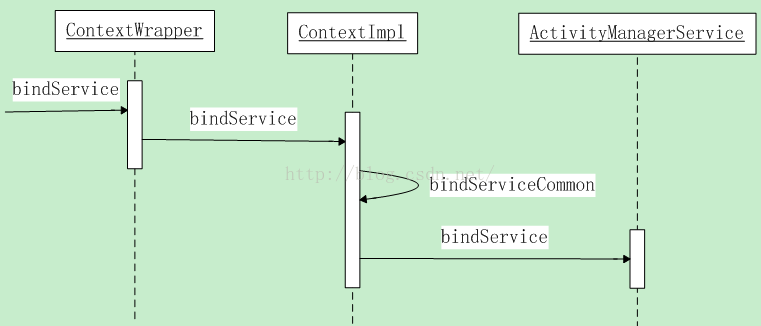
上一篇分析startService时没有画出调用ActivityManagerService之前的时序图,这里画出bindService的时序图。它们的调用流程是一致的。
先看ContextWrapper的bindService方法:
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
调用ContextImpl类的bindService方法:
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
// 假设是系统进程调用会打印一个log。
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, Process.myUserHandle());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
// mPackageInfo是LoadedApk类的实例,在构造方法中赋值
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
// mMainThread是一个ActivityThread实例。调用getHandler()方法获取到一个Handler对象。
// 这个Handler对象就是ActivityThread内部类H的实例,这里把它保存在ServiceDispatcher中了
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
// 验证service的有效性,android5.1之后不同意使用隐式调用
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
// 准备离开应用程序进程。进人ActivityManagerService进程
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
// 调用ActivityManagerProxy类的bindService方法。ActivityManagerProxy是
// 一个Binder对象的远程接口。而这个Binder对象就是ActivityManagerService
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
}
LoadedApk类的getServiceDispatcher方法返回一个IServiceConnection对象,它是一个Binder对象,后面传递给了ActivityManagerService。ActivityManagerService兴许就是要通过这个Binder对象和ServiceConnection通信的。
ActivityManagerNative类的getDefault()方法上一篇已经解说过。就是通过一个懒载入的单例模式得到一个ActivityManagerProxy代理对象。
这里不再具体解说。
ActivityManagerProxy类的bindService方法把传递进来的參数写入到data本地变量中,接着通过mRemote.transact方法进入到Binder驱动程序,然后Binder驱动程序唤醒正在等待Client请求的ActivityManagerService进程,最后进入到ActivityManagerService的bindService方法中。这里先看下时序图:
ActivityManagerService类中的bindService方法:
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 运行依据调用者uid推断调用者不是独立进程的操作
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
synchronized(this) {
// mServices是ActiveServices的实例,在构造方法中完毕初始化
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
运行到ActiveServices类中的bindServiceLocked方法:
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "bindService: " + service
+ " type=" + resolvedType + " conn=" + connection.asBinder()
+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(flags));
// mAm是ActivityManagerService对象,在构造方法中完毕初始化操作
// 通过ApplicationThread对象从ActivityManagerService的成员变量mLruProcesses
// 列表中查找启动服务的进程(调用者)在ActivityManagerService中的ProcessRecord对象
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()
+ ") when binding service " + service);
}
ActivityRecord activity = null;
if (token != null) {
// 通过token将代表调用者的ActivityRecord取出
activity = ActivityRecord.isInStackLocked(token);
if (activity == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
int clientLabel = 0;
PendingIntent clientIntent = null;
if (callerApp.info.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
// Hacky kind of thing -- allow system stuff to tell us
// what they are, so we can report this elsewhere for
// others to know why certain services are running.
try {
clientIntent = service.getParcelableExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
}
if (clientIntent != null) {
clientLabel = service.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL, 0);
if (clientLabel != 0) {
// There are no useful extras in the intent, trash them.
// System code calling with this stuff just needs to know
// this will happen.
service = service.cloneFilter();
}
}
}
if ((flags&Context.BIND_TREAT_LIKE_ACTIVITY) != 0) {
mAm.enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.MANAGE_ACTIVITY_STACKS,
"BIND_TREAT_LIKE_ACTIVITY");
}
final boolean callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE;
// 调用retrieveServiceLocked方法解析service。将解析结果保存在res.record中
// 调用该方法后,为被调用者构造了相应的ServiceRecord对象
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg);
if (res == null) {
return 0;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return -1;
}
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
/*能够加入关联唤醒的推断逻辑:如依据被调用者包名/类名前缀推断是否属于第三方push平台在开启服务,假设是则直接返回0*/
/*能够加入自启动的推断逻辑:如被调用者包名在禁止自启动的列表中,则直接返回0*/
/*另外:syncManager和JobScheduler都能够通过系统调用bindServiceAsUser把自己拉起来,故这里能够添加*/
/*对调用者是系统uid时候的推断逻辑:推断被调用者包名是否在禁止自启动列表中。假设在则直接返回0*/
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(s, callerApp.info.uid, false)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "BIND SERVICE WHILE RESTART PENDING: "
+ s);
}
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (!s.hasAutoCreateConnections()) {
// This is the first binding, let the tracker know.
ProcessStats.ServiceState stracker = s.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setBound(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),
s.lastActivity);
}
}
}
mAm.startAssociationLocked(callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName,
s.appInfo.uid, s.name, s.processName);
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
// 将传进来的參数封装成ConnectionRecord对象。connection是一个Binder对象
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
// 多种方式保存ConnectionRecord对象c,都是为了兴许用到时方便取出
clist.add(c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
if (activity.connections == null) {
activity.connections = new HashSet<ConnectionRecord>();
}
activity.connections.add(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.hasAboveClient = true;
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// 參数为BIND_AUTO_CREATE时。启动服务,兴许流程和startService一致,这里不再解说
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
if (s.app != null) {
if ((flags&Context.BIND_TREAT_LIKE_ACTIVITY) != 0) {
s.app.treatLikeActivity = true;
}
// This could have made the service more important.
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(s.app, s.app.hasClientActivities
|| s.app.treatLikeActivity, b.client);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(s.app);
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Bind " + s + " with " + b
+ ": received=" + b.intent.received
+ " apps=" + b.intent.apps.size()
+ " doRebind=" + b.intent.doRebind);
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
// 假设服务已经在运行,则直接运行连接成功的回调
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
// 绑定该Service
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
getServiceMap(s.userId).ensureNotStartingBackground(s);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
bringUpServiceLocked方法后的运行流程跟startService一致,这里不再解说。具体能够參考上一篇文章。服务运行完onCreate方法之后才干绑定。以下解说绑定服务的过程:
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can‘t yet bind.
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
// 调用ActivityThread类的scheduleBindService方法
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r);
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
通过Binder驱动程序调用ActivityThread类中的scheduleBindService方法:
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
private class H extends Handler {
. . .
public static final int BIND_SERVICE = 121;
. . .
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
. . .
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
. . .
}
}
}
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
// 前面在运行handleCreateService方法时。通过mServices.put(data.token, service);
// 方法保存了起来,如今取出
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
// 回调Service的onBind方法
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
// 通知ActivityManagerService服务已经连接成功
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
// 回调Service的onRebind方法
s.onRebind(data.intent);
// 通知ActivityManagerService。当前Service创建完毕
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
以下看服务连接成功的ActivityManagerService类中的publicService方法:
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
调用ActiveServices类中的publishServiceLocked方法:
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Not publishing to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Bound intent: " + c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
// 运行连接成功的回调,c.conn是IServiceConnection类型
// 这里会运行LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection.connected方法
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.name +
" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +
" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection类中的connected方法:
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
private final int mFlags;
private RuntimeException mUnbindLocation;
private boolean mDied;
private boolean mForgotten;
private static class ConnectionInfo {
IBinder binder;
IBinder.DeathRecipient deathMonitor;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
// 调用ServiceDispatcher的connected方法
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
private final ArrayMap<ComponentName, ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo> mActiveConnections
= new ArrayMap<ComponentName, ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo>();
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
// mActivityThread是一个Handler实例。它是通过ActivityThread.getHandler方法得到的
// 调用它的post方法后,就会把一个消息放到ActivityThread的消息队列中了
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
// 给service设置死亡代理
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don‘t do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
// service死亡时通知死亡代理
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
// 回调ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected方法
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
// 回调ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected方法
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
// 运行连接成功的操作
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}
。。。
}
到这里bindService的启动过程就分析完了。因为在bindServiceLocked方法中添加了对SyncManager和JobScheduler的推断,兴许会具体解说SyncManager和JobScheduler的运行流程。