ,这就到了 spring 框架的 Aop 动态代理的基础上了,沿着这条路线跟踪代码。
首先, JdkDynamicAopProxy 继承了委托类,而且还拥有一个目标对象的创建源类型 TargetSource。
它的每个方法【除了 toString,hashCode,equals 外】,都通过 invoke 方法做了增强:

注意,这里的 MethodInvocation 是 JoinPoint 的子类,就是 AOP 的连接点。创建的具体实现类是 ReflectiveMethodInvocation ,它调用了 MethodInterceptor 的 invoke 方法:
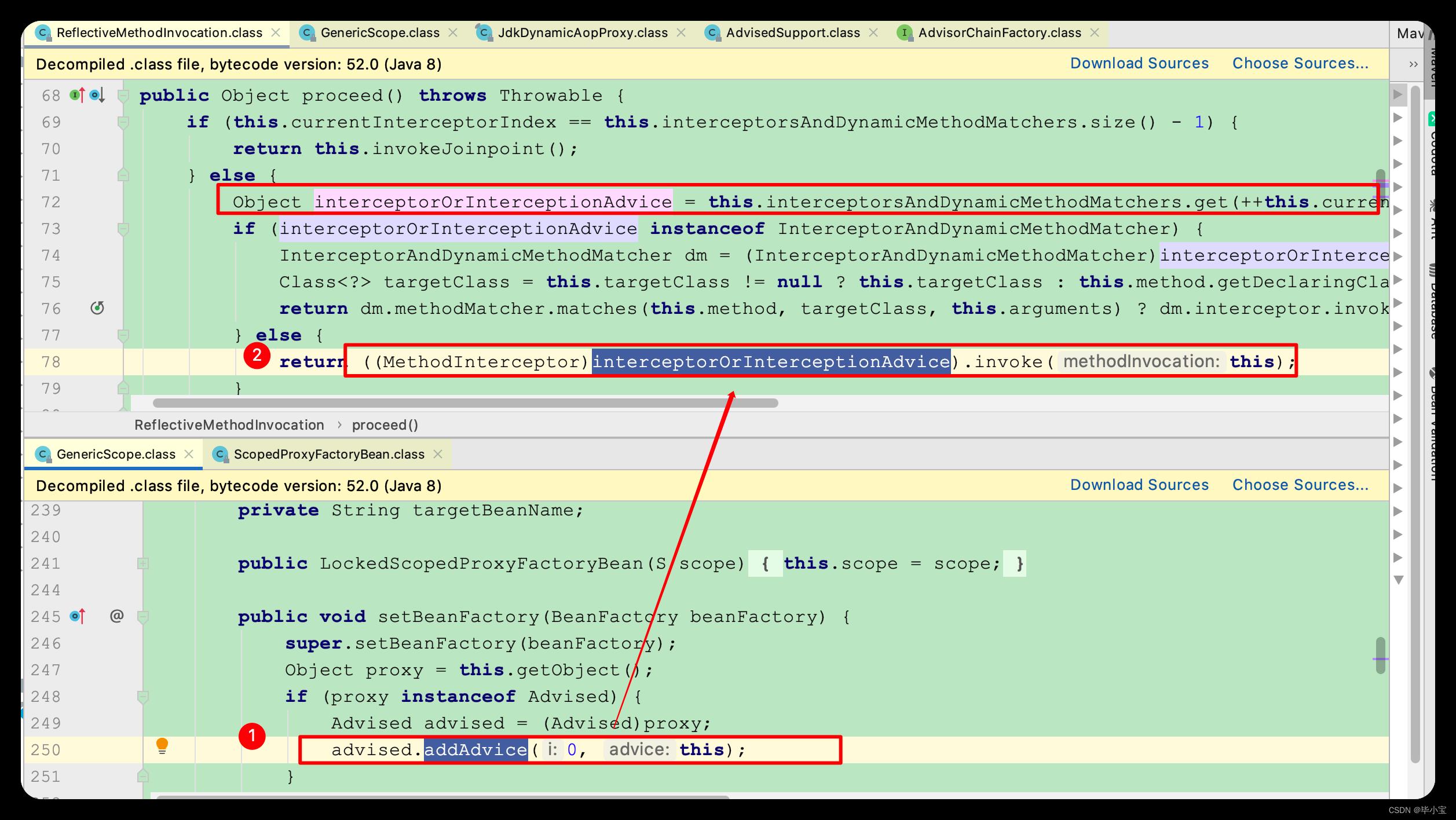
250 行, LockedScopedProxyFactory 代理类重写父类的 Advice,把它换成了自己实现的 MethodInterceptor :
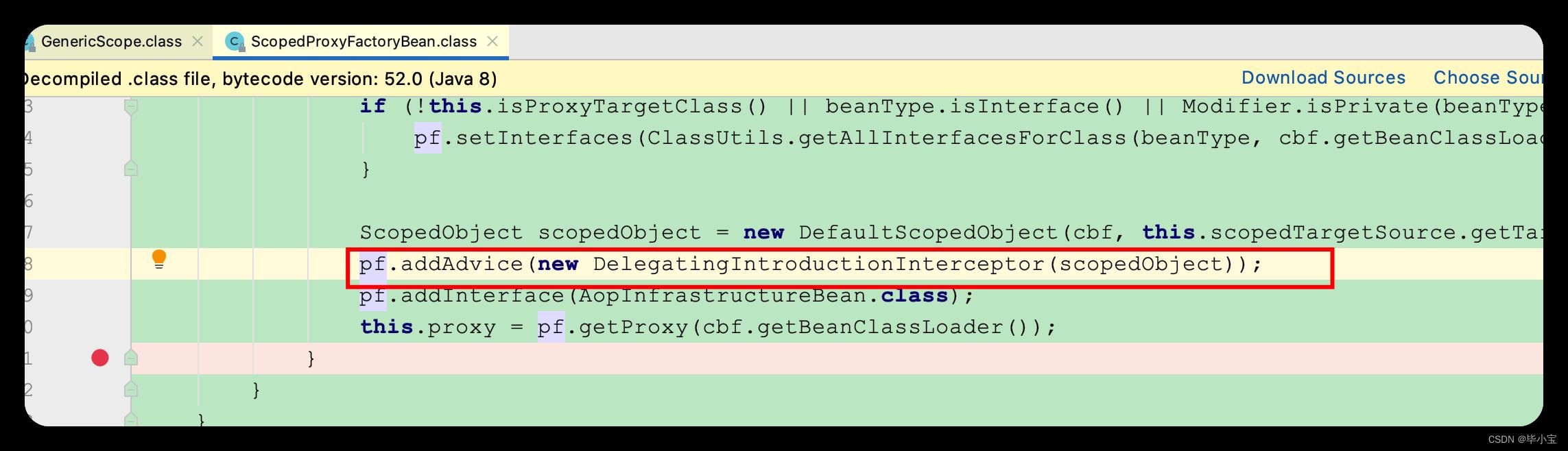
原始默认的增强类型是 DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor,这两个的区别是:

- 默认的方法拦截器, AOP 回调时直接调用委托对象的方法。
- 而
GenericScope.LockedScopedProxyFactory实现的代理,传入的是委托对象的工厂,它包装了真正的委托对象,所以继续拆解,触发targetSource.getTarget()的方法。
SimpleBeanTargetSource
首先,上一步 GenericScope.LockedScopedProxyFactory 创建的代理类,它的 targetSource 类型是 SimpleBeanTargetSource。
其次,SimpleBeanTargetSource 的 getTarget() 方法,就是从 BeanFactory 获取 targetName 的实例,即以 "scopedTarget." + originalBeanName 命名的实例,它的 BeanDefinition 的 Scope 属性值是 refresh ,对应的 Scope 对象是 RefreshScope 。

我们知道,Spring 托管的实例在创建过程中,不同 scope 类,由不同 Scope 实现类提供。而 @Scope("refresh") 的类,都会通过 RefreshScope 的 父类 GenericScope 的 get 获取:

最后,因为 RefreshScope 管理全部的 scopedTarget.beanName 对象,当环境变量变动时,会触发 refresh 或者 refreshAll :

清空所有缓存的真实对象,下一次调用时发现缓存不存在,就会新建:
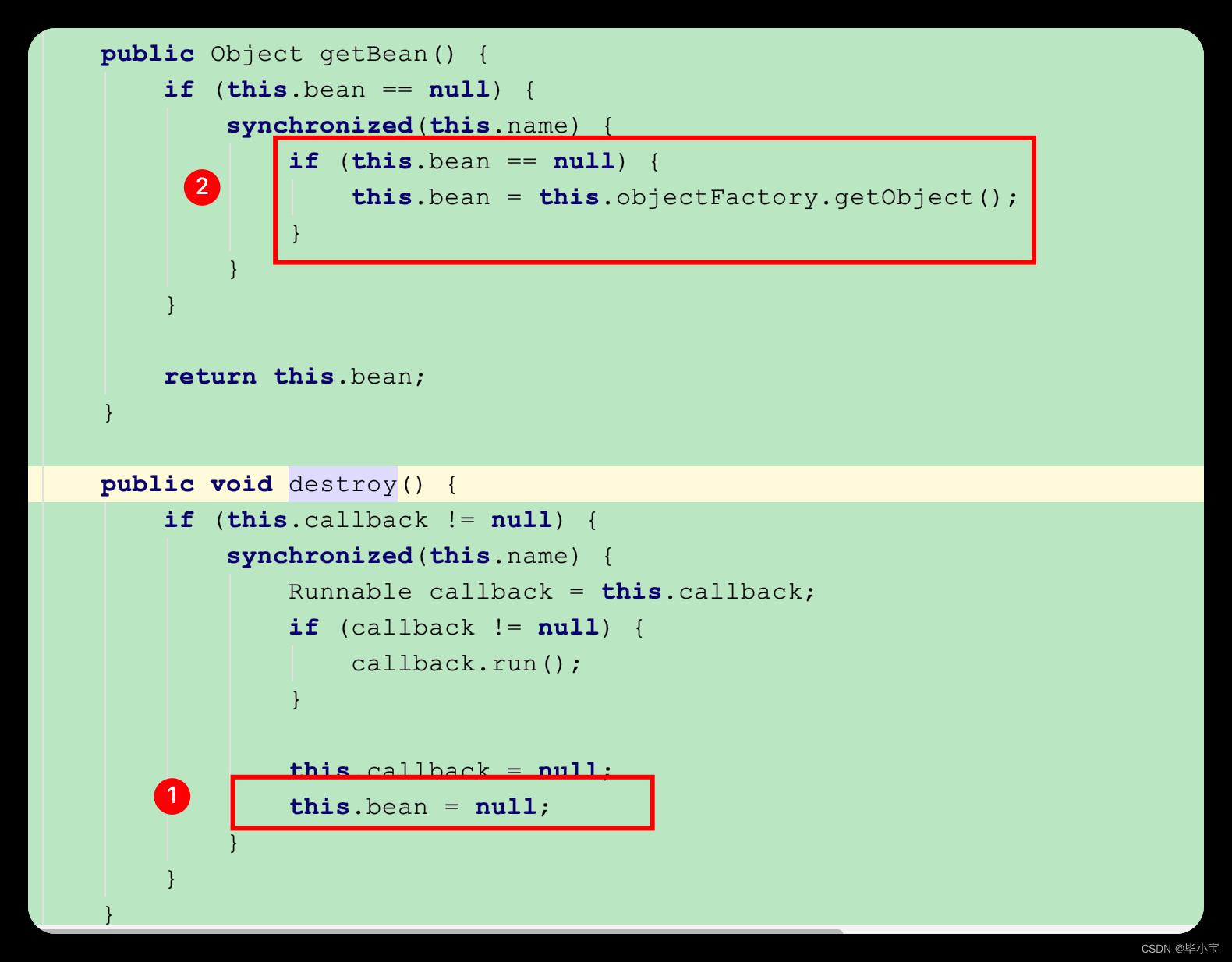
这样就可以保证 @RefreshScope 注解的类在配置变动时能够实时生效。
启示录
从最后代理类型来看,AOP 用的是 JDK 的动态代理,并不是 CGLIB 代理呢。这个调用的关键在于 AOP 代理的设计模式,JDK 的动态代理,基于接口、且提供一个 InvocationHandler 增强方法,而代理类实现的每个方法,都是通过 invoke 完成的,它会调用真正的委托对象的方法,并在真正的方法执行时做一些增强操作。
温故一个简单的 JDK 动态代理的例子就明白了:
public class JdkProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler
private Object realSubject;
public JdkProxyInvocationHandler(Object realSubject)
this.realSubject = realSubject;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
System.out.println("Before method called.");
Object result = method.invoke(realSubject, args);
System.out.println("After method called.");
return result;
public static void main(String[] args)
ISubject subject = (ISubject) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] ISubject.class, // 或RealSubject.class.getInterfaces()
new JdkProxyInvocationHandler(new RealISubject1())); // RealSubject必须实现Subject接口,否则无法强转后调用业务方法
subject.request("hello");
subject.request1("hello1");
subject.request2("hello2");
参考
看到一篇很完整的文章,可以参考补充:《SpringCloud @RefreshScope动态刷新配置原理浅析》
以上是关于Spring Cloud @RefreshScope 原理分析:代理类调用流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Spring Cloud实战Spring Cloud GateWay服务网关
spring-cloud-config——Quick Start
Spring Cloud入门 - Spring Cloud保护机制