深度学习
So far this week
- Edge detection
- RANSAC
- SIFT
- K-Means
- Linear classifier
- Mean-shift
- PCA/Eigenfaces
- Image features
Current Research

- Learning hierarchical representations from data
- End-to-end learning: raw inputs to predictions
- can use a small set of simple tools to solve many problems
- has led to rapid progress on many problems
- Inspired by the brain(very loosely!)
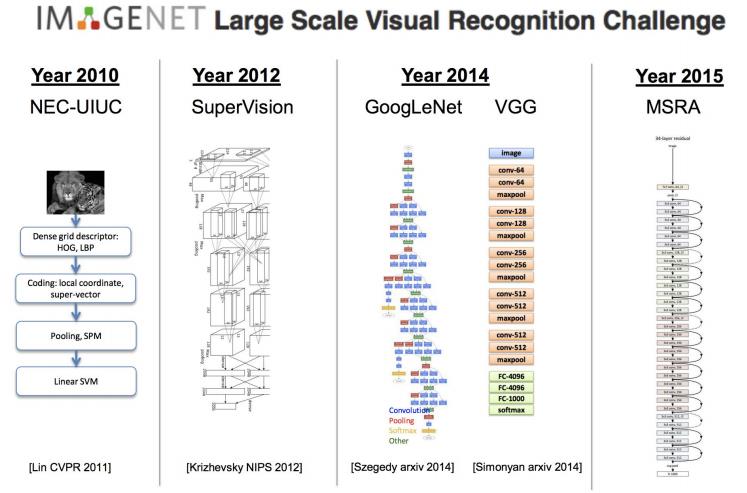
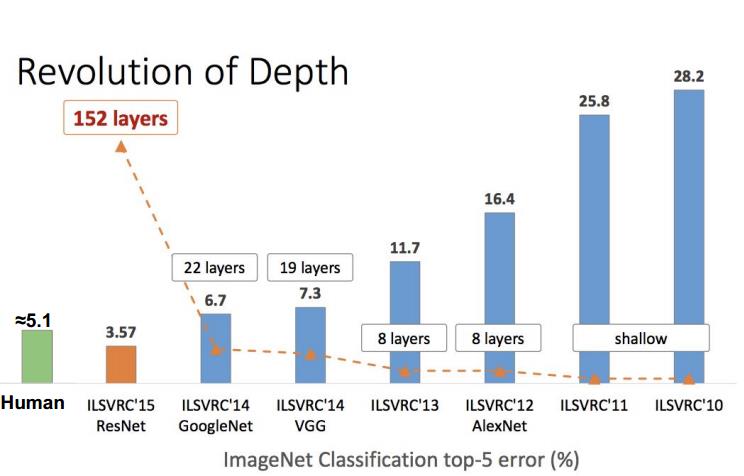
Deep learning for different problems
vision tasks
-
visual recognition
-
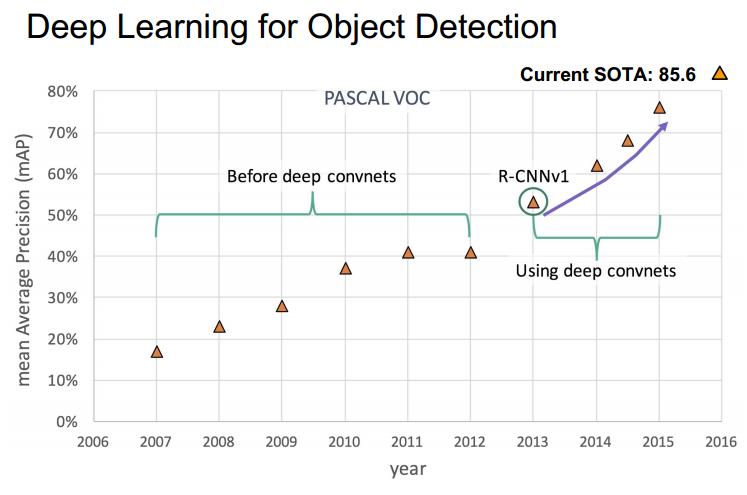
object detection: what and where
-
object segmentation
-
image caption
-
visual question answering
-
super resolution
-
image retrieval
-
style transfer
outside vision tasks
- Machine Translation
- Text Synthesis
- Speech Recognition
- Speech Synthesis
Motivation
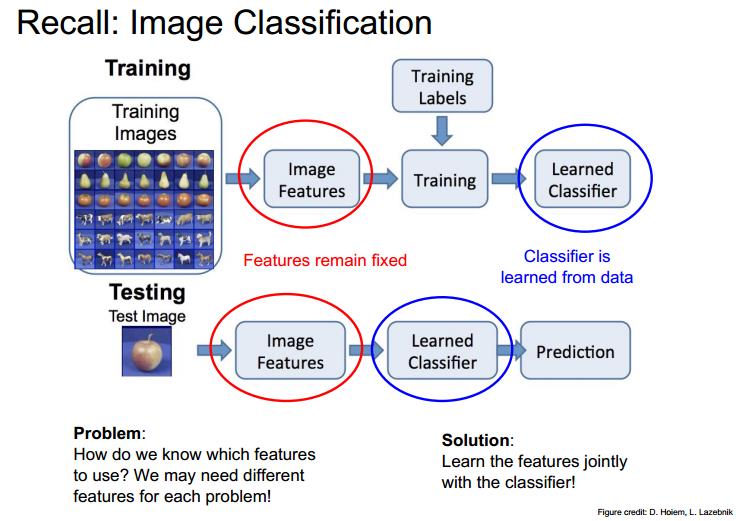
Data-driven approach:
- collect a dataset of images and labels
- use machine learning to train an image calssifier
- evaluate the classifier on a withheld set of test images
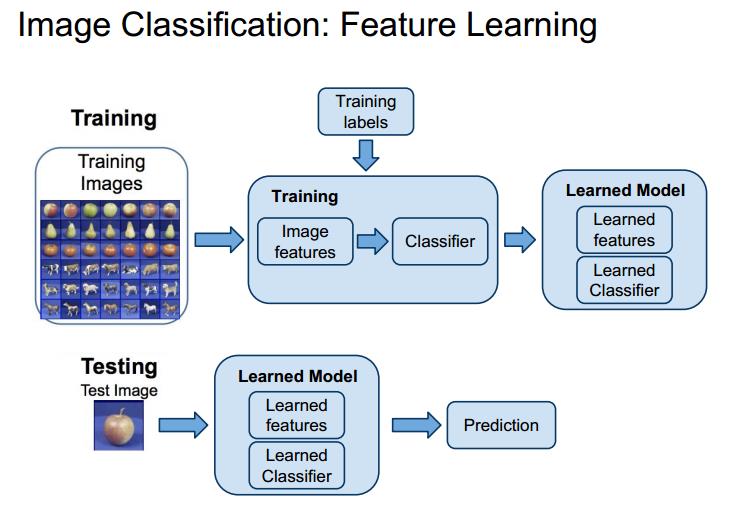
feature learning
what is feature learning?[^what is feature learning]
deep learning
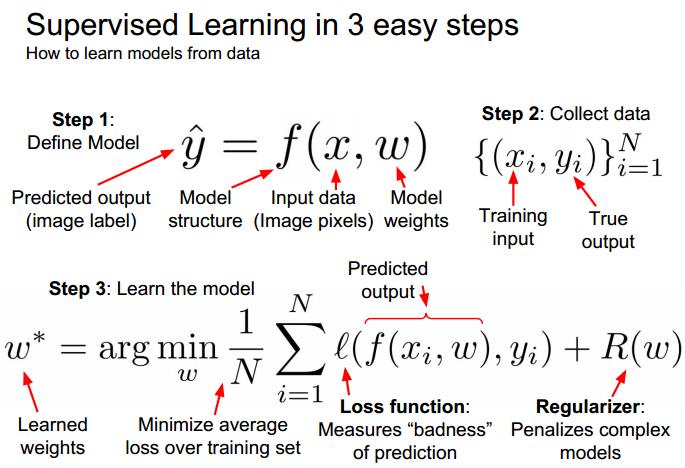
Supervised learning
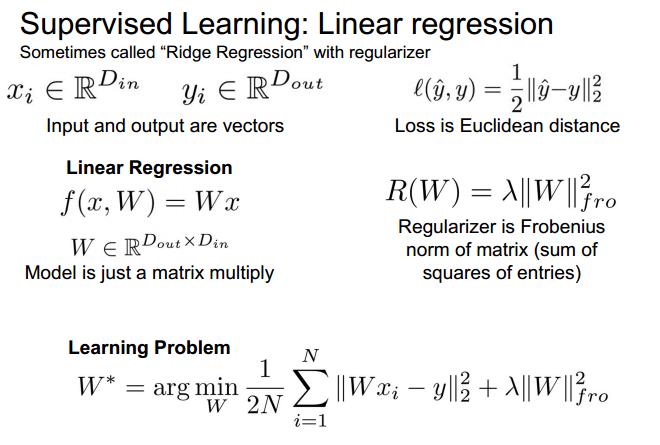
linear regression
neural network
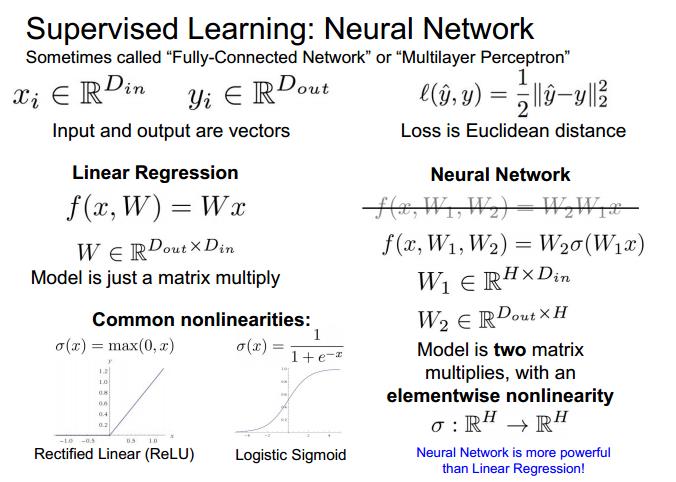
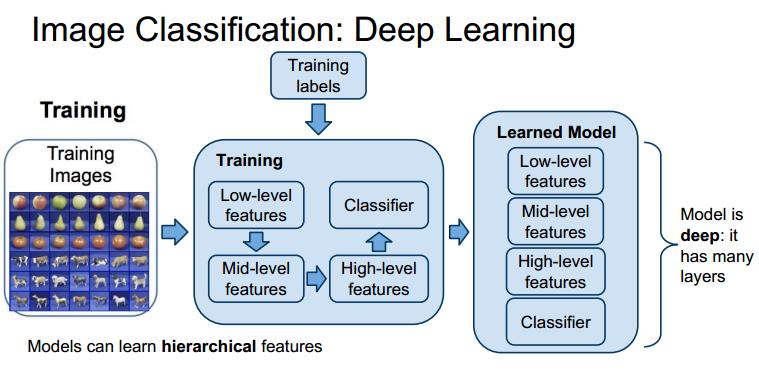
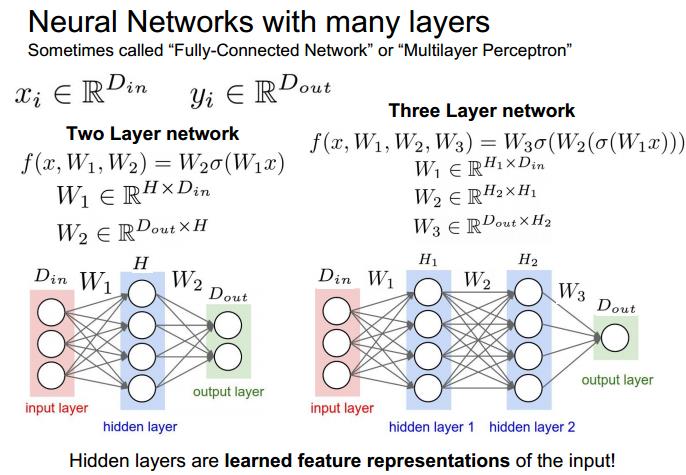
neural networks with many layers
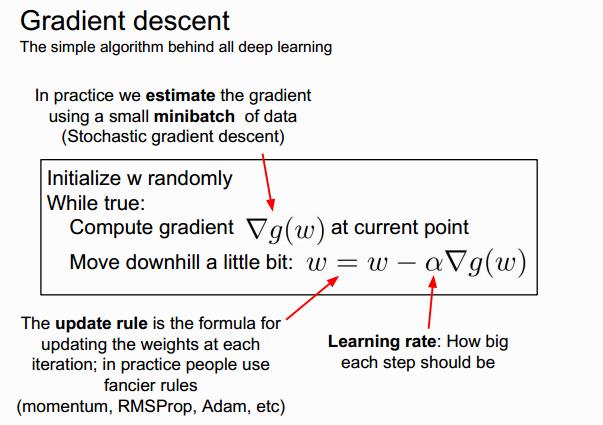
Gradient descent
how to find the best weights \\(w^T\\)

which way is down hill?

gradient descent
fancier rules:
- Momentum
- NAG
- Adagrad
- Adadelta
- Rmsprop
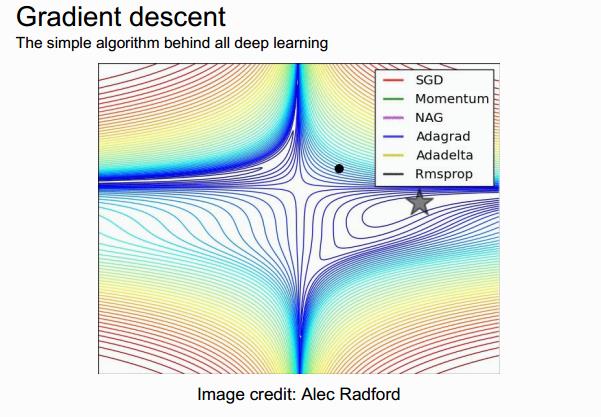
这里以后可以再 看看!
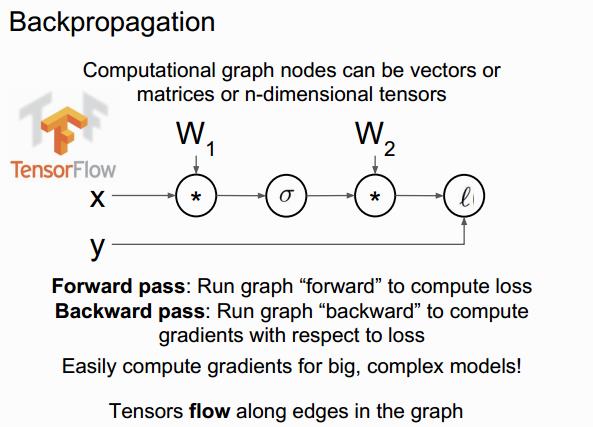
Backpropagation
a two-layer neural network in 25 lines of code
import numpy as np
D,H,N = 8, 64,32
#randomly initialize weights
W1 = np.random.randn(D,H)
W2 = np.random.randn(H,D)
for t in xrange(10000):
x = np.random.randn(N,D)
y = np.sin(x)
s = x.dot(W1)
a = np.maxium(s,0)
y_hat = a.dot(W2)
loss = 0.5*np.sum((y_hat-y)**2.0)
dy_hat = y_hat - y
dW2 = a.T.dot(W2.T)
da = dy_hat.dot(W2.T)
ds = (s > 0)*da
dW1 = x.T.dot(ds)
W1 -= learning_rate*dW1
W2 -= learning_rate*dW2
[^what is feature learning]:
In Machine Learning, feature learning or representation learningis a set of techniques that learn a feature: a transformation of raw data input to a representation that can be effectively exploited in machine learning tasks. This obviates manual feature engineering, which is otherwise necessary, and allows a machine to both learn at a specific task (using the features) and learn the features themselves.
Feature learning is motivated by the fact that machine learning tasks such as classification often require input that is mathematically and computationally convenient to process. However, real-world data such as images, video, and sensor measurement is usually complex, redundant, and highly variable. Thus, it is necessary to discover useful features or representations from raw data. Traditional hand-crafted features often require expensive human labor and often rely on expert knowledge. Also, they normally do not generalize well. This motivates the design of efficient feature learning techniques, to automate and generalize this.
Feature learning can be divided into two categories: supervised and unsupervised feature learning, analogous to these categories in machine learning generally.
In supervised feature learning, features are learned with labeled input data. Examples include Supervised Neural Networks, Multilayer Perceptron, and (supervised) dictionary Learning.
In unsupervised feature learning, features are learned with unlabeled input data. Examples include dictionary learning, independent component analysis, autoencoders, and various forms of clustering.