KotlinKotlin 与 Java 互操作 ② ( @JvmField 注解字段给 Java | @JvmOverloads 注解修饰函数 | @JvmStatic 注解声明静态成员 )
Posted 韩曙亮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了KotlinKotlin 与 Java 互操作 ② ( @JvmField 注解字段给 Java | @JvmOverloads 注解修饰函数 | @JvmStatic 注解声明静态成员 )相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、使用 @JvmField 注解暴露 Kotlin 字段给 Java
1、Java 类中通过 Getter 和 Setter 方法访问 Kotlin 字段
在 Java 中是 不能直接访问 Kotlin 中的字段 的 , 必须 调用相应的 Getter 和 Setter 方法 , 才能进行访问 ;
代码示例 :
Kotlin 类 : 在 Kotlin 中声明的成员属性 , 默认就是 private 私有属性 , 默认为其生成了 Getter 和 Setter 方法 ;
class Hello
var name = "Tom"
Java 类直接调用 : 在 Java 类中 , 不能直接调用 Kotlin 字段 ;
public class HelloJava
public static void main(String[] args)
Hello hello = new Hello();
System.out.println(hello.name);
在 Java 类中会报错 :
'name' has private access in 'Hello'
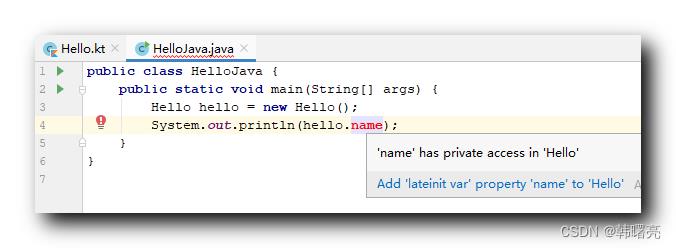
在 Java 类中 , 只能通过 Getter 和 Setter 方法 , 调用 Kotlin 字段 ;
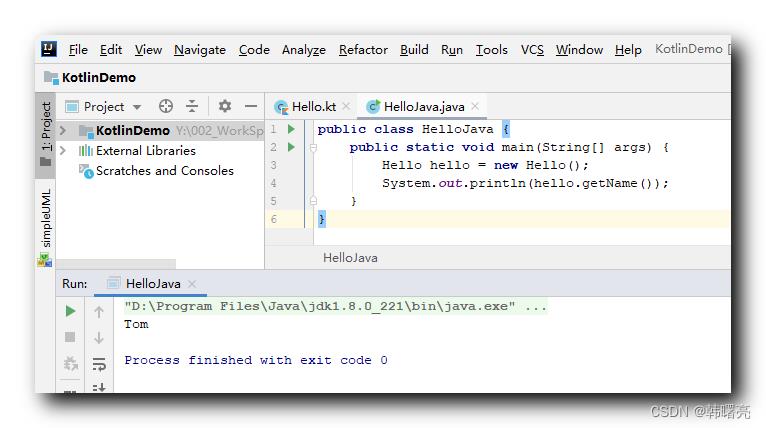
public class HelloJava
public static void main(String[] args)
Hello hello = new Hello();
System.out.println(hello.getName());
执行结果 :
2、Java 类中直接访问被 @JvmField 注解修饰的 Kotlin 字段
如果在 Kotlin 中 , 使用 @JvmField 注解 修饰 成员属性 , 其作用是将 Kotlin 字段暴露给 Java , 在 Java 中可以不使用 Getter 和 Setter 方法 而直接访问 Kotlin 字段 ;
Kotlin 代码 :
class Hello
@JvmField
var name = "Tom"
Java 代码 :
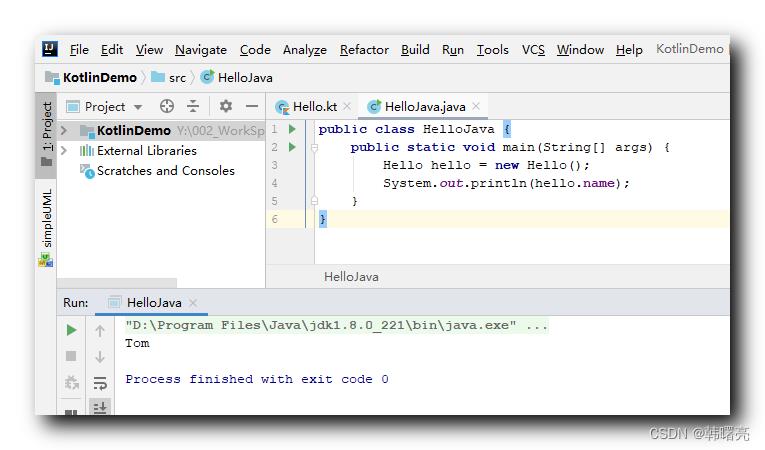
public class HelloJava
public static void main(String[] args)
Hello hello = new Hello();
System.out.println(hello.name);
执行结果 :
@JvmField 注解 相当于 将 Kotlin 中的字段声明为 Java 字段 , 此时 Kotlin 不会为该字段自动生成 Getter 和 Setter 方法 ;
二、使用 @JvmOverloads 注解修饰 Kotlin 函数
在 Kotlin 中 , 函数参数 可以 自带默认值 , 调用时可以 直接传入 想要的参数即可 ;
但是在 Java 调用 Kotlin 函数 中 , Java 语言不支持 函数参数 自带默认值的 语法 , 如果传入指定的参数 , 就需要对函数进行重载 ;
在 Kotlin 中 使用 @JvmOverloads 注解修饰 Kotlin 函数 , 会自动 为 Java 用户实现 一系列的 重载函数 ;
如 : 参数列表是 ( String , age ) , 使用 @JvmOverloads 注解修饰该函数 , 会自动生成
- 0 个参数 ,
- 1 个参数 ,
- 2 个参数
的函数 ;
1、Kotlin 默认参数函数调用示例
Kotlin 代码示例 : 在下面的 helloStudent 函数中 , 两个参数都设置了默认参数值 , Kotlin 中调用该函数 , 可以传入 0 , 1 , 2 个参数 , 其中传入 1 个参数还可以选择传入哪个参数 ;
class Hello
fun helloStudent(name: String = "Tom", age: Int = 18)
println("Student $name is $age years old , say hello !")
fun main()
var hello = Hello();
hello.helloStudent()
hello.helloStudent("Jerry")
hello.helloStudent(age = 22)
hello.helloStudent("Bill", 12)
执行结果 :
Student Tom is 18 years old , say hello !
Student Jerry is 18 years old , say hello !
Student Tom is 22 years old , say hello !
Student Bill is 12 years old , say hello !

分析上述 Kotlin 代码的字节码数据 , 在 Kotlin Bytecode 中查看字节码数据 , 反编译成 Java 代码内容如下 :
// Hello.java
import kotlin.Metadata;
import kotlin.jvm.internal.Intrinsics;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
@Metadata(
mv = 1, 1, 16,
bv = 1, 0, 3,
k = 1,
d1 = "\\u0000\\u001e\\n\\u0002\\u0018\\u0002\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\b\\u0002\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u000e\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\b\\n\\u0000\\u0018\\u00002\\u00020\\u0001B\\u0005¢\\u0006\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002J\\u001a\\u0010\\u0003\\u001a\\u00020\\u00042\\b\\b\\u0002\\u0010\\u0005\\u001a\\u00020\\u00062\\b\\b\\u0002\\u0010\\u0007\\u001a\\u00020\\b¨\\u0006\\t",
d2 = "LHello;", "", "()V", "helloStudent", "", "name", "", "age", "", "KotlinDemo"
)
public final class Hello
public final void helloStudent(@NotNull String name, int age)
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
String var3 = "Student " + name + " is " + age + " years old , say hello !";
boolean var4 = false;
System.out.println(var3);
// $FF: synthetic method
public static void helloStudent$default(Hello var0, String var1, int var2, int var3, Object var4)
if ((var3 & 1) != 0)
var1 = "Tom";
if ((var3 & 2) != 0)
var2 = 18;
var0.helloStudent(var1, var2);
// HelloKt.java
import kotlin.Metadata;
@Metadata(
mv = 1, 1, 16,
bv = 1, 0, 3,
k = 2,
d1 = "\\u0000\\b\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002\\n\\u0000\\u001a\\u0006\\u0010\\u0000\\u001a\\u00020\\u0001¨\\u0006\\u0002",
d2 = "main", "", "KotlinDemo"
)
public final class HelloKt
public static final void main()
Hello hello = new Hello();
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, (String)null, 0, 3, (Object)null);
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, "Jerry", 0, 2, (Object)null);
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, (String)null, 22, 1, (Object)null);
hello.helloStudent("Bill", 12);
// $FF: synthetic method
public static void main(String[] var0)
main();
2、Java 中调用 Kotlin 默认参数函数
如果 在 Java 代码中 , 想要 像 Kotlin 那样传入任意个数和类型的参数 , 就需要使用 函数重载实现 ;
如果 直接像 Kotlin 中那样调用 , 肯定会报错 :
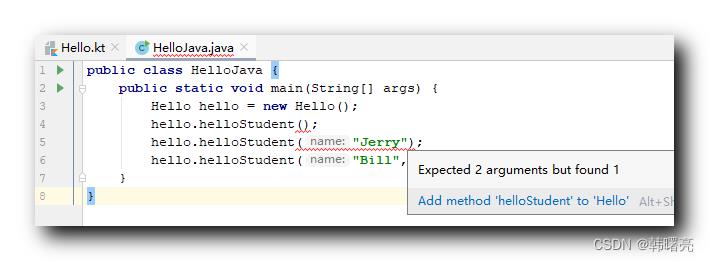
使用 @JvmOverloads 注解修饰 Kotlin 函数 , 会自动为 Java 用户实现 一系列的 重载函数 ;
Kotlin 代码示例 :
class Hello
@JvmOverloads
fun helloStudent(name: String = "Tom", age: Int = 18)
println("Student $name is $age years old , say hello !")
fun main()
var hello = Hello();
hello.helloStudent()
hello.helloStudent("Jerry")
hello.helloStudent(age = 22)
hello.helloStudent("Bill", 12)
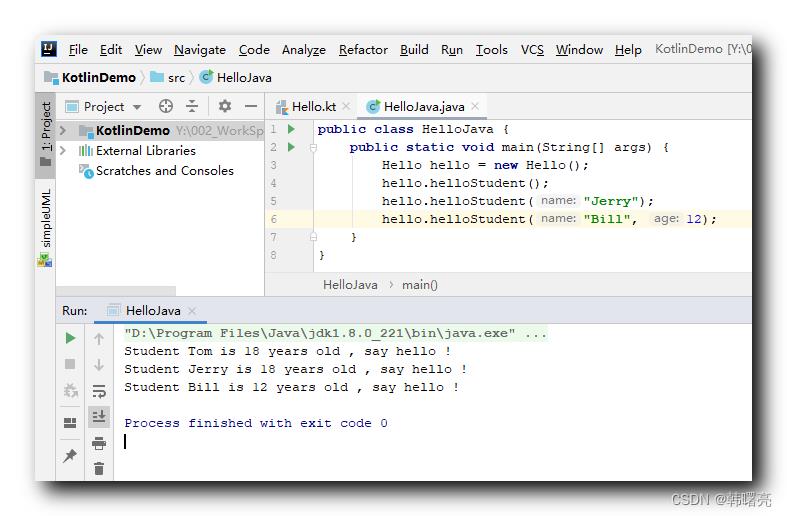
Java 代码示例 :
public class HelloJava
public static void main(String[] args)
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.helloStudent();
hello.helloStudent("Jerry");
hello.helloStudent("Bill", 12);
执行结果 :
Student Tom is 18 years old , say hello !
Student Jerry is 18 years old , say hello !
Student Bill is 12 years old , say hello !
分析上述 使用了 @JvmOverloads 注解 的 Kotlin 类对应的字节码数据 , 将字节码反编译回 Java 代码 , 内容如下 :
// Hello.java
import kotlin.Metadata;
import kotlin.jvm.JvmOverloads;
import kotlin.jvm.internal.Intrinsics;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
@Metadata(
mv = 1, 1, 16,
bv = 1, 0, 3,
k = 1,
d1 = "\\u0000\\u001e\\n\\u0002\\u0018\\u0002\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\b\\u0002\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u000e\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\b\\n\\u0000\\u0018\\u00002\\u00020\\u0001B\\u0005¢\\u0006\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002J\\u001c\\u0010\\u0003\\u001a\\u00020\\u00042\\b\\b\\u0002\\u0010\\u0005\\u001a\\u00020\\u00062\\b\\b\\u0002\\u0010\\u0007\\u001a\\u00020\\bH\\u0007¨\\u0006\\t",
d2 = "LHello;", "", "()V", "helloStudent", "", "name", "", "age", "", "KotlinDemo"
)
public final class Hello
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent(@NotNull String name, int age)
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
String var3 = "Student " + name + " is " + age + " years old , say hello !";
boolean var4 = false;
System.out.println(var3);
// $FF: synthetic method
public static void helloStudent$default(Hello var0, String var1, int var2, int var3, Object var4)
if ((var3 & 1) != 0)
var1 = "Tom";
if ((var3 & 2) != 0)
var2 = 18;
var0.helloStudent(var1, var2);
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent(@NotNull String name)
helloStudent$default(this, name, 0, 2, (Object)null);
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent()
helloStudent$default(this, (String)null, 0, 3, (Object)null);
// HelloKt.java
import kotlin.Metadata;
@Metadata(
mv = 1, 1, 16,
bv = 1, 0, 3,
k = 2,
d1 = "\\u0000\\b\\n\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002\\n\\u0000\\u001a\\u0006\\u0010\\u0000\\u001a\\u00020\\u0001¨\\u0006\\u0002",
d2 = "main", "", "KotlinDemo"
)
public final class HelloKt
public static final void main()
Hello hello = new Hello();
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, (String)null, 0, 3, (Object)null);
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, "Jerry", 0, 2, (Object)null);
Hello.helloStudent$default(hello, (String)null, 22, 1, (Object)null);
hello.helloStudent("Bill", 12);
// $FF: synthetic method
public static void main(String[] var0)
main();
使用了 @JvmOverloads 注解后 ,
在编译时 , 自动为 helloStudent 函数 , 生成了 0 , 1, 2 个参数的重载函数 ,
这样在 Java 中调用时 , 可以直接调用这些方法 ;
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent(@NotNull String name, int age)
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(name, "name");
String var3 = "Student " + name + " is " + age + " years old , say hello !";
boolean var4 = false;
System.out.println(var3);
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent(@NotNull String name)
helloStudent$default(this, name, 0, 2, (Object)null);
@JvmOverloads
public final void helloStudent()
helloStudent$default(this, (String)null, 0, 3, (Object)null);
三、使用 @JvmStatic 注解声明静态成员
在 Kotlin 中 , 没有静态成员概念 , 需要声明静态成员时 , 一般都在其 Companion 伴生对象中声明 ;
在 Java 中 调用 Kotlin 的 Companion 伴生对象 中的成员时 , 需要通过如下形式进行调用 :
Kotlin类.Companion.成员属性
Kotlin类.Companion.成员函数
如果想要 在不使用 Companion 的前提下 直接调用 Kotlin 中的 Companion 伴生对象 成员 ,
可以 在 companion object 中 ,
使用 @JvmStatic 注解 将伴生对象中的成员 声明 为 Java 静态成员 ,
Java 中可以按照静态成员的方式进行访问 ;
1、Java 正常访问 Kotlin 伴生对象成员
在下面的代码中 , 在 Java 语言中访问 Kotlin 伴生对象成员 , 需要先获取 Hello.Companion 类的伴生对象 , 然后再访问 伴生对象 中的成员 ;
Kotlin 代码 :
class Hello
companion object
var name = "Tom"
fun say()
println("Hello World")
Java 代码 :
public class HelloJava
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println(Hello.Companion.getName());
Hello.Companion.say();
执行结果 :
Tom
Hello World

查看该 Kotlin 类生成的字节码 反编译 的 Java 代码 :
import kotlin.Metadata;
import kotlin.jvm.internal.DefaultConstructorMarker;
import kotlin.jvm.internal.Intrinsics;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
@Metadata(
mv = 1, 1, 16,
bv = 1, 0, 3,
k = 1,
d1 = "\\u0000\\f\\n\\u0002\\u0018\\u0002\\n\\u0002\\u0010\\u0000\\n\\u0002\\b\\u0003\\u0018\\u0000 \\u00032\\u00020\\u0001:\\u0001\\u0003B\\u0005¢\\u0006\\u0002\\u0010\\u0002¨\\u0006\\u0004",
d2 = "LHello;", "", "()V", "Companion", "KotlinDemo"
)
public