JUC学习笔记
Posted Shinka_YXS
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC学习笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
尚硅谷JUC源码讲授实战教程完整版(java juc线程精讲)
1.volatile 关键字与内存可见性
当程序运行,JVM会为每一个执行任务的线程分配独立的缓存用于提高效率。
内存可见性问题是,当多个线程操作共享数据时,彼此不可见。
volatile 关键字:当多个线程进行操作共享数据时,可以保证内存中的数据可见。相较于synchronized是一种较为轻量级的同步策略。
volatile 不具备"互斥性",也不能保证变量的"原子性"
public class VolatileTest
public static void main(String[] args)
ThreadDemo threadDemo = new ThreadDemo();
new Thread(threadDemo).start();
while (true)
// synchronized (threadDemo)
if (threadDemo.isFlag())
System.out.println("---------");
break;
//
class ThreadDemo implements Runnable
// private boolean flag = false;
private volatile boolean flag = false;
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(200);
catch (Exception e)
flag = true;
System.out.println("flag=" + isFlag());
public boolean isFlag()
return flag;
2.原子变量与CAS算法
原子变量:jdk1.5后java.util.concurrent.atomic包下提供了常用的原子变量(其中有AtomicInteger)
1、volatile保证内存可见性
2、CAS (Compare-And-Swap)算法保证数据的原子性CAS算法是硬件对于并发操作共享数据的支持
CAS包含了三个操作数:内存值V、预估值A、更新值B。当且仅当V == A 时,V = B(将B赋值给A)。否则,将不做任何操作
public class AtomicTest
public static void main(String[] args)
AtomicDemo atomicDemo = new AtomicDemo();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
new Thread(atomicDemo).start();
class AtomicDemo implements Runnable
// private int serialNum = 0;
private AtomicInteger serialNum = new AtomicInteger();
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + getSerialNum());
public int getSerialNum()
// return serialNum++;
return serialNum.getAndIncrement();
3.模拟CAS算法
public class CompareAndSwapTest
public static void main(String[] args)
final CompareAndSwap cas = new CompareAndSwap();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
new Thread(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
int expectedValue = cas.get();
boolean flag = cas.compareAndSet(expectedValue, (int)(Math.random() * 100));
System.out.println(flag);
).start();
class CompareAndSwap
private int value;
// 获取内存值
public synchronized int get()
return value;
// 比较
public synchronized int compareAndSwap(int expectedValue, int newValue)
int oldValue = value;
if (oldValue == expectedValue)
this.value = newValue;
return oldValue;
// 设置
public synchronized boolean compareAndSet(int expectedValue, int newValue)
return expectedValue == compareAndSwap(expectedValue, newValue);
4.同步容器类ConcurrentHashMap
- Java 5.0在java.util.concurrent包中提供了多种并发容器类来改进同步容器的性能。
- ConcurrentHashMap同步容器类是Java 5增加的一个线程安全的哈希表。
对于多线程的操作,介于HashMap 与 Hashtable之间。
java1.8之前内部采用“锁分段”机制替代 Hashtable的独占锁。进而提高性能,1.8之后是CAS - 此包还提供了设计用于多线程上下文中的collection实现:
ConcurrentHashMap、ConcurrentSkipListMap、ConcurrentSkipListSet、CopyOnWriteArrayList和CopyOnWriteArraySet。
当期望许多线程访问一个给定collection时,ConcurrentHashMap通常优于同步的HashMap,
ConcurrentSkipListMap通常优于同步的TreeMap。
当期望的读数和遍历远远大于列表的更新数时,CopyOnWriteArrayList优于同步的ArrayList。
/**
* CopyOnWriteArrayList/CopyOnWriteArraySet : 写入并复制
* 注意:不适合添加操作多的场景,因为每次添加都会进行复制,开销大,效率低
* 适合并发迭代操作多的场景
*/
public class CopyOnWriteArrayListTest
public static void main(String[] args)
HelloThread ht = new HelloThread();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
new Thread(ht).start();
class HelloThread implements Runnable
// private static List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
private static CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
static
list.add("AA");
list.add("BB");
list.add("CC");
@Override
public void run()
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
// 使用的是List<String>时 此处会抛出java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常
list.add("AA");
5.CountDownLatch闭锁
-
Java 5.0在java.util.concurrent包中提供了多种并发容器类来改进同步容器的性能。
-
CountDownLatch一个同步辅助类,在完成一组正在其他线程中执行的操作之前,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待。
-
闭锁可以延迟线程的进度直到其到达终止状态,闭锁可以用来确保某些活动直到其他活动都完成才继续执行:
确保某个计算 在其需要的所有资源都被初始化之后 才继续执行;
确保某个服务 在其依赖的所有其他服务都已经启动之后 才启动;
等待直到某个操作所有参与者都准备就绪再继续执行。
/**
* CountDownLatch闭锁:在完成某些运算时,只有其他线程的运算全部完成后,当前运算才继续执行
*/
public class CountDownLatchTest
public static void main(String[] args)
// 后面开了5个线程,此处就传入计数5
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(5);
LatchDemo latchDemo = new LatchDemo(countDownLatch);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
new Thread(latchDemo).start();
try
countDownLatch.await();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 当计数减到0时才执行
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + (end - start));
class LatchDemo implements Runnable
public CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public LatchDemo(CountDownLatch countDownLatch)
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
@Override
public void run()
synchronized (this)
try
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++)
if (i % 2 == 0)
System.out.println(i);
finally
countDownLatch.countDown();
6.实现Callable接口
/**
* 创建线程方式三:实现Callable接口
* 相较于实现Runnable接口的方式,方法可以有返回值,并且可以抛出异常
*/
public class CallableTest
public static void main(String[] args)
CallableImpl callableImpl = new CallableImpl();
// 执行Callable方式,需要FutureTask实现类的支持,用于接收运算结果。FutureTask是Future接口的实现类
// 还有另外一个构造方法是FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
FutureTask<Integer> result = new FutureTask<>(callableImpl);
new Thread(result).start();
// 接收线程运算后的结果
try
Integer sum = result.get(); // futureTask也可用于闭锁
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println("---------当分线程执行完 get()拿到结果了才执行此处---------");
catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e)
e.printStackTrace();
class CallableImpl implements Callable<Integer>
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
7.Lock同步锁
—、用于解决多线程安全问题的方式:
1.同步代码块(synchronized隐式锁)
2.同步方法(synchronized隐式锁)
3.同步锁Lock(jdk 1.5后出现,是个显式锁,需要通过lock()方法上锁,必须通过unlock()方法进行释放锁,所以有一定的风险,比如锁未成功释放)
public class LockTest
public static void main(String[] args)
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
new Thread(ticket, "1号窗口").start();
new Thread(ticket, "2号窗口").start();
new Thread(ticket, "3号窗口").start();
class Ticket implements Runnable
private int ticketNum = 100;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run()
while (true)
lock.lock(); // 上锁
try
if (ticketNum > 0)
try
Thread.sleep(10);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "完成售票,余票为:" + --ticketNum);
finally
lock.unlock(); // 释放锁
8.生产者消费者案例-虚假唤醒
如何用Lock同步锁实现等待唤醒机制,也就是像synchronized关键字的wait()和notify()的等待唤醒机制
8.1未使用等待唤醒机制出现的问题
public class ProductorAndConsumerTest
public static void main(String[] args)
Clerk clerk = new Clerk();
Productor productor = new Productor(clerk);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(clerk);
new Thread(productor, "生产者A").start();
new Thread(consumer, "消费者B").start();
// 店员
class Clerk
private int productNum = 0;
// 进货
public synchronized void get()
if (productNum >= 5)
System.out.println("商品仓位已满!");
// try
// this.wait();
// catch (InterruptedException e)
// e.printStackTrace();
//
else
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进货:" + ++productNum);
// this.notifyAll();
// 卖货
public synchronized void sale()
if (productNum <= 0)
System.out.println("商品已售罄!");
// try
// this.wait();
// catch (InterruptedException e)
// e.printStackTrace();
//
else
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出:" + --productNum);
// this.notifyAll();
// 生产者
class Productor implements Runnable
private Clerk clerk;
public Productor(Clerk clerk)
this.clerk = clerk;
@Override
public void run()
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
clerk.get();
// 消费者
class Consumer implements Runnable
private Clerk clerk;
public Consumer(Clerk clerk)
this.clerk = clerk;
@Override
public void run()
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
clerk.sale();
即使仓位满了,生产者还是不停地进货;即使商品售罄了,消费者还是不停地想要去消费、
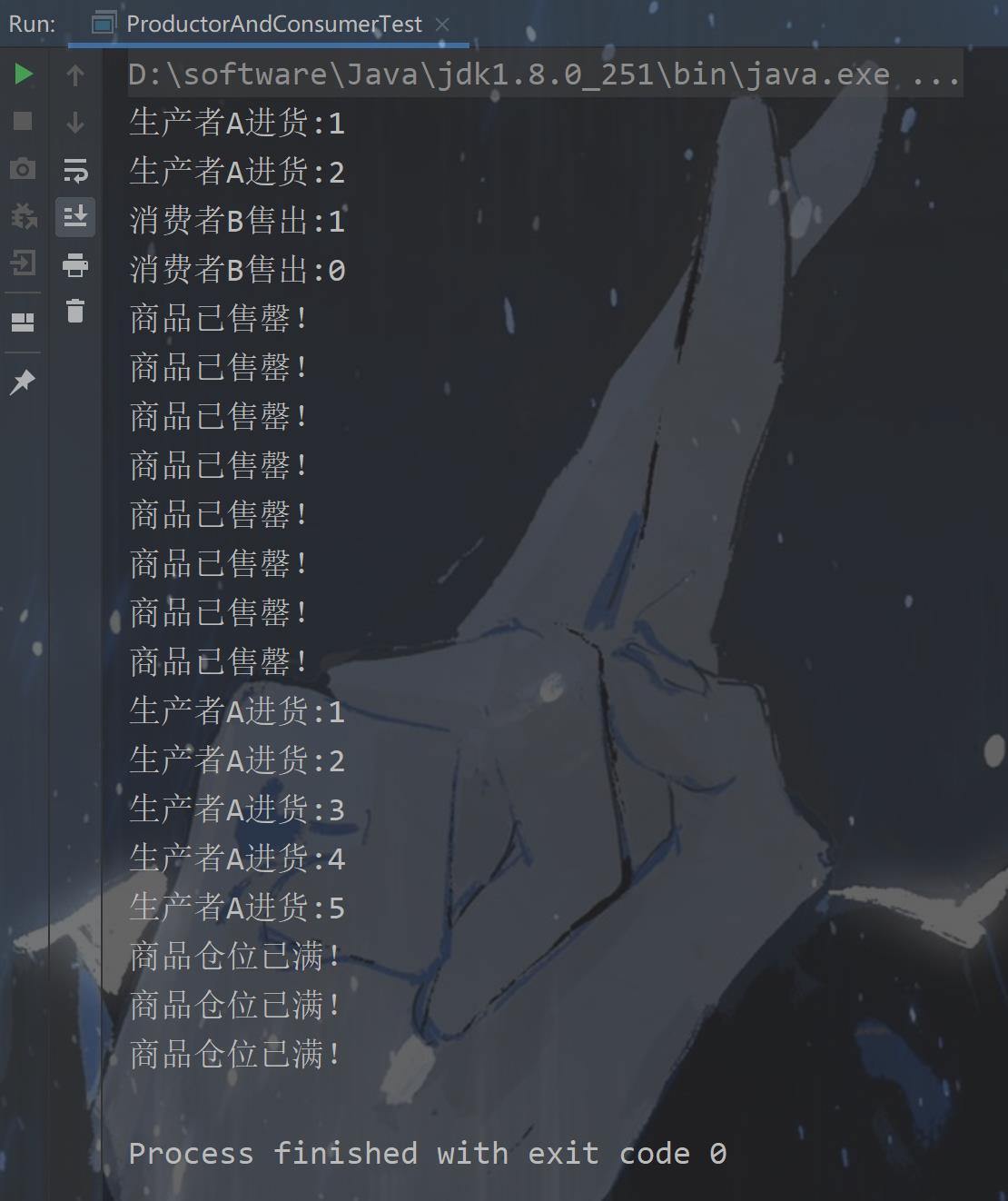
8.2使用等待唤醒机制
将8.1中注释的代码放开、此时运行结果都是有效的数据、
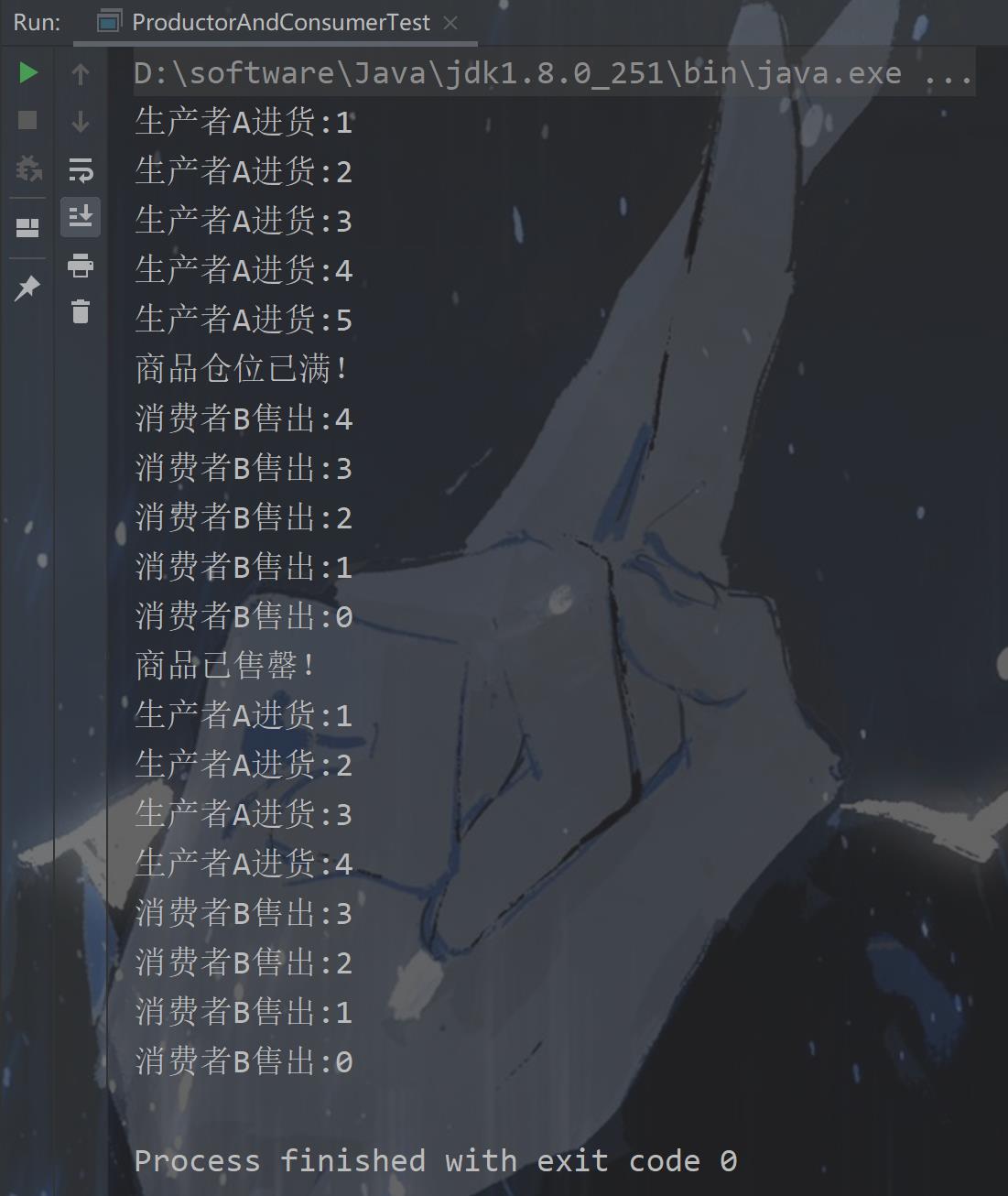
8.3问题修正1
8.2的等待唤醒机制有些问题、
当把仓位改为1,并给生产者加0.2秒的延迟、
// 进货
public synchronized void get()
if (productNum >= 1) // 把仓位改为1
System.out.println("商品仓位已满!");
try
this.wait();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
else
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进货:" + ++productNum);
this.notifyAll();
@Override
public void run()
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
try
Thread.sleep(200); // 给生产者加0.2秒的延迟
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace()