Spring08-----IoC容器ApplicationContext
Posted Hermioner
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring08-----IoC容器ApplicationContext相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
作为Spring提供的较之BeanFactory更为先进的IoC容器实现,ApplicationContext除了拥有 BeanFactory支持的所有功能之外,还进一步扩展了基本容器的功能,包括BeanFactoryPostProces- sor、BeanPostProcessor以及其他特殊类型bean的自动识别、容器启动后bean实例的自动初始化、 国际化的信息支持、容器内事件发布等。真是“青出于蓝而胜于蓝”啊!
在介绍ApplicationContext之前先引入资源的概念。
一. Resource接口
在日常程序开发中,处理外部资源是很繁琐的事情,我们可能需要处理URL资源、File资源资源、ClassPath相关 资源、服务器相关资源(JBoss AS 5.x上的VFS资源)等等很多资源。因此处理这些资源需要使用不同的接口,这就 增加了我们系统的复杂性;而且处理这些资源步骤都是类似的(打开资源、读取资源、关闭资源),因此如果能抽象 出一个统一的接口来对这些底层资源进行统一访问,是不是很方便,而且使我们系统更加简洁,都是对不同的底层资 源使用同一个接口进行访问。
Spring 提供一个Resource接口来统一这些底层资源一致的访问,而且提供了一些便利的接口,从而能提供我们 的生产力。
1. Resource接口API
Spring的Resource接口代表底层外部资源,提供了对底层外部资源的一致性访问接口。
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { boolean exists(); boolean isReadable(); boolean isOpen(); URL getURL() throws IOException; URI getURI() throws IOException; File getFile() throws IOException; long contentLength() throws IOException; long lastModified() throws IOException; Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; String getFilename(); String getDescription(); }
(1)InputStreamSource接口解析
getInputStream:每次调用都将返回一个新鲜的资源对应的java.io. InputStream字节流,调用者在使用完毕 后必须关闭该资源。
(2)Resource接口继承InputStreamSource接口,并提供一些便利方法:
exists:返回当前Resource代表的底层资源是否存在,true表示存在。
isReadable:返回当前Resource代表的底层资源是否可读,true表示可读。
isOpen:返回当前Resource代表的底层资源是否已经打开,如果返回true,则只能被读取一次然后关闭以避 免资源泄露;常见的Resource实现一般返回false。
getURL:如果当前Resource代表的底层资源能由java.util.URL代表,则返回该URL,否则抛出IOException。
getURI:如果当前Resource代表的底层资源能由java.util.URI代表,则返回该URI,否则抛出IOException。
getFile:如果当前Resource代表的底层资源能由java.io.File代表,则返回该File,否则抛出IOException。
contentLength:返回当前Resource代表的底层文件资源的长度,一般是值代表的文件资源的长度。
lastModified:返回当前Resource代表的底层资源的最后修改时间。
createRelative:用于创建相对于当前Resource代表的底层资源的资源,比如当前Resource代表文件资源 “d:/test/”则createRelative(“test.txt”)将返回表文件资源“d:/test/test.txt”Resource资源。
getFilename:返回当前Resource代表的底层文件资源的文件路径,比如File资源“file://d:/test.txt”将返回 “d:/test.txt”,而URL资源http://www.javass.cn将返回“”,因为只返回文件路径。
getDescription:返回当前Resource代表的底层资源的描述符,通常就是资源的全路径(实际文件名或实际 URL地址)。
Resource接口提供了足够的抽象,足够满足我们日常使用。而且提供了很多内置Resource实现: ByteArrayResource、InputStreamResource 、FileSystemResource 、UrlResource 、ClassPathResource、 ServletContextResource、VfsResource等。
2. 内置Resource实现
(1)ByteArrayResource
ByteArrayResource代表byte[]数组资源,对于“getInputStream”操作将返回一个 ByteArrayInputStream。
首先让我们看下使用ByteArrayResource如何处理byte数组资源:

1 package helloworld; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.InputStream; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 import org.springframework.core.io.ByteArrayResource; 7 import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; 8 9 10 public class HelloTest { 11 @Test 12 public void testByteArrayResource() { 13 Resource resource=new ByteArrayResource("Hello World!".getBytes()); 14 if(resource.exists()) { 15 dumpStream(resource); 16 } 17 } 18 19 private void dumpStream(Resource resource) { 20 InputStream is=null; 21 try { 22 //1.获取文件资源 23 is=resource.getInputStream(); 24 //2.读取资源 25 byte[] descBytes=new byte[is.available()]; 26 is.read(descBytes); 27 System.out.println(new String(descBytes)); 28 }catch (IOException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 }finally { 31 try { 32 //3.关闭资源 33 is.close(); 34 }catch (IOException e) { 35 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 Hello World!
说明:ByteArrayResource可多次读取数组资源,即isOpen ()永远返回false。
(2)InputStreamResource
InputStreamResource代表java.io.InputStream字节流,对于“getInputStream ”操作将直接返回该字节 流,因此只能读取一次该字节流,即“isOpen”永远返回true。

1 @Test 2 public void testInputStreamResource() { 3 ByteArrayInputStream bis=new ByteArrayInputStream("Hello World!".getBytes()); 4 Resource resource=new InputStreamResource(bis); 5 if(resource.exists()) { 6 dumStream(resource); 7 } 8 Assert.assertEquals(true, resource.isOpen()); 9 } 10 11 测试代码几乎和ByteArrayResource测试完全一样,注意“isOpen”此处用于返回true。
(3)FileSystemResource
FileSystemResource代表java.io.File资源,对于“getInputStream ”操作将返回底层文件的字节流, “isOpen”将永远返回false,从而表示可多次读取底层文件的字节流。
假设存在test.txt文件,它中间的内容是haha

1 public class HelloTest { 2 @Test 3 public void testByteArrayResource() { 4 File file=new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\houuumin\\\\Desktop\\\\test.txt"); 5 Resource resource=new FileSystemResource(file); 6 if(resource.exists()) { 7 dumpStream(resource); 8 } 9 Assert.assertEquals(false, resource.isOpen()); 10 } 11 12 private void dumpStream(Resource resource) { 13 InputStream is=null; 14 try { 15 //1.获取文件资源 16 is=resource.getInputStream(); 17 //2.读取资源 18 byte[] descBytes=new byte[is.available()]; 19 is.read(descBytes); 20 System.out.println(new String(descBytes)); 21 }catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally { 24 try { 25 //3.关闭资源 26 is.close(); 27 }catch (IOException e) { 28 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 haha
(4)ClassPathResource
ClassPathResource代表classpath路径的资源,将使用ClassLoader进行加载资源。classpath 资源存在于类路 径中的文件系统中或jar包里,且“isOpen”永远返回false,表示可多次读取资源。
ClassPathResource加载资源替代了Class类和ClassLoader类的“getResource(String name)”和 “getResourceAsStream(String name)”两个加载类路径资源方法,提供一致的访问方式。
ClassPathResource提供了三个构造器:
public ClassPathResource(String path):使用默认的ClassLoader加载“path”类路径资源; public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader):使用指定的ClassLoader加载 “path”类路径资源; public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz):使用指定的类加载“path”类路径资源,将加 载相对于当前类的路径的资源;
eg:最后一个举例:
比如当前类路径是“cn.javass.spring.chapter4.ResourceTest”,而需要加载的资源路径是“cn/javass/spring/ chapter4/test1.properties”,则将加载的资源在“cn/javass/spring/chapter4/cn/javass/spring/chapter4/ test1.properties”;
而如果需要 加载的资源路径为“test1.properties”,将加载的资源为“cn/javass/spring/chapter4/ test1.properties”。
1)使用默认的加载器加载资源,将加载当前ClassLoader类路径上相对于根路径的资源;

1 public class HelloTest { 2 @Test 3 public void testClasspathResourceByDefaultClassLoader() throws IOException { 4 Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("test1.properties"); 5 if(resource.exists()) { 6 dumpStream(resource); 7 } 8 System.out.println("path:"+resource.getFile().getAbsolutePath()); 9 Assert.assertEquals(false, resource.isOpen()); 10 } 11 12 private void dumpStream(Resource resource) { 13 InputStream is=null; 14 try { 15 //1.获取文件资源 16 is=resource.getInputStream(); 17 //2.读取资源 18 byte[] descBytes=new byte[is.available()]; 19 is.read(descBytes); 20 System.out.println(new String(descBytes)); 21 }catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally { 24 try { 25 //3.关闭资源 26 is.close(); 27 }catch (IOException e) { 28 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 }
resource目录下有一个文件叫做test1.properties,它中间的内容为hello world。
运行结果如下:

1 hello world 2 path:C:\\Users\\hermioner\\eclipse-workspace\\helloworld\\target\\test-classes\\test1.properties
2)使用指定的ClassLoader进行加载资源,将加载指定的ClassLoader类路径上相对于根路径的资源;

1 public class HelloTest { 2 @Test 3 public void testClasspathResourceByClassLoader() throws IOException { 4 ClassLoader cl=this.getClass().getClassLoader(); 5 Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("test1.properties",cl); 6 if(resource.exists()) { 7 dumpStream(resource); 8 } 9 System.out.println("path:"+resource.getFile().getAbsolutePath()); 10 Assert.assertEquals(false, resource.isOpen()); 11 } 12 13 private void dumpStream(Resource resource) { 14 InputStream is=null; 15 try { 16 //1.获取文件资源 17 is=resource.getInputStream(); 18 //2.读取资源 19 byte[] descBytes=new byte[is.available()]; 20 is.read(descBytes); 21 System.out.println(new String(descBytes)); 22 }catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 }finally { 25 try { 26 //3.关闭资源 27 is.close(); 28 }catch (IOException e) { 29 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }

1 hello world 2 path:C:\\Users\\hermioner\\eclipse-workspace\\helloworld\\target\\test-classes\\test1.properties
note: classpath指的是编译后的路径地址,可以通过build path来查看:
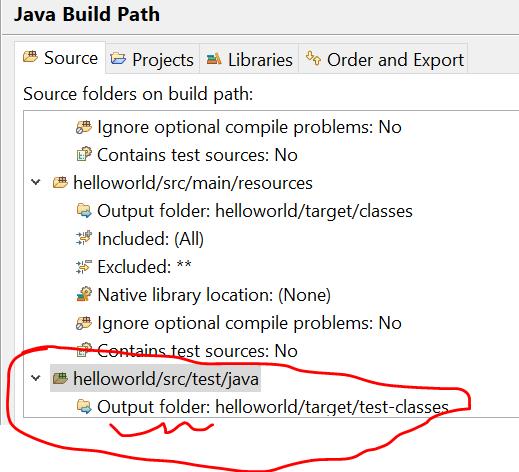
可以看到build path的目的地是helloworld/target/test-classes中
二.访问资源(ResourceLoader)
ResourceLoader接口用于返回Resource对象;其实现可以看作是一个生产Resource的工厂类。
1. ResourceLoader的API

1 public interface ResourceLoader { 2 String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX; 3 Resource getResource(String location); 4 ClassLoader getClassLoader(); 5 }
getResource接口用于根据提供的location参数返回相应的Resource对象;而getClassLoader则返回加载这些 Resource的ClassLoader
Spring提供了一个适用于所有环境的DefaultResourceLoader实现,可以返回ClassPathResource、 UrlResource;还提供一个用于web环境的ServletContextResourceLoader,它继承了DefaultResourceLoader的 所有功能,又额外提供了获取ServletContextResource的支持。
ResourceLoader在进行加载资源时需要使用前缀来指定需要加载:“classpath:path”表示返回 ClasspathResource,“http://path”和“file:path”表示返回UrlResource资源,如果不加前缀则需要根据当前上 下文来决定,DefaultResourceLoader默认实现可以加载classpath资源,如代码所示

1 @Test 2 public void testResourceLoad() { 3 ResourceLoader loader=new DefaultResourceLoader(); 4 Resource resource=loader.getResource("classpath:com/test"); 5 Assert.assertEquals(ClassPathResource.class, resource.getClass()); 6 7 Resource resource2=loader.getResource("file:com/test"); 8 Assert.assertEquals(UrlResource.class, resource2.getClass()); 9 10 Resource resource3=loader.getResource("com/test"); 11 Assert.assertTrue(resource3 instanceof ClassPathResource); 12 }
2. ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext都实现了ResourceLoader,因此可以使用其来加载资源。主要有以下实现类:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:不指定前缀将返回默认的ClassPathResource资源,否则将根据前缀来 加载资源;
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:不指定前缀将返回FileSystemResource,否则将根据前缀来加载资源;
WebApplicationContext:不指定前缀将返回ServletContextResource,否则将根据前缀来加载资源;
其他:不指定前缀根据当前上下文返回Resource实现,否则将根据前缀来加载资源。
3. ResourceLoaderAware接口
ResourceLoaderAware是一个标记接口,用于通过ApplicationContext上下文注入ResourceLoader。
API如下:

1 public interface ResourceLoaderAware { 2 void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader); 3 }
举例说明Application是一个ResourceLoader:

1 public class ResourceBean implements ResourceLoaderAware{ 2 private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; 3 4 public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { 5 this.resourceLoader=resourceLoader; 6 } 7 8 public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() { 9 return resourceLoader; 10 } 11 }

1 <bean class="com.test.spring.ResourceBean"/>

1 @Test 2 public void test() { 3 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); 4 ResourceBean resourceBean=context.getBean(ResourceBean.class); 5 ResourceLoader loader=resourceBean.getResourceLoader(); 6 Assert.assertTrue(loader instanceof ApplicationContext); 7 }
注意此处“loader instanceof ApplicationContext”,说明了ApplicationContext就是个ResoureLoader.
4. 注入Resource
Spring提供了一个PropertyEditor “ResourceEditor”用于在注入的字符串和Resource之间进行转换。因此可 以使用注入方式注入Resource。
ResourceEditor完全使用ApplicationContext根据注入的路径字符串获取相应的Resource.

1 public class ResourceBean2 { 2 private Resource resource; 3 4 public Resource getResource() { 5 return resource; 6 } 7 8 public void setResource(Resource resource) { 9 this.resource = resource; 10 } 11 12 13 }

1 <bean id="bean1" class="com.test.spring.ResourceBean2"> 2 <property name="resource" value="test1.properties"/> 3 </bean>

1 @Test 2 public void test() { 3 ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); 4 ResourceBean2 resourceBean2=context.getBean("bean1",ResourceBean2.class); 5 Assert.assertTrue(resourceBean2.getResource() instanceof ClassPathResource); 6 }
note: 也可以支持Resource数组
note:还可以使用通配符进行匹配一批路径
参考文献
《spring揭秘》
https://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/1416320
以上是关于Spring08-----IoC容器ApplicationContext的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
